Mixtures and Solutions
Science
aqueous solution

A solution in which water is the solvent. Aqueous solution. An aqueous solution is simply when a substance is dissolved in water.
boiling point elevation

The increase in boiling point caused by a solute that is dissolved in a solvent. Boiling point elevation. Boiling point elevation is when adding a solute to a liquid makes it boil at a higher temperature than usual.
Brownian motion
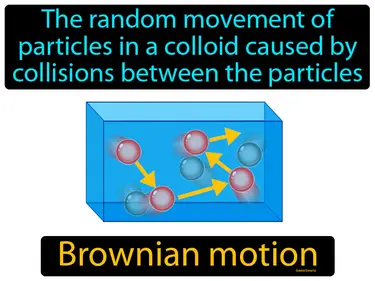
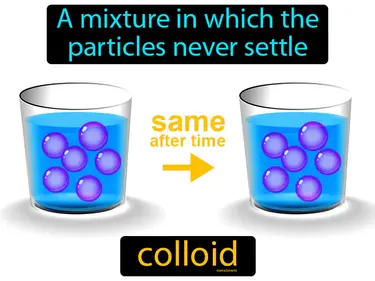
The random movement of particles in a colloid caused by collisions between the particles. Brownian motion. Brownian motion is the jittery movement of tiny particles in a fluid, caused by collisions with molecules in the liquid or gas.
colligative property

A property of a solution that depends on the concentration of the solute, not its identity. Colligative property. Colligative properties are changes in a solution that happen because of how much stuff is dissolved in it, like lowering the freezing point or raising the boiling point.
concentration

The amount of a particular solute in a given volume of solution. Concentration. It describes how much of a substance is dissolved in a certain amount of liquid.
dissociation
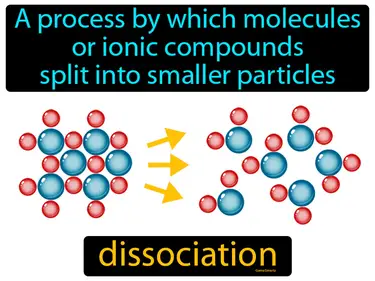
A process by which molecules or ionic compounds split into smaller particles. Dissociation. In simple terms, dissociation is when a compound breaks apart into smaller pieces, like how salt separates into ions in water.
electrolyte

A substance that conducts electricity when dissolved in a solvent. Electrolyte. An electrolyte is a chemical that helps electricity flow through solutions by allowing ions to move.
emulsion

A mixture of two or more immiscible liquids. Emulsion. An emulsion is a mixture where tiny droplets of one liquid are dispersed in another liquid, like oil in water.
freezing point depression

The difference in temperature between a solution's freezing point and the freezing point of its pure solvent. Freezing point depression. Freezing point depression is when adding a substance to a solvent lowers the temperature at which the liquid freezes.
Henrys law
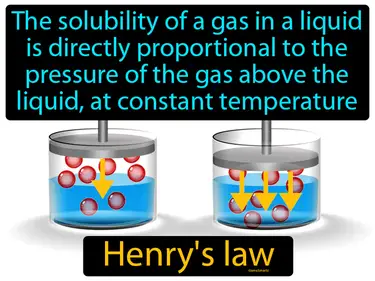
The solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas above the liquid, at constant temperature. Henry's law. Henry's law means that if you increase the pressure of a gas above a liquid, more of that gas will dissolve into the liquid.
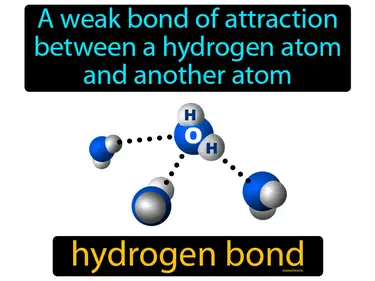
hydration
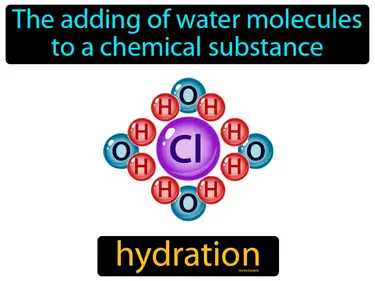
The adding of water molecules to a chemical substance. Hydration. It is the process where a substance absorbs or combines with water.
immiscible

A term used to describe liquids that do not mix with each other to form a solution immiscible. Immiscible means that two liquids, like oil and water, don't blend together and stay separate.
insoluble

