Scientific Measurement
Science
accepted value

The standard value for a measurement, used by the scientific community. Accepted value. The accepted value is the correct or agreed-upon value that scientists use as a benchmark for their measurements.
accuracy

How close a measurement is to the true or accepted value. Accuracy. In Science, accuracy refers to how correct or exact a measurement is compared to the true value.
base unit
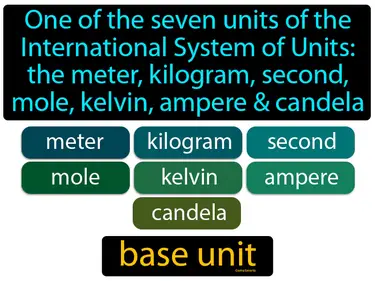
One of the seven units of the International System of Units the meter, kilogram, second, mole, kelvin, ampere candela. Base units are the fundamental units of measurement that define the standards for measuring physical quantities in science.
Celsius scale

The temperature scale where water freezes at 0 degrees and boils at 100 degrees. Celsius scale. The Celsius scale is a scientific system for measuring temperature based on the freezing and boiling points of water.
conversion factor

A ratio used to convert a quantity from one unit to another. Conversion factor. In Science, a conversion factor is a number used to change measurements from one unit to another, like converting inches to centimeters.
derived unit
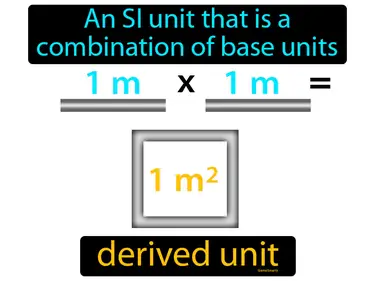
An SI unit that is a combination of base units. Derived unit. Derived units are created by combining base units to measure things like speed or area.
dimensional analysis

The technique of converting units using the numerical relationship between them, like 60 minutes 1 hour, is dimensional analysis. In Science, dimensional analysis is used to convert one unit of measurement to another by using conversion factors.
error value

The difference between an experimental value and an accepted value. error value. In science, an error value indicates how much an experimental measurement deviates from the standard or expected result.
gram

A metric mass unit equal to the mass of 1 cm of water at 4C. A gram is a basic unit of mass in the metric system commonly used to measure small amounts of substances.
international system of units

The internationally accepted system of units used by scientists. International System of Units. It is a standard set of measurements used worldwide to ensure consistency in scientific data.
kelvin

The SI unit of temperature kelvin. Kelvin is a scale used to measure absolute temperature, starting from absolute zero, where all molecular motion stops.
Kelvin scale
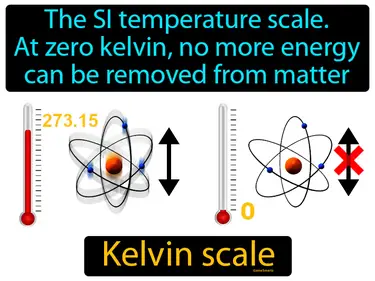
The SI temperature scale. At zero kelvin, no more energy can be removed from matter. Kelvin scale. The Kelvin scale is a scientific temperature scale where absolute zero, the point at which no heat energy remains in a substance, is zero.
liter

The metric unit for volume equal to 1000 cm3. Liter. A liter is a basic unit used to measure liquid volume, like water or milk, in the metric system.
measurement

A quantitative description with both a numerical value and a unit. Measurement. Measurement is the process of determining the size, quantity, or amount of something using specific units.
meter
The basic SI unit of length. meter. A meter is the distance light travels in a vacuum in 1299,792,458 seconds.
percent error

The error of a reading expressed as a percentage of the accepted value. Percent error. Percent error in science is a way to compare how accurate a measurement is by showing how far off it is from the true or accepted value.
precision
How exact a measurement is. Precision. In science, precision refers to how closely repeated measurements of the same quantity agree with each other.
scientific notation

A method of writing numbers using powers of ten. Scientific notation. It's a way to express very large or very small numbers conveniently by using powers of ten.
significant figure

The digits in a measurement that are exact, plus one digit whose value is estimated. Significant figure. In Science, significant figures indicate the precision of a measurement.