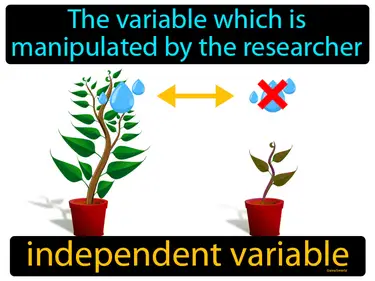
Water on Earth
Science
ballast water

A compartment within a boat that holds water, which is used to provide stability for a vessel. Ballast water is the water carried in tanks of ships to improve stability and balance during their voyage.
basin

A large water covered area between continents. Basin. In science, a basin is a depression in the Earth's surface where water collects.
cooling
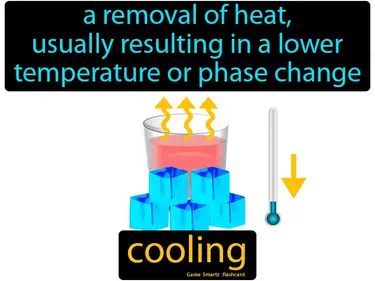
A removal of heat, usually resulting in a lower temperature or phase change. Cooling. Cooling is the process of decreasing heat to lower a substance's temperature.
dry ice

The solid form of carbon dioxide. Dry ice. Dry ice is the frozen form of carbon dioxide and is used to keep things cold without leaving any liquid residue.
freezing
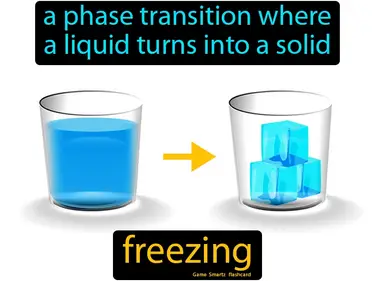
A phase transition where a liquid turns into a solid. Freezing. Freezing is the process where a liquid cools down and becomes a solid as its molecules slow down and arrange into a fixed structure.
latent heat
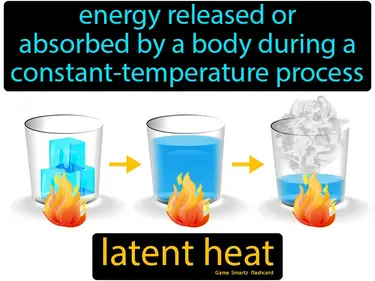
Energy released or absorbed by a body during a constant-temperature process. Latent heat. It is the energy required to change the state of a substance without changing its temperature.
neutral buoyancy

Occurs when an object's density is equal to the density of the fluid in which it is immersed. Neutral buoyancy. This means the object will neither sink nor float in the fluid.
overfishing

The removal of a fish from water at a rate that they cannot replenish. Overfishing depletes fish populations faster than they can naturally recover.
phase diagram
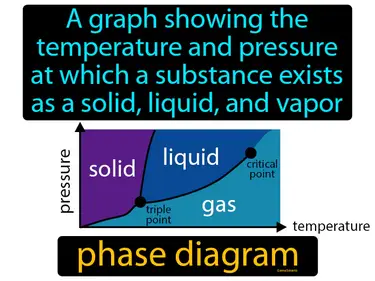
A graph showing the temperature and pressure at which a substance exists as a solid, liquid, and vapor. Phase diagram. A phase diagram shows the conditions under which a substance changes states, like solid, liquid, or gas.
sea ice

Arises as seawater freezes. Sea ice. Sea ice is frozen ocean water that forms and floats on the sea surface.