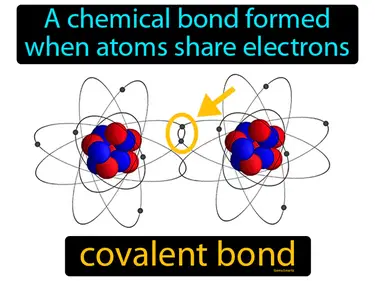
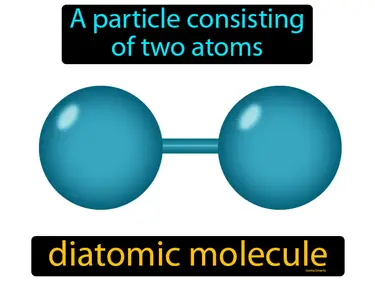
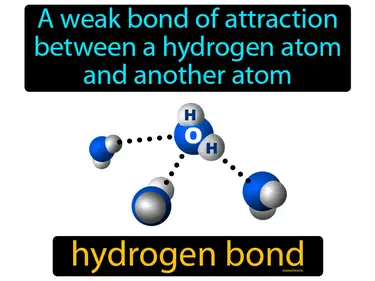
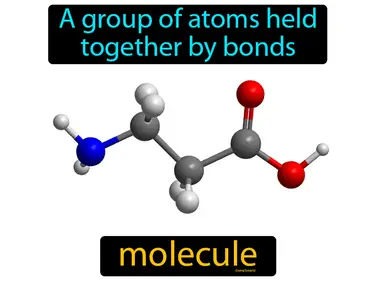
Covalent Bonding
Science
coordinate covalent bond
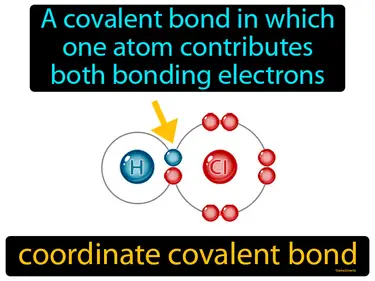
A covalent bond in which one atom contributes both bonding electrons. Coordinate covalent bond. In a coordinate covalent bond, one atom provides both of the electrons needed to form the bond with another atom.
dipole
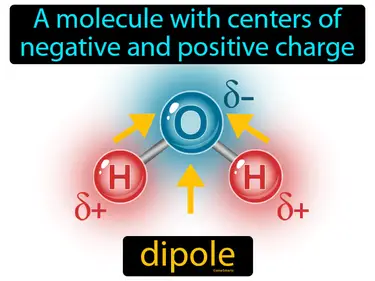
A molecule with centers of negative and positive charge. Dipole. A dipole is when a molecule has a slight positive charge on one side and a slight negative charge on the other, like a tiny magnet.
dispersion force
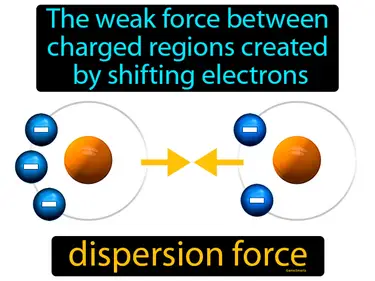
The weak force between charged regions created by shifting electrons dispersion force. Dispersion force is a temporary attraction between molecules due to randomly shifting electrons forming slight charges.
double covalent bond
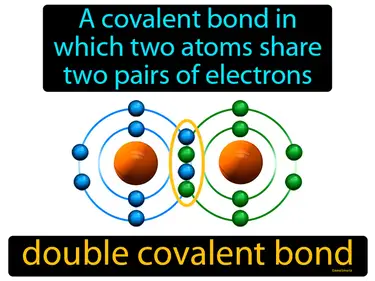
A covalent bond in which two atoms share two pairs of electrons. Double covalent bond. A double covalent bond is when two atoms share two pairs of electrons to be more stable.
