Acids, Bases, and Salts
Science
acid ionization constant

The equilibrium constant for a reaction where an acid gives a proton to water. Acid ionization constant. It measures how well an acid releases protons in water, indicating its strength.
acidic solution

A solution that contains more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions. Acidic solution. An acidic solution is a liquid with a sour taste and a pH less than 7.
amphoteric
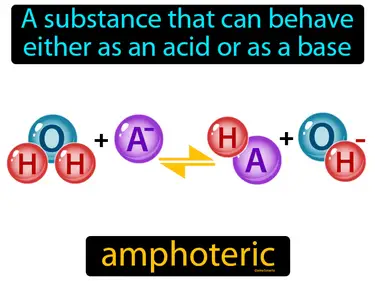
A substance that can behave either as an acid or as a base. Amphoteric. An amphoteric substance can react with both acids and bases, like water doing double duty in chemical reactions.
Arrhenius model

A concept that acids produce hydrogen ions in aqueous solution and bases produce hydroxide ions. Arrhenius model. The Arrhenius model explains how acids and bases behave in water by releasing specific ions.
base dissociation constant

A constant that indicates the strength of a base base dissociation constant. The base dissociation constant measures how well a base separates into ions in water, showing its strength.
basic solution

Contains more hydroxide ions than hydrogen ions. Basic solution. A basic solution is a liquid with a pH greater than 7.
Bronsted-Lowry model
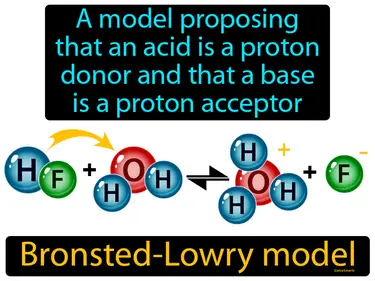
A model proposing that an acid is a proton donor and that a base is a proton acceptor. Bronsted-Lowry model. The Bronsted-Lowry model explains acids and bases in terms of their ability to donate or accept protons, respectively.
buffer capacity

