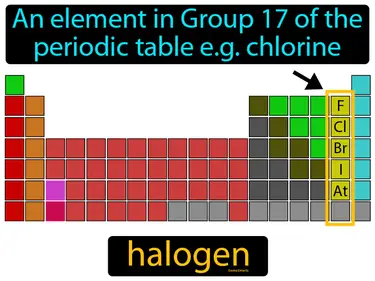
The Periodic Table
Science
actinide series
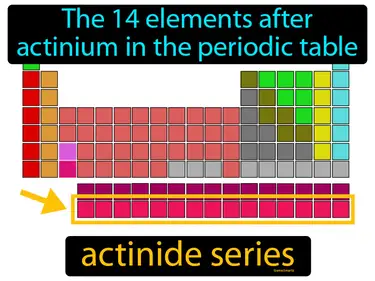
The 14 elements after actinium in the periodic table actinide series. The actinide series consists of heavy, radioactive elements used in nuclear energy and research.
alkaline earth metal
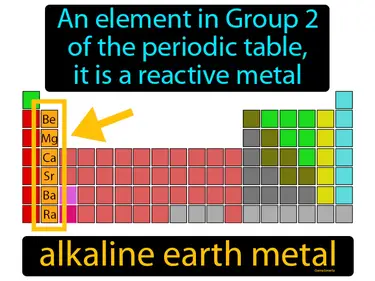
An element in Group 2 of the periodic table. It is a reactive metal. Alkaline earth metals are a group of shiny, silvery metals that are highly reactive and are commonly found in various minerals.
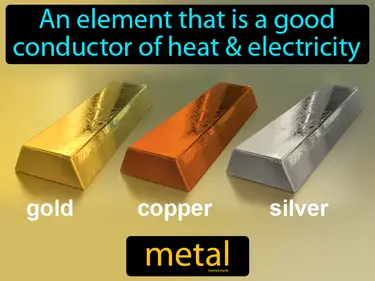
alloy

A mixture of two metals or of a metal and a nonmetal. Alloy. An alloy is a combination of metals, or a metal mixed with a nonmetal, that creates a new material with improved properties.
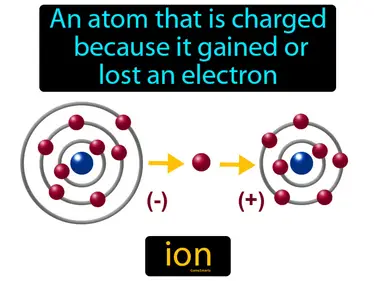
anion

An ion that has a negative charge. Anion. An anion is a type of ion that gains electrons, which gives it a negative charge.
atomic radius
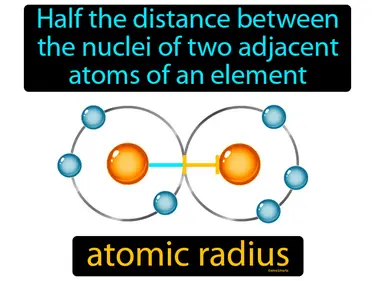
Half the distance between the nuclei of two adjacent atoms of an element is called the atomic radius. The atomic radius is the size of an atom.
cation
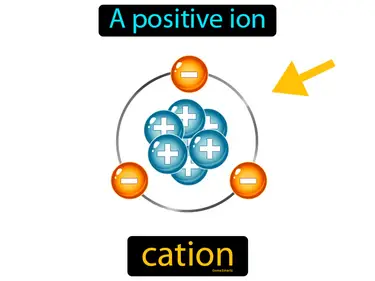
A positive ion. Cation. A cation is an atom or molecule that has lost one or more electrons, resulting in a positive charge.
electronegativity
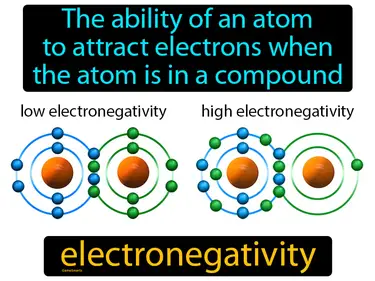
The ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound. Electronegativity. Electronegativity is how strongly an atom pulls on electrons in a chemical bond.
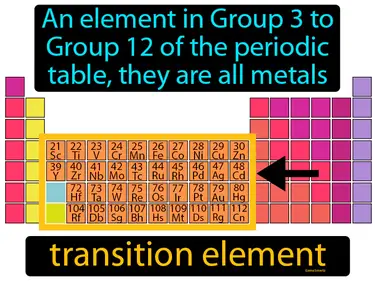
inner transition metal
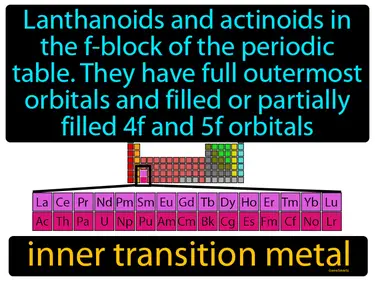
Lanthanoids and actinoids in the f-block of the periodic table, they have full outermost orbitals and filled or partially filled 4f and 5f orbitals. Inner transition metals are elements in the f-block of the periodic table that have electrons filling their inner f orbitals.
ionization energy

The energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom or ion ionization energy. Ionization energy is the amount of energy needed to take an electron away from an atom.
lanthanide series
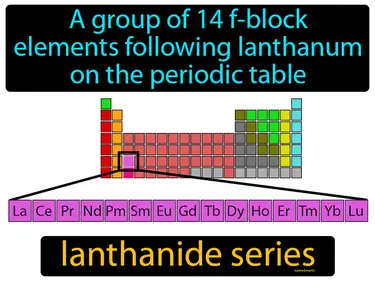
A group of 14 f-block elements following lanthanum on the periodic table. Lanthanide series. The lanthanide series consists of elements with atomic numbers 58 to 71 that are shiny and often used in electronics.
octet rule
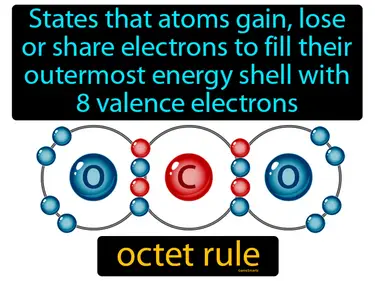
States that atoms gain, lose or share electrons to fill their outermost energy shell with 8 valence electrons. Octet rule. The octet rule is a guideline that atoms are most stable when they have eight electrons in their outer shell.
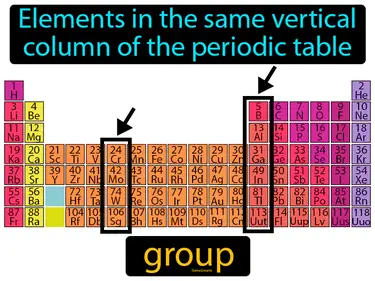
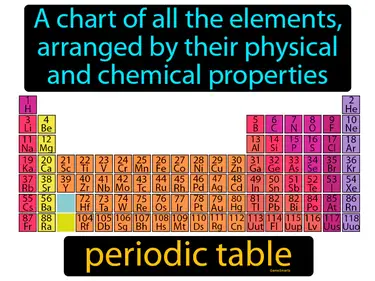
periodic law
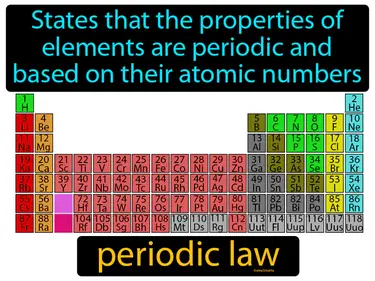
States that the properties of elements are periodic and based on their atomic numbers. Periodic law. Periodic law means that elements show repeating patterns of properties when arranged by their atomic numbers.
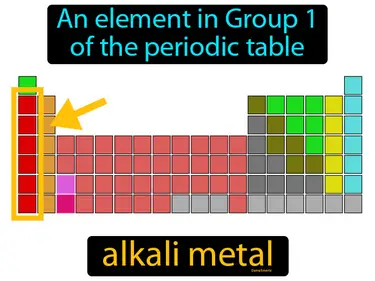
representative element
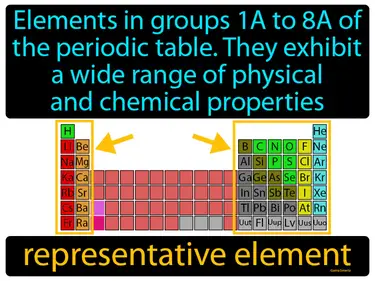
Elements in groups 1A to 8A of the periodic table, they exhibit a wide range of physical and chemical properties. Representative element. Representative elements are the elements in the s and p blocks of the periodic table that display a wide variety of properties and behaviors.