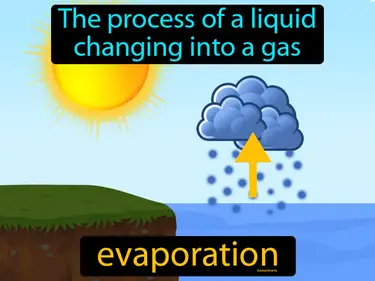
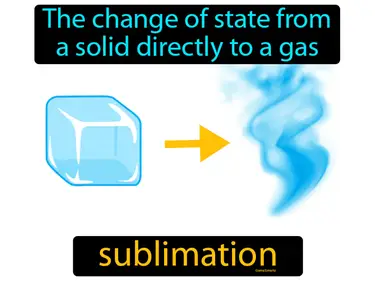
States of Matter, Liquids and Solids
Science
allotrope
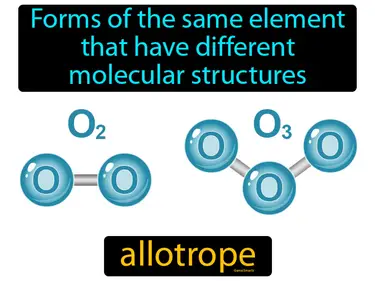
Forms of the same element that have different molecular structures. Allotrope. An allotrope is a different form of the same element that has distinct physical or chemical properties due to variations in its molecular structure.
amorphous solid

A solid made up of particles that are not arranged in a regular pattern. Amorphous solid. An amorphous solid is a type of solid where the particles are arranged randomly, like in glass or plastic.
crystalline solid
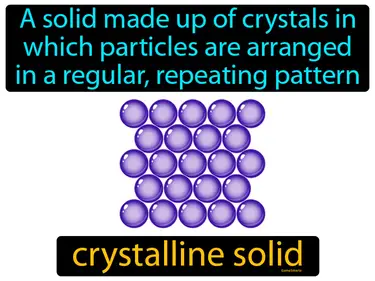
A solid made up of crystals in which particles are arranged in a regular, repeating pattern. Crystalline solid. Crystalline solids are materials where atoms or molecules are arranged in an orderly repeating structure.
deposition phase change
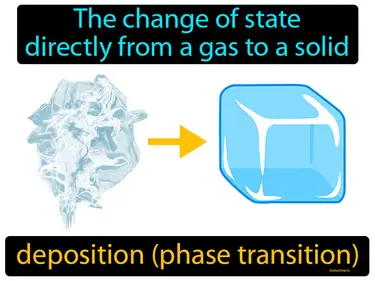
The change of state directly from a gas to a solid. Deposition phase change. Deposition phase change is when gas particles transform directly into a solid without becoming a liquid first.
dipole-dipole force
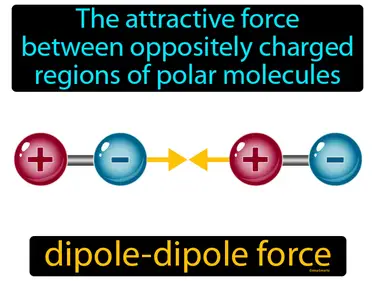
The attractive force between oppositely charged regions of polar molecules. Dipole-dipole force. This force occurs when the positive end of one polar molecule attracts the negative end of another polar molecule.
dispersion force
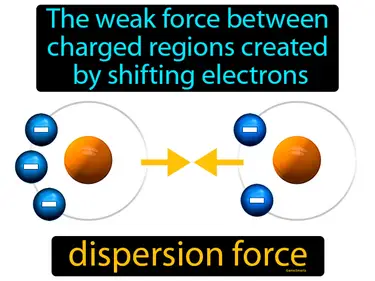
The weak force between charged regions created by shifting electrons. Dispersion force. A dispersion force is a weak attraction between molecules due to temporary shifts in electron density.
elastic collision

A collision where kinetic energy is transferred between particles but their total kinetic energy remains the same. Elastic collision. It is a type of collision where no energy is lost, and the objects bounce off each other completely.
heat of fusion

The energy required to change a substance from a solid to a liquid. Heat of fusion. It is the amount of energy needed to melt a solid into a liquid without changing its temperature.
heat of vaporization