The amount of acid or a base a buffer solution can absorb without a significant change in pH. Buffer capacity. Buffer capacity is the ability of a solution to resist changes in pH when acids or bases are added.
conjugate acid
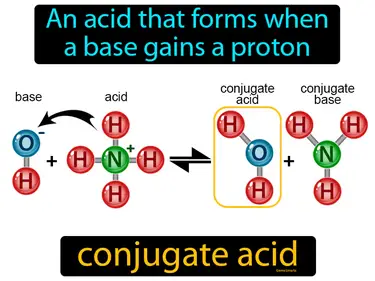
An acid that forms when a base gains a proton. Conjugate acid. A conjugate acid is simply what you get when a base picks up an extra proton during a chemical reaction.
conjugate acid-base pair
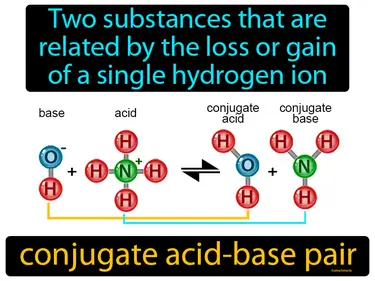
Two substances that are related by the loss or gain of a single hydrogen ion conjugate acid-base pair. In science, a conjugate acid-base pair consists of two molecules, where one can donate a hydrogen ion and the other can accept it.
conjugate base
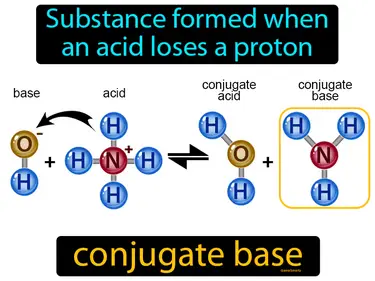
Substance formed when an acid loses a proton. Conjugate base. A conjugate base is what remains of an acid after it donates a proton during a chemical reaction.
diprotic acid
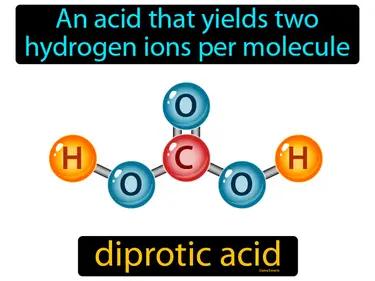
An acid that yields two hydrogen ions per molecule. Diprotic acid. A diprotic acid can give away two hydrogen ions when it reacts with other substances.
end point
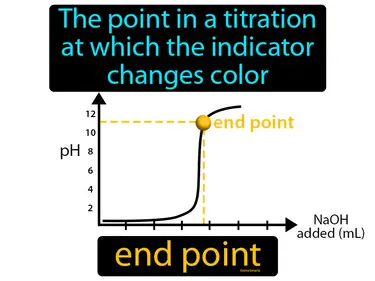
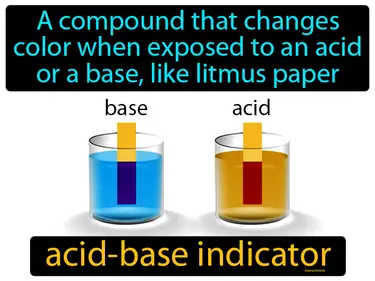
The point in a titration at which the indicator changes color. End point. The end point is when a chemical reaction is complete, shown by the indicator changing color.
equivalence point
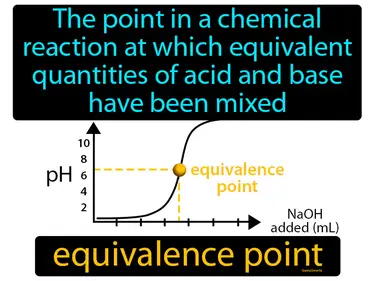
The point in a chemical reaction at which equivalent quantities of acid and base have been mixed. Equivalence point. It is the stage in a titration where the amount of acid equals the amount of base, neutralizing each other completely.
hydronium ion
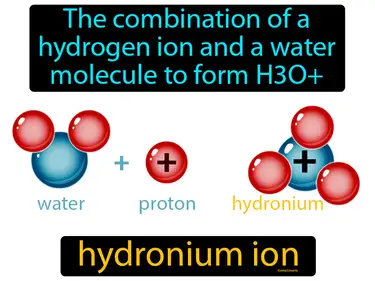
The combination of a hydrogen ion and a water molecule to form H3O hydronium ion. The hydronium ion is a water molecule with an added hydrogen ion, making it an important player in determining the acidity of solutions.
ion-product constant
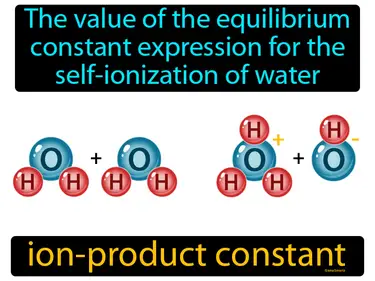
The value of the equilibrium constant expression for the self-ionization of water. Ion-product constant. The ion-product constant is the product of the concentrations of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions in water, which remains constant at a given temperature.
Lewis acid
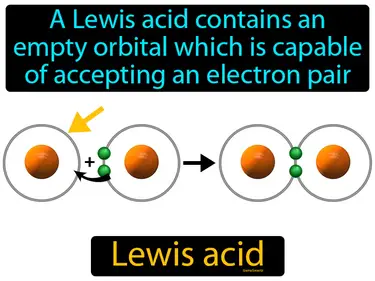
A Lewis acid contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair. Lewis acid. In simple terms, a Lewis acid is a substance that can accept a pair of electrons from another molecule.
Lewis base
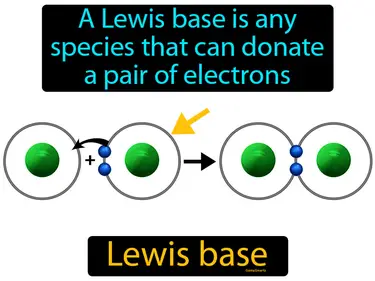
A Lewis base is any species that can donate a pair of electrons. Lewis base. In simple terms, a Lewis base is a molecule or ion that gives away electrons to form bonds.
neutralization reaction