A term used to describe a substance that cannot be dissolved in a given solvent. Insoluble. In Science, insoluble means a substance won't mix or dissolve in a liquid.
miscible
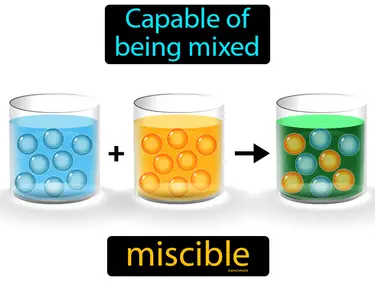
Capable of being mixed. Miscible. In Science, miscible means that two liquids can mix together completely without separating.
molality

The ratio of moles of solute dissolved in one kilogram of solvent. Molality is a measure of the concentration of a solution that expresses how many moles of a solute are present in a kilogram of the solvent.
molarity

The number of moles of solute dissolved per liter of solution. Molarity. Molarity is a measure of how concentrated a solution is, telling us how much solute is present in a specific volume of liquid.
mole fraction

A fraction equal to the number of moles of a component, divided by the total number of moles in a solution. Mole fraction. It is a way to express the concentration of a specific component in a mixture or solution.
nonelectrolyte

A substance that does not form ions in water, and cannot conduct electricity. Nonelectrolyte. A nonelectrolyte is a substance that dissolves in water without separating into ions, so it doesn't conduct electricity.
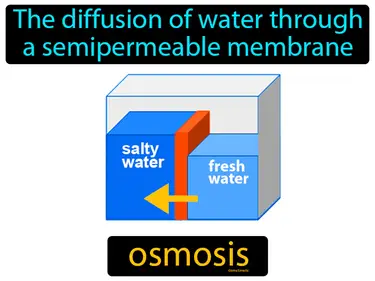
osmotic pressure
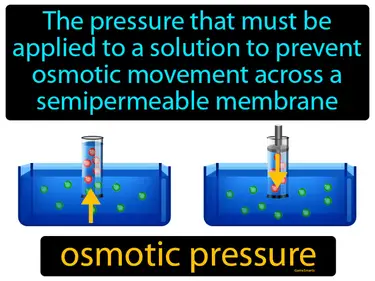
The pressure that must be applied to a solution to prevent osmotic movement across a semipermeable membrane. Osmotic pressure. Osmotic pressure is the force needed to stop water from moving through a membrane to balance concentration.
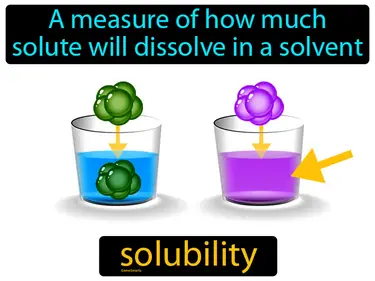
soluble
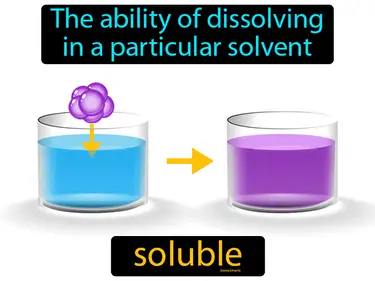
Refers to the ability for a given substance, the solute, to dissolve in a solvent. Soluble. In simple terms, soluble means a substance can mix into a liquid and disappear.
solvation
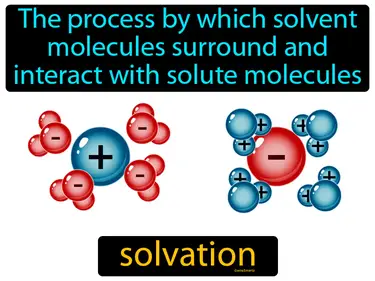
The process by which solvent molecules surround and interact with solute molecules solvation. Solvation is when a liquid, like water, helps dissolve a substance by surrounding its particles.
strong electrolyte

A compound that can completely dissociate into its ions when dissolved in water. Strong electrolyte. A strong electrolyte is a substance that fully separates into ions in water, conducting electricity very well.
surfactant
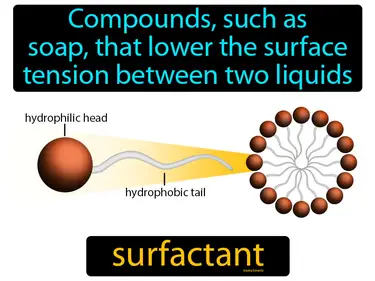
Compounds, such as soap, that lower the surface tension between two liquids. Surfactant. A surfactant is a substance that helps liquids spread out more easily by reducing surface tension.
Tyndall effect

The scattering of a light beam when it passes through a colloid. Tyndall effect. The Tyndall effect is when particles in a mixture scatter light, making a beam visible.
weak electrolyte

Is an electrolyte that does not completely dissociate split into ions in aqueous solution. Weak electrolyte. A weak electrolyte is a substance that only partially breaks into ions when dissolved in water.