The Oceans Waves
Science
fetch

The length of water over which a given wind has blown without obstruction. Fetch. Fetch is the distance over water that wind travels uninterrupted, affecting wave size and energy.
forest zone

Area consisting of trees and plants, far enough from salt spray and wave action. forest zone. A forest zone is a region where trees are the dominant living organisms, providing a complex habitat for diverse species.
orbital wave

A wave that moves in circular motion, like an ocean wave. orbital wave. An orbital wave is a circular wave pattern where particles move in loops, similar to how objects in space orbit.
pioneer zone

The first line area to the shore, in which plants are adapted to the marine environment. Pioneer zone. The pioneer zone is the initial region near the shore where plants first establish and adapt to survive in salty conditions.
rogue wave
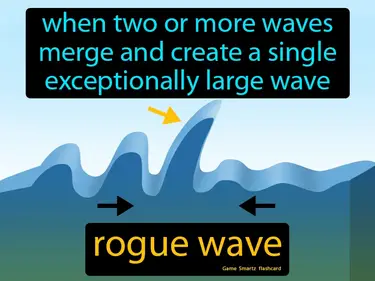
When two or more waves merge and create a single exceptionally large wave. Rogue wave. A rogue wave is a sudden, massive wave much larger than the surrounding waves, often appearing unexpectedly at sea.
scatter plot
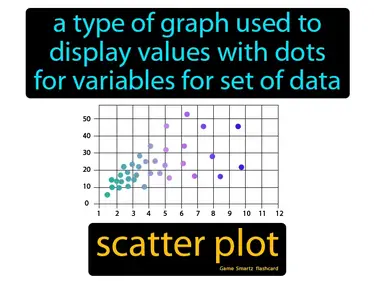
A type of graph used to display values with dots for variables for a set of data. Scatter plot. In science, a scatter plot is a graph that shows the relationship between two variables by displaying data points on a grid.
scrub zone

Area after the pioneer zone, where wave actions are infrequent. Scrub zone. The scrub zone is a coastal area with fewer disturbances from waves, allowing hardy shrubs and vegetation to grow.
wave period
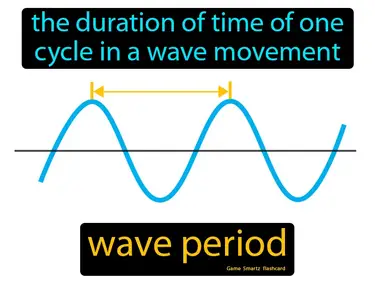
The duration of time of one cycle in a wave movement. Wave period. In simple terms, the wave period is the time it takes for a full cycle of a wave to pass a fixed point.
wave train

A set of waves passing at even intervals. wave train. A wave train is a sequence of waves traveling together, often seen in the ocean or other wave contexts.