hybridization
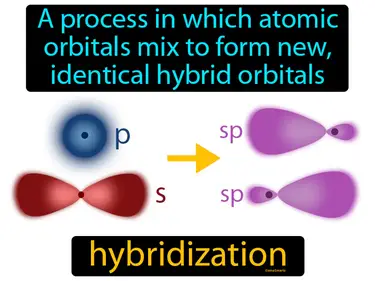
A process in which atomic orbitals mix to form new, identical hybrid orbitals. Hybridization. Hybridization is when atoms blend their orbitals to make new ones that help them bond better with other atoms.
molecular compound
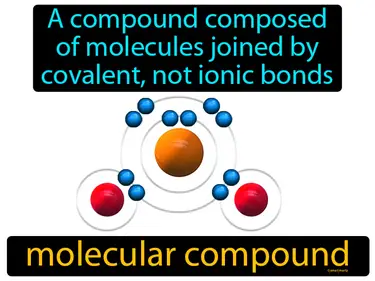
A compound composed of molecules joined by covalent, not ionic bonds. Molecular compound. A molecular compound is made up of atoms that share electrons through covalent bonds.
network solid
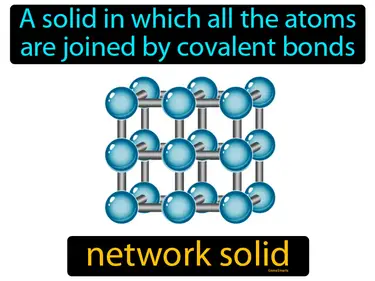
A solid in which all the atoms are joined by covalent bonds. Network solid. A network solid is a type of material where atoms are connected in a continuous, repeating pattern through covalent bonds, making it very strong and hard.
nonpolar covalent bond
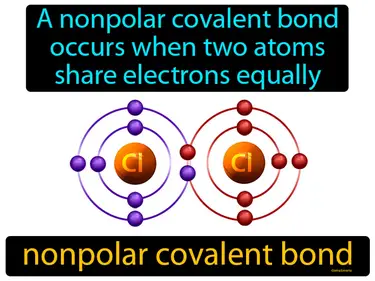
A nonpolar covalent bond occurs when two atoms share electrons equally. Nonpolar covalent bond. It's a type of chemical bond where atoms share electrons evenly because they have similar electronegativities.
pi bond
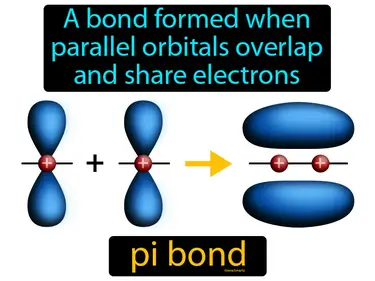
A bond formed when parallel orbitals overlap and share electrons. Pi bond. A pi bond is a type of chemical bond where electrons are shared in overlapping orbitals, typically above and below the bonding atoms.
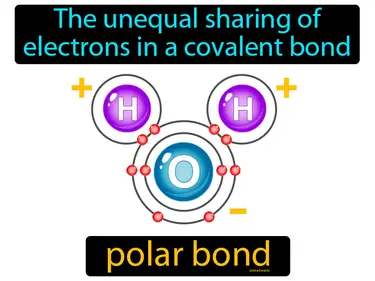
polar molecule
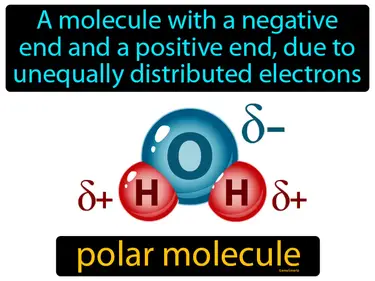
A molecule with a negative end and a positive end, due to unequally distributed electrons. Polar molecule. A polar molecule has parts with different charges because electrons are not shared equally.