A chemical reaction where an acid and a base are combined, destroying the properties of both, producing water and salt. Neutralization reaction. In a neutralization reaction, an acid and base mix to cancel each other out and form water and salt.
oxyacid

An acid that contains an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom and at least one other element. Oxyacid. Oxyacids are acids that have oxygen bonded to hydrogen and another element, often playing a key role in chemistry and biology.
pOH
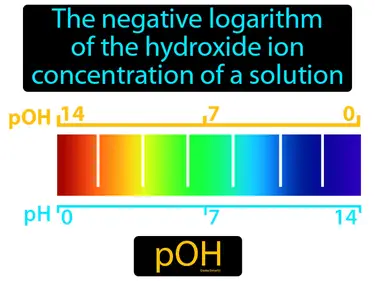
The negative logarithm of the hydroxide ion concentration of a solution. pOH. pOH is a measure of how basicalkaline a solution is.
salt
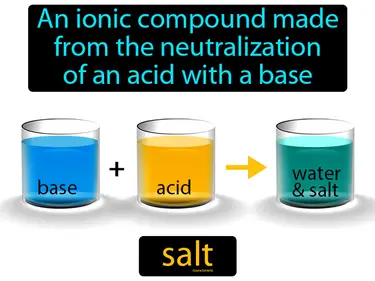
An ionic compound made from the neutralization of an acid with a base. Salt. In Science, salt is a substance that results from the chemical reaction between an acid and a base.
salt hydrolysis

A chemical reaction between water and a dissolved salt may produce an acidic or basic solution. Salt hydrolysis is when the ions from a dissolved salt react with water to form an acidic or basic solution.
standard solution

Are solutions that contain a known and accurate amount of a substance or element. standard solution. A standard solution is a liquid mixture with a precisely measured amount of a substance used in experiments for accurate results.
strong acid

An acid which is completely ionized in an aqueous solution. Strong acid. A strong acid is one that breaks apart fully in water, releasing lots of hydrogen ions.
strong base
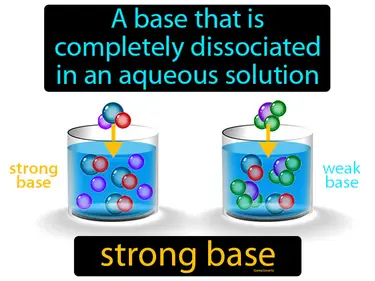
A base that is completely dissociated in an aqueous solution. Strong base. A strong base is a substance that fully breaks apart into its ions in water, making the solution very basic.
titrant

A solution of known concentration that is added to another solution in order to determine the concentration. Titrant. A titrant is a chemical solution used to precisely measure the concentration of another solution.
titration
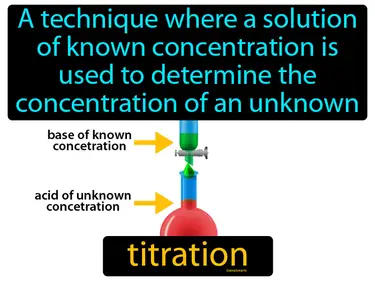
A technique where a solution of known concentration is used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution. Titration. Titration is a method in Science to find out how much of a substance is in a liquid by adding another liquid with a known concentration until a reaction shows the end point.
weak acid

Any acid that only partly dissociates splits into ions in a solution. Weak acid. A weak acid is an acid that does not completely break apart into ions in water, resulting in a less acidic solution.
weak base

Any base that does not dissociate split into ions completely in solution. Weak base. A weak base is a substance that only partially ionizes in water, resulting in fewer available ions.