Energy and Chemical Change
Science
calorie

A unit of heat used to measure the energy content of food, a calorie is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1C. A calorie is a measure of energy in food.
calorimeter
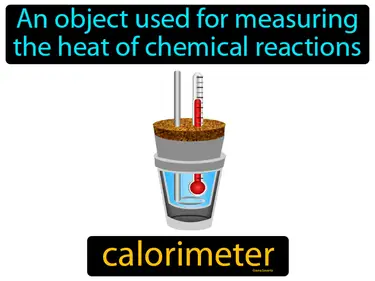
An object used for measuring the heat of chemical reactions. Calorimeter. A calorimeter is a device that helps us measure the amount of heat released or absorbed during a chemical reaction.
calorimetry

The science of measuring heat flow. Calorimetry. Calorimetry is a method used to determine the amount of heat released or absorbed during a chemical reaction, physical change, or heat capacity measurement.
chemical potential energy
The energy stored in the chemical bonds of a substance. Chemical potential energy. It is the energy that can be released when chemical reactions occur.
enthalpy
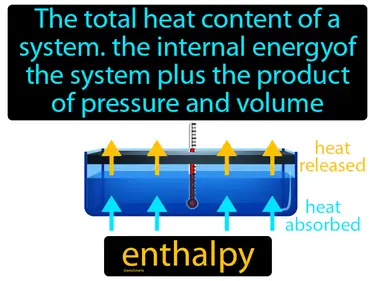
The total heat content of a system, the internal energy of the system plus the product of pressure and volume. Enthalpy. Enthalpy is the measure of energy in a system, including internal energy and the energy needed to make room for it by displacing its environment.
enthalpy of combustion

Energy released when 1 mole of a substance is burned. Enthalpy of combustion. It is the heat produced when a substance completely burns in oxygen.
entropy
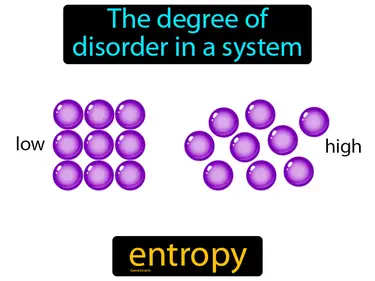
Term used to describe and measure the degree of disorder in a system entropy. In simple terms, entropy is the measure of how mixed up or disordered things are in a system.
free energy

The energy available to do work. Free energy. In simple terms, free energy is the portion of a system's energy that can perform work when temperature and pressure are uniform.
heat capacity
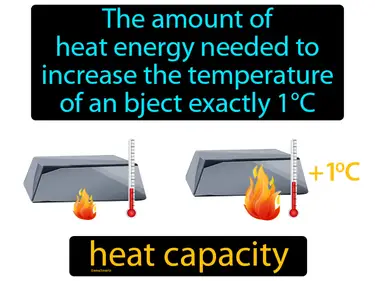
The amount of heat energy needed to increase the temperature of an object exactly 1C. Heat capacity. Heat capacity is the measure of how much heat energy an object can absorb before its temperature rises by 1C.
Hess law
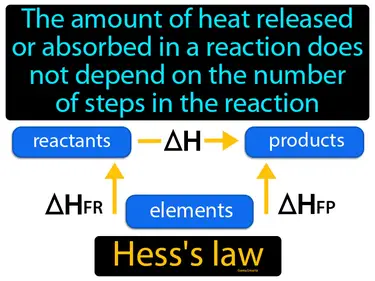
The amount of heat released or absorbed in a reaction does not depend on the number of steps in the reaction. Hess's law. Hess's law states that the total energy change in a chemical reaction is the same, no matter how many steps the reaction takes.
molar enthalpy of fusion
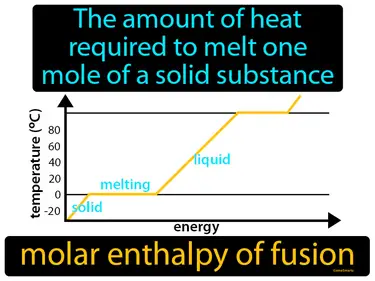
The amount of heat required to melt one mole of a solid substance. Molar enthalpy of fusion. It is the energy needed to change one mole of a solid into a liquid without changing its temperature.
molar enthalpy of vaporization
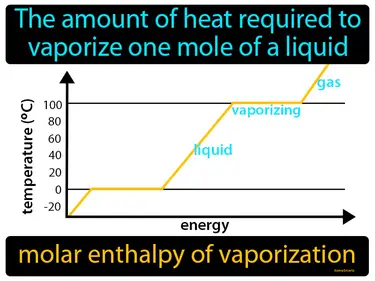
The amount of heat required to vaporize one mole of a liquid is called the molar enthalpy of vaporization. It is the energy needed to turn a liquid into a gas at its boiling point.
surrounding
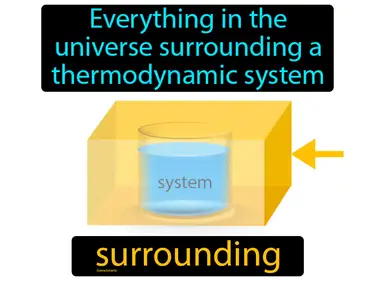
Everything in the universe surrounding a thermodynamic system. Surrounding. In Science, "surrounding" refers to everything outside the boundaries of a system that can affect or be affected by it.
thermochemical equation
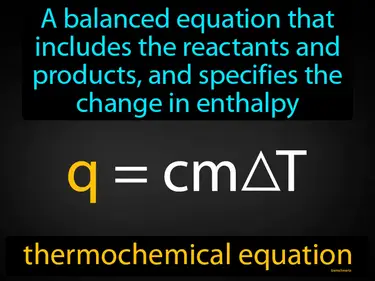
A balanced equation that includes the reactants and products, and specifies the change in enthalpy thermochemical equation. A thermochemical equation shows the energy change in a chemical reaction.
thermochemistry

Is the study of the heat released or absorbed as a result of chemical reactions. Thermochemistry. It examines how energy changes during chemical reactions.















