Conjugate Acid-base Pair
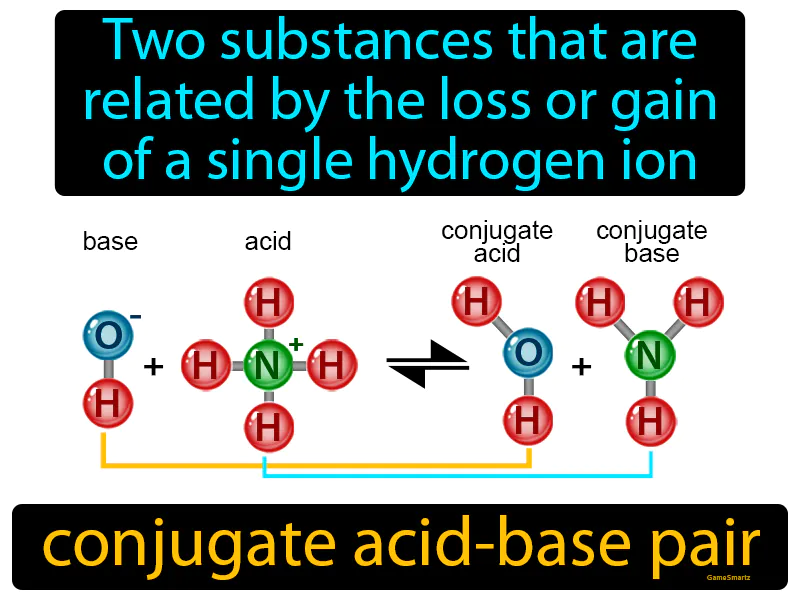
Imagine you have two identical twins who each have their own favorite hat; when one twin loses their hat, they become a little different from the other. This situation is similar to a conjugate acid-base pair, where the two substances are almost identical except for the presence or absence of a single hydrogen ion, like the hat. Just as the twin with the hat can give it away to become more like their hatless sibling, an acid can donate a hydrogen ion to become its conjugate base, showing how small changes can lead to significant shifts in identity.
Practice Version
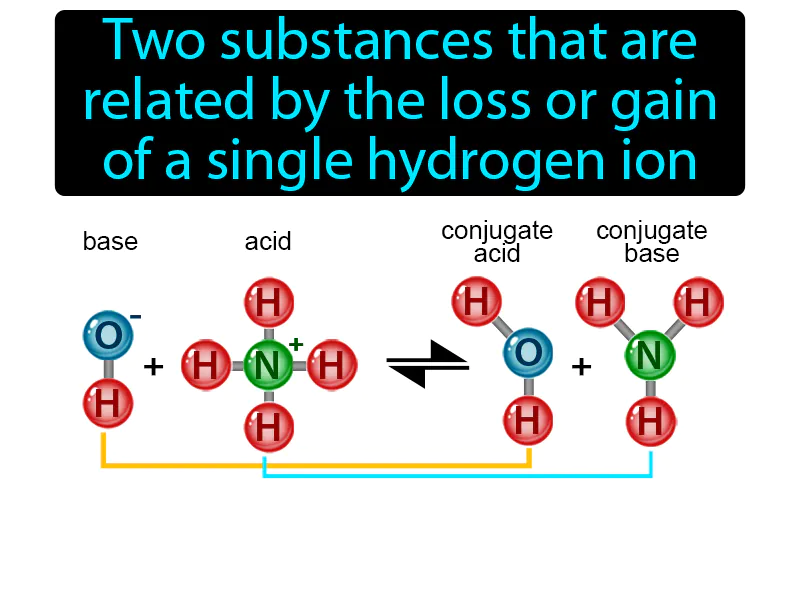
Conjugate Acid-base Pair: Two substances that are related by the loss or gain of a single hydrogen ion conjugate acid-base pair. In science, a conjugate acid-base pair consists of two molecules, where one can donate a hydrogen ion and the other can accept it.