Voyage to the Deep
Science
bioluminescence

A production and emission of light by a living organism. Bioluminescence is when a living creature glows naturally like a firefly or some deep-sea fish.
CTD device

An instrument used to measure the conductivity, temperature and pressure of seawater. CTD device. A CTD device is a tool scientists use to study seawater by measuring its saltiness, heat, and depth pressure.
fluorescence

An emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light. Fluorescence. In simple terms, fluorescence is when something glows after it absorbs light or other electromagnetic radiation.
global conveyor belt
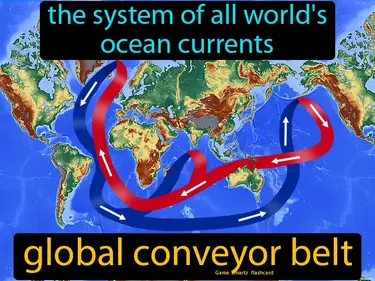
The system of all world's ocean currents. Global conveyor belt. The global conveyor belt is a continuous loop of ocean currents that circulate warm and cold water around the planet, influencing climate and weather patterns.
thermocline
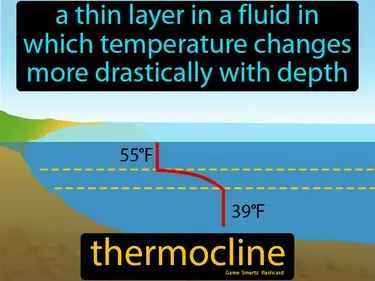
A thin layer in a fluid in which temperature changes more drastically with depth. Thermocline. The thermocline is the layer in a body of water where the temperature changes quickly with depth.
thermohaline circulation
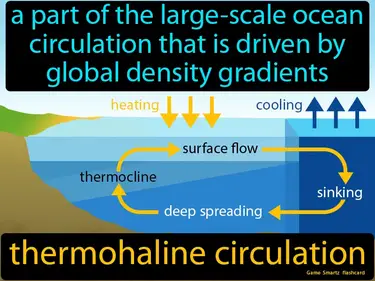
A part of the large-scale ocean circulation that is driven by global density gradients. Thermohaline circulation. It is the movement of ocean water caused by differences in temperature and salt levels, which helps regulate Earth's climate.