Gases
Science
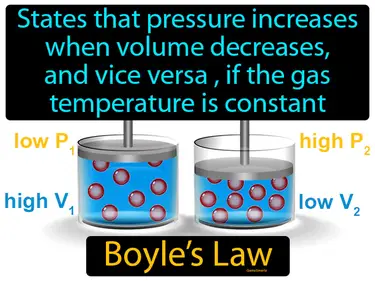
Avogadros law

States that equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain an equal number of particles. Avogadro's law. It means that if you have two balloons of the same size at the same temperature and pressure, they contain the same number of gas molecules.
combined gas law
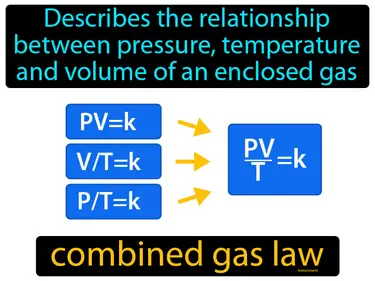
Describes the relationship between pressure, temperature and volume of an enclosed gas. Combined gas law. It shows how these three properties of a gas change together when conditions change, keeping the amount of gas constant.
Daltons law of partial pressures

The total pressure of a mixture of gases equals the sum of the pressures of all the gases. Dalton's law of partial pressures. Dalton's law states that in a mixture of gases, each gas contributes to the total pressure independently of the others.
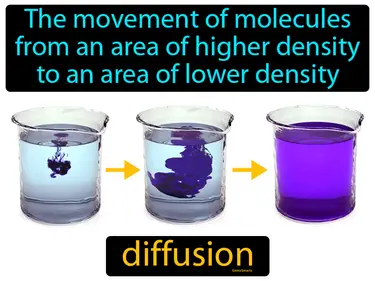
effusion

The escape of gas from a container through a tiny hole due to a pressure difference. Effusion. Effusion is when gas particles pass through a small opening from high pressure to low pressure.
Gay Lussacs law

The pressure of a gas is directly proportional to the Kelvin temperature if the volume remains constant. Gay Lussac's law. In simple terms, Gay Lussac's law explains that if you heat a gas inside a sealed container, its pressure will increase.
Grahams law of effusion

The rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass. Graham's law of effusion states that lighter gases escape through a tiny opening faster than heavier gases.
ideal gas
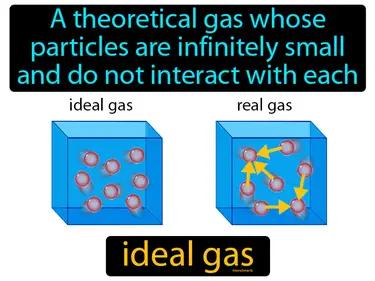
A theoretical gas whose particles are infinitely small and do not interact with each other. Ideal gas. An ideal gas is a simplified model that helps scientists understand and calculate the behavior of real gases under certain conditions.
ideal gas constant

A constant used in the ideal gas law, its value depends on the units used. Ideal gas constant. The ideal gas constant is a number that relates the energy of gas particles with temperature and pressure in calculations.
ideal gas law

The relationship between pressure P, volume V, and temperature T of an ideal gas PVnRT. Ideal gas law. The ideal gas law is a formula that describes how the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas are related, assuming the gas behaves perfectly.
molar volume

The volume of one mole of gas at 1 atm and 0C, equal to 22.4L, is known as molar volume. Molar volume is the space one mole of gas occupies under specific conditions.
partial pressure

The pressure of one gas in a mixture of gases. Partial pressure. Partial pressure is the pressure that a single type of gas in a mixture would exert if it occupied the entire volume on its own.
pascal
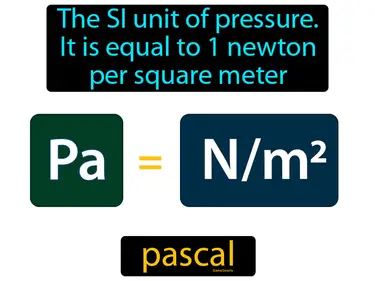
The SI unit of pressure, it is equal to 1 newton per square meter. Pascal. It measures how much force is applied over a specific area.
standard atmosphere

A unit of pressure equal to 101,325 Pa, or which supports a 760 mm column of mercury. Standard atmosphere. It is the average pressure at sea level on Earth.
standard temperature and pressure (STP)
.webp)
A temperature of 0C and pressure of 101.3 kPa 1 atm. Standard temperature and pressure STP. STP is a reference point used in science to measure gases under consistent conditions.