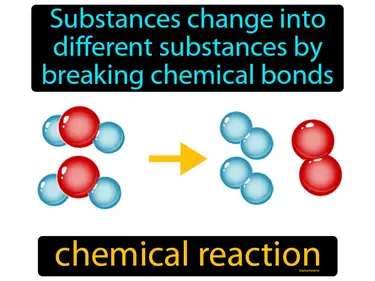
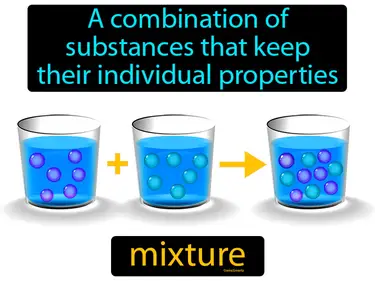
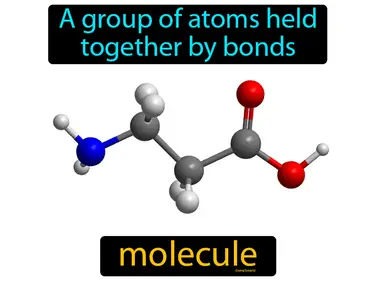
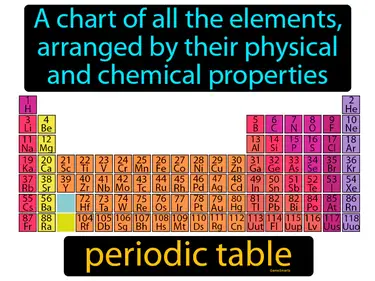
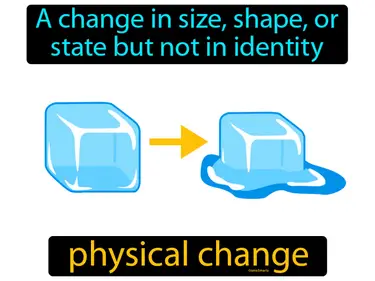
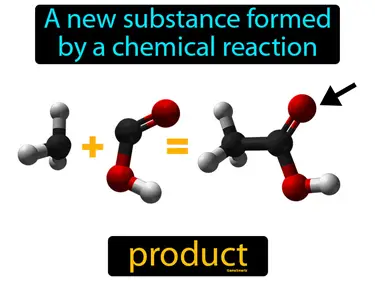
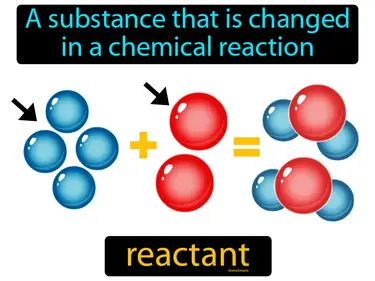
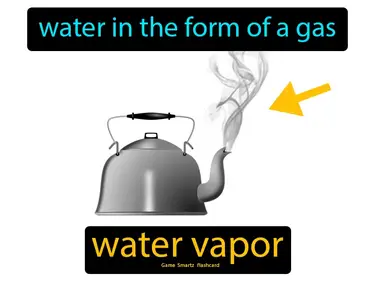
Matter
Science
distillation

The separation of substances in a liquid mixture by evaporating it and condensing the vapor. Distillation. Distillation is a process used to purify or separate liquids by heating them to create vapor and then cooling the vapor back into a liquid.
extensive property

A property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample. e.g. mass, length. extensive property. An extensive property changes when the size or amount of the sample changes.
filtration

The process of passing a liquid or gas through a filter to remove waste. Filtration. Filtration is a method where unwanted particles are removed from a liquid or gas by using a filter.
intensive property

A property independent of the amount of matter in a sample. e.g. density, temperature. intensive property. Intensive properties do not change with the size of the sample, like how boiling point remains constant regardless of how much liquid you have.
law of definite proportion
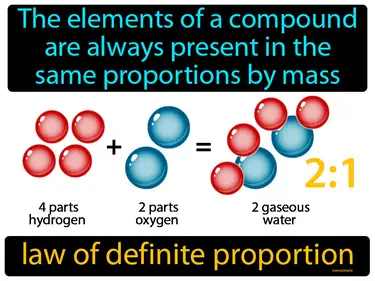
The elements of a compound are always present in the same proportions by mass. Law of definite proportion. This law means that no matter how much of a compound you have, the ratio of its elements by weight is constant and unchanging.
law of multiple proportion
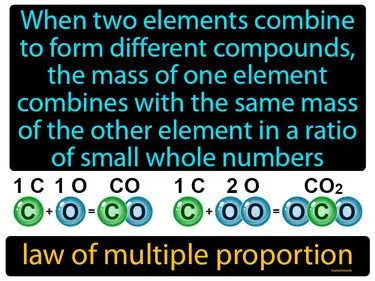
When two elements combine to form different compounds, the mass of one element combines with the same mass of the other element in a ratio of small whole numbers. Law of multiple proportion. This law states that elements can combine in different ways to form different compounds, but the ratios of the masses of these compounds will be simple whole numbers.
pure substance

An element or compound that consists of only one type of particle. e.g. oxygen, honey. pure substance. A pure substance is a material with a uniform and definite composition.
states of matter

The three forms of matter - solid, liquid, and gas. States of matter. States of matter refer to the different forms in which matter can exist, based on the arrangement and movement of its particles.