resonance structure
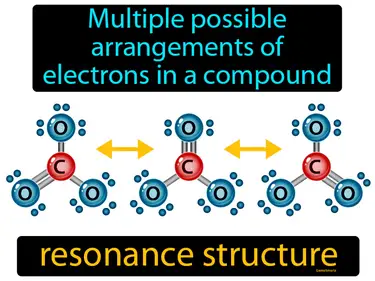
Multiple possible arrangements of electrons in a compound. Resonance structure. Resonance structure refers to different ways of representing the placement of electrons in a molecule that cannot be captured by a single drawing.
sigma bond
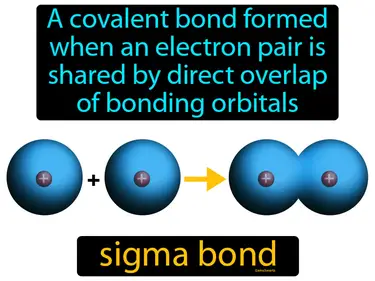
A covalent bond formed when an electron pair is shared by direct overlap of bonding orbitals. Sigma bond. A sigma bond is a type of covalent bond where two atoms share electrons in an overlapping manner, creating a strong bond.
single covalent bond
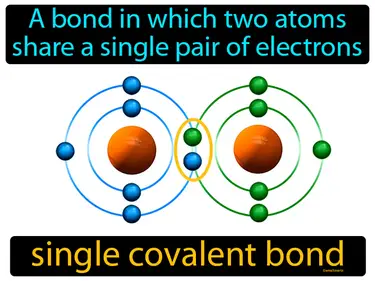
A bond in which two atoms share a single pair of electrons. Single covalent bond. In a single covalent bond, each atom provides one electron to form a pair that is shared between them, holding the atoms together.
structural formula
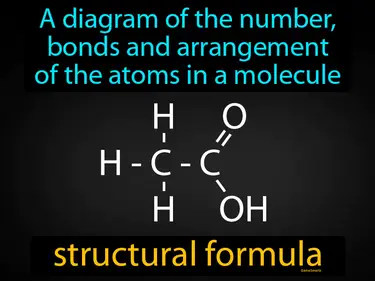
A diagram of the number, bonds and arrangement of the atoms in a molecule. Structural formula. A structural formula shows how atoms are connected and arranged in a molecule.
triple covalent bond
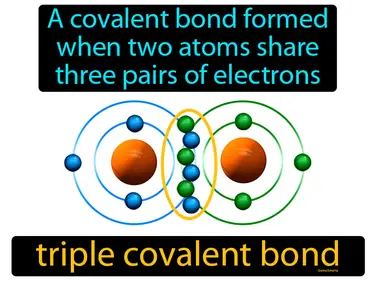
A covalent bond formed when two atoms share three pairs of electrons. Triple covalent bond. In simple terms, a triple covalent bond is when two atoms share three pairs of electrons to stay connected.
unshared pair
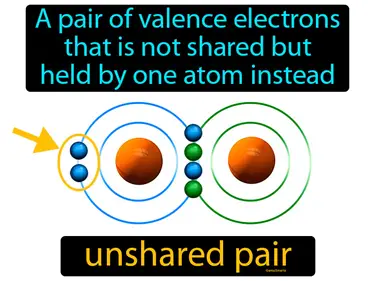
A pair of valence electrons that is not shared but held by one atom instead. Unshared pair. An unshared pair, or lone pair, is when two electrons in an atom's outer shell are not involved in bonding with another atom.
VSEPR model
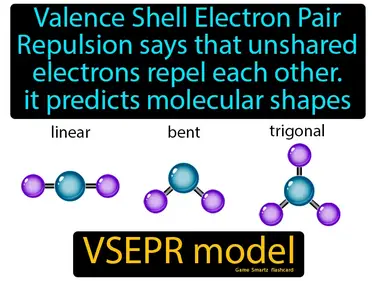
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion says that unshared electrons repel each other, it predicts molecular shapes. VSEPR model. The VSEPR model helps determine the 3D shape of molecules by considering how electron pairs push each other apart.