The energy required to change a liquid at its boiling point into a gas. Heat of vaporization. Heat of vaporization is the amount of energy needed to turn a liquid into a gas at its boiling point without changing its temperature.
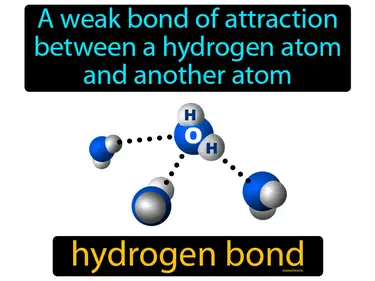
intermolecular force
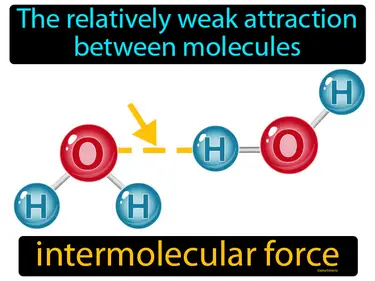
The relatively weak attraction between molecules. Intermolecular force. Intermolecular force is the force that holds molecules close to each other, affecting their physical properties like boiling and melting points.
kinetic-molecular theory
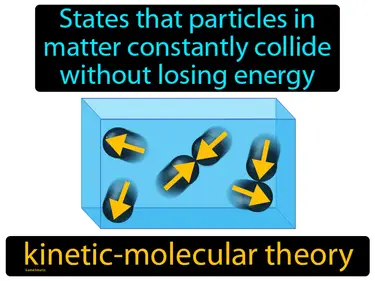
States that particles in matter constantly collide without losing energy. Kinetic-molecular theory. It explains how the tiny particles in matter move around and interact, helping us understand things like gases and temperature.
London dispersion force
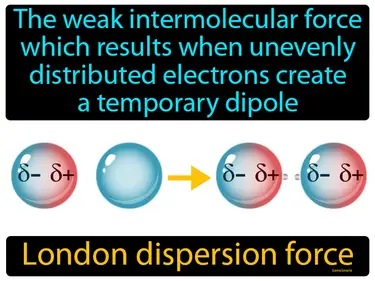
The weak intermolecular force which results when unevenly distributed electrons create a temporary dipole. London dispersion force. London dispersion force is a temporary attractive force that occurs when electrons in adjacent atoms shift, causing a fleeting attraction.
normal boiling point

The boiling point of a liquid at 1 atm pressure. Normal boiling point. The normal boiling point is the temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas when the atmospheric pressure is at sea level.
pascal
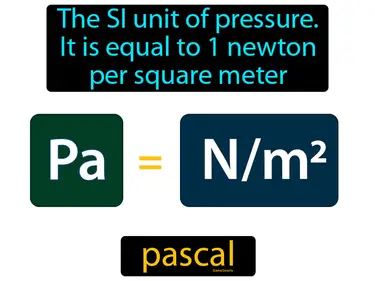
The SI unit of pressure, it is equal to 1 newton per square meter. Pascal. A pascal measures how much force is applied over a certain area.
phase diagram
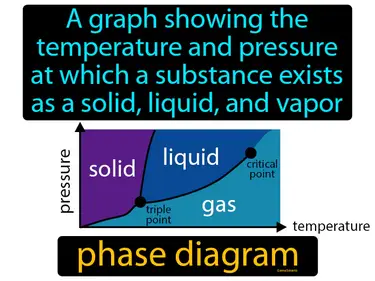
A graph showing the temperature and pressure at which a substance exists as a solid, liquid, and vapor. Phase diagram. A phase diagram displays the conditions under which a substance transitions between solid, liquid, and gas.
standard atmosphere

A unit of pressure equal to 101,325 Pa, or which supports a 760 mm column of mercury. Standard atmosphere. It is the average pressure at sea level on Earth.
triple point
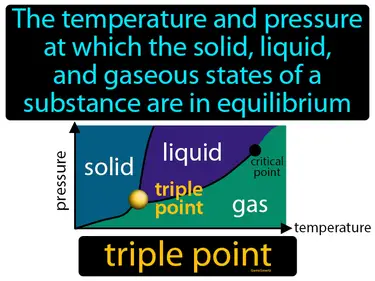
The temperature and pressure at which the solid, liquid, and gaseous states of a substance are in equilibrium. Triple point. The triple point is where a substance can exist in all three statessolid, liquid, and gasat the same time.
unit cell
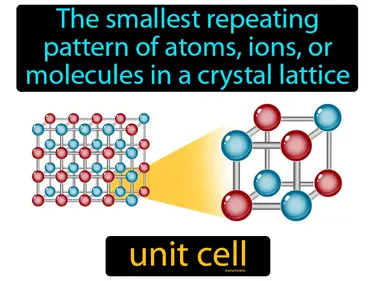
The smallest repeating pattern of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystal lattice. Unit cell. In simple terms, a unit cell is the basic building block of a crystal, like a tiny Lego piece that repeats to form the whole structure.
vapor pressure

The pressure exerted by a vapor on a liquid when they are in equilibrium. Vapor pressure. Vapor pressure is the force exerted by a vapor above a liquid when both are in balance and no net evaporation or condensation occurs.