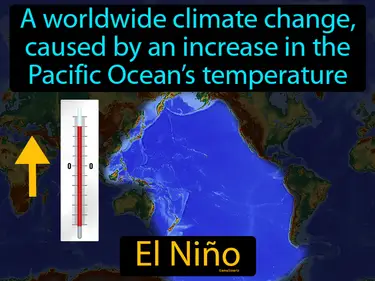
Changing Climate
Science
anomaly

A persisting deviation in a quantity from its expected value. Anomaly. In Science, an anomaly is something unusual or unexpected that doesn't fit the normal pattern.
bleaching

Occurs when coral polyps expel algae that live inside their tissues. Bleaching. Bleaching is when corals lose their color due to stress, often from warmer water, which can harm or kill them.
glacial ice

Arises as freshwater freezes over land. glacial ice. Glacial ice is a large, dense mass of frozen freshwater that forms over land from compacted snow.
global climate change

The mainly human-caused rise of the average temperature of the Earth's climate system. Global climate change. It refers to the long-term changes in Earth's weather patterns, mainly caused by human activities like burning fossil fuels.
ice core

A core sample that is extracted from an ice sheet or a high mountain glacier. Ice core. An ice core is a cylindrical sample from ice layers that helps scientists learn about past climates.
meltwater

Water released by the melting of snow or ice. Meltwater. Meltwater is the water that flows from melting snow or ice, often seen in spring when temperatures rise.
range of tolerance
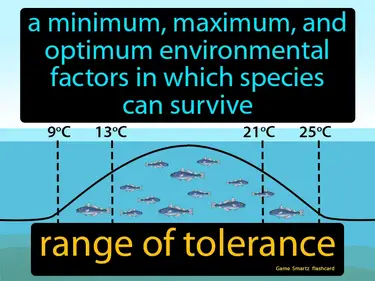
A minimum, maximum, and optimum environmental factors in which species can survive. Range of tolerance. It is the span of environmental conditions within which a species can live and thrive.
sea ice

Arises as seawater freezes. Sea ice. Sea ice is frozen ocean water that forms, grows, and melts in the ocean.
sediment core

A section of a naturally-occurring substance, such as sediment or rock. Sediment core. A sediment core is a cylindrical sample taken from the ground to study layers of soil, rock, or ice and learn about Earth's history.
trade winds
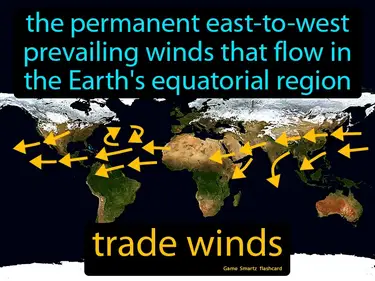
The permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. Trade winds. Trade winds are steady winds that blow towards the equator, helping ships travel across oceans.
zooxanthellae

A single-celled algae that are able to live in symbiosis with marine invertebrates. Zooxanthellae are algae that provide energy to corals by photosynthesis.