The Chemistry of Life
Science
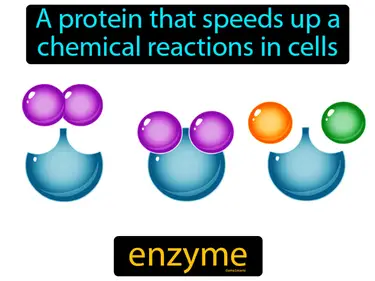
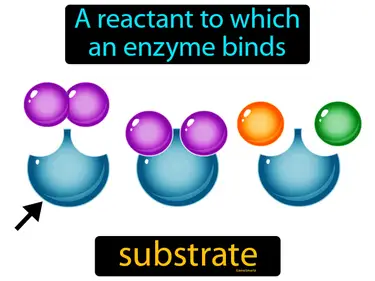
active site
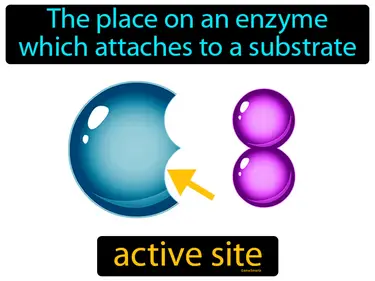
The place on an enzyme which attaches to a substrate is called the active site. The active site is the specific part of an enzyme where the substrate binds and the chemical reaction occurs.
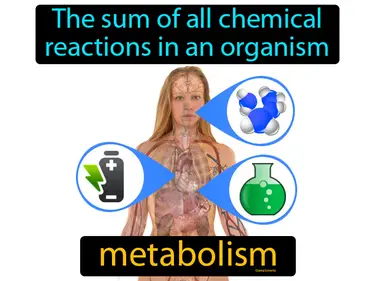
anabolism
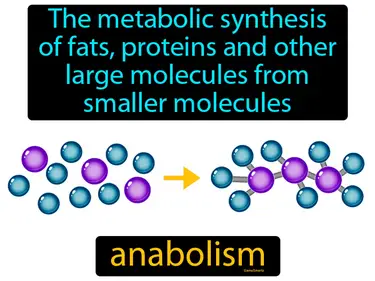
The metabolic synthesis of fats, proteins, and other large molecules from smaller molecules. Anabolism. It is the process where the body builds up complex molecules from simpler ones for growth and repair.
biochemistry

The study of the chemistry of living things. biochemistry. Biochemistry is the science that explores the chemical processes within and related to living organisms.
catabolism
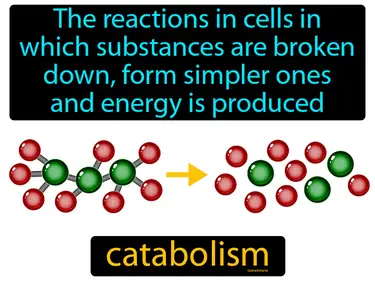
The reactions in cells in which substances are broken down, form simpler ones and energy is produced. Catabolism. In simple terms, catabolism is the process where your body breaks down food to release energy.
denaturation
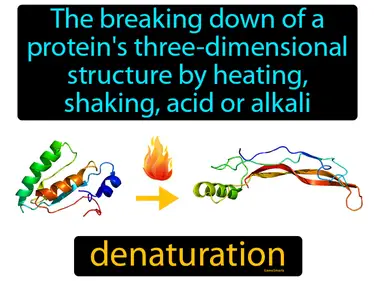
The breaking down of a protein's three-dimensional structure by heating, shaking, acid or alkali. Denaturation. It's when a protein loses its shape and can't perform its usual function.
fatty acid

A fatty acid is a carboxylic acid, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Fatty acids are building blocks of fats that store energy in the body.
monosaccharide
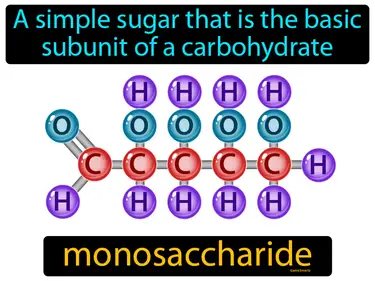
A simple sugar that is the basic subunit of a carbohydrate. Monosaccharide. It is a single sugar molecule, like glucose, that is used for energy.
peptide
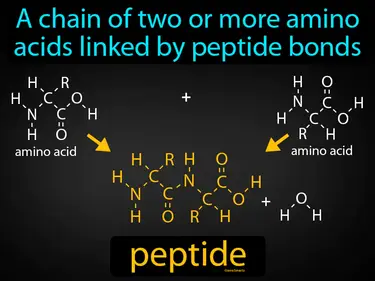
A chain of two or more amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Peptide. In simple terms, a peptide is a small protein made up of a few amino acids joined together.
peptide bond
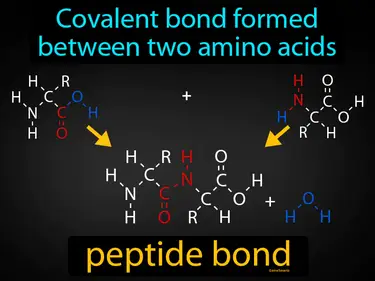
Covalent bond formed between two amino acids. Peptide bond. A peptide bond is a link that connects amino acids together to form proteins.
polysaccharide
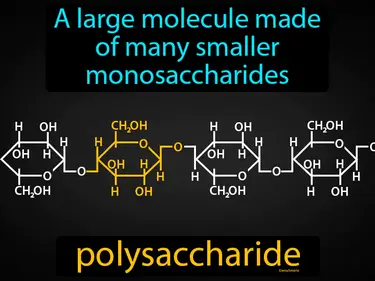
A large molecule made of many smaller monosaccharides. Polysaccharide. In simple terms, a polysaccharide is a carbohydrate made up of long chains of sugar molecules bonded together.
saponification
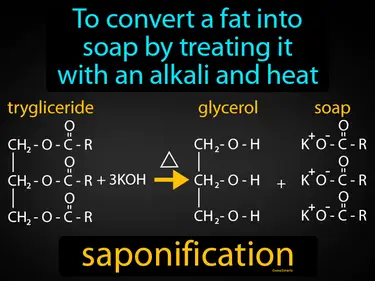
To convert a fat into soap by treating it with an alkali and heat. Saponification. Saponification is a chemical process where fats or oils react with an alkali to produce soap and glycerol.
steroid
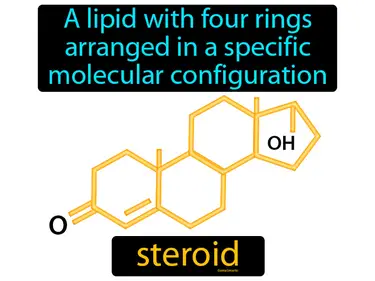
A lipid with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroid. Steroids are organic compounds that act as powerful signaling molecules in the body, such as hormones like testosterone and estrogen.
triglyceride
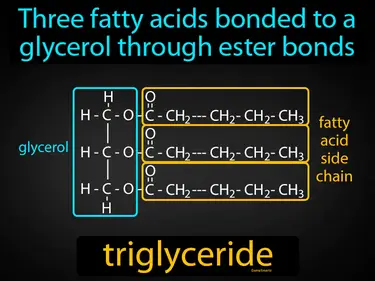
Three fatty acids bonded to a glycerol through ester bonds. Triglyceride. A triglyceride is a type of fat found in your blood that's used for energy storage.
wax

A simple lipid which is an ester of a long-chain fatty acid and alcohol. Wax. Wax is a natural substance produced by plants and animals that provides a protective coating.