Seasons of Change
Science
albedo

The measure of the diffuse reflection of solar radiation out of the total solar radiation. Albedo. Albedo is a measure of how much sunlight a surface reflects back into space.
angle of insolation
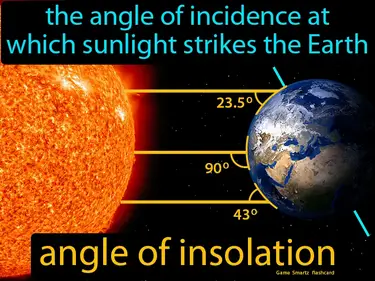
The angle of incidence at which sunlight strikes the Earth. angle of insolation. The angle of insolation refers to the angle at which sunlight hits the Earth's surface, affecting the intensity and distribution of solar energy.
Autumnal Equinox

A day in year when the Sun is directly over the equator, heading southward. Autumnal Equinox. It is the moment in fall when day and night are nearly the same length because the Sun is exactly above the equator.
differential heating

The amount of heat energy received at different parts of Earth. Differential heating. Differential heating occurs because the Sun's energy heats the Earth unevenly due to its shape and tilt.
diurnal cycle
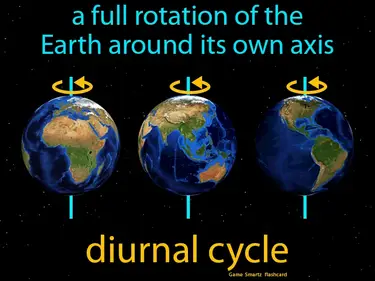
A full rotation of the Earth around its own axis. diurnal cycle. The diurnal cycle is the process that causes day and night as the Earth rotates, exposing different parts to the Sun.
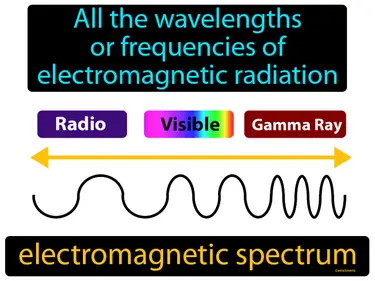
electromagnetic radiation
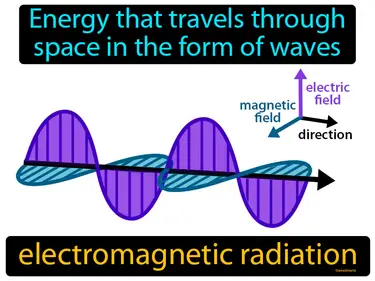
Energy that travels through space in the form of waves. Electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation is a type of energy that moves through space as waves, like light and radio waves.
insolation

The solar radiation that reaches the earth's surface. Insolation. It is the sunlight energy received by a specific area on the Earth.
Summer Solstice

A day in year when the North pole has its maximum tilt toward the Sun. Summer Solstice. It's the day when the Northern Hemisphere experiences the longest period of daylight.
Vernal Equinox

A day in year when the Sun is directly over the equator, heading northward. Vernal Equinox. It is the first day of spring in the Northern Hemisphere when day and night are approximately equal in length.
Winter Solstice

A day in year when the South pole has its maximum tilt toward the Sun. Winter Solstice. The Winter Solstice is the shortest day of the year when one hemisphere is tilted farthest away from the Sun.