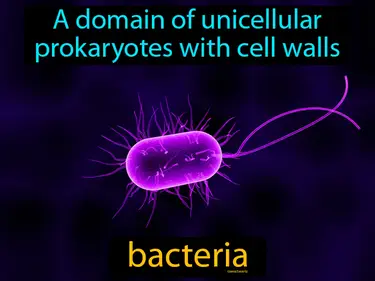
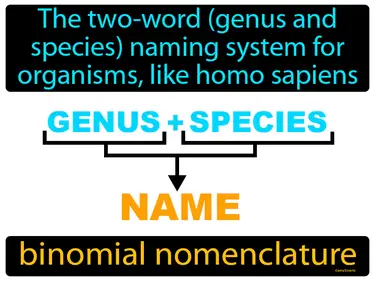
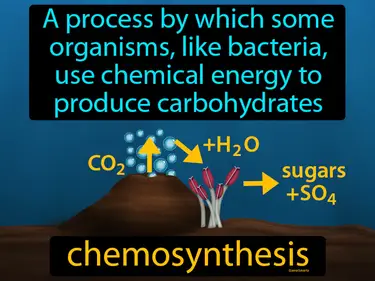
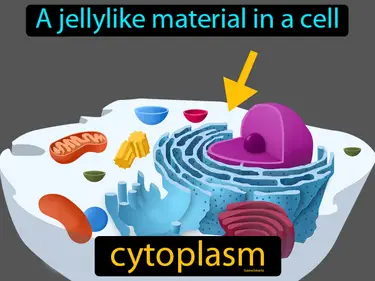
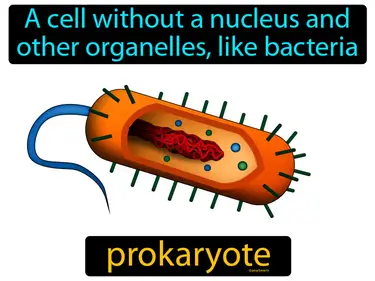
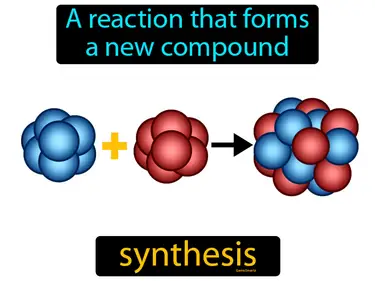
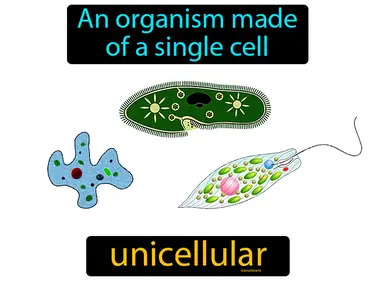
Biodiversity in the Ocean
Science
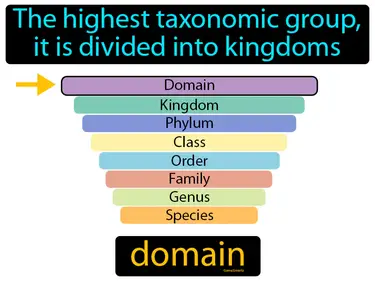
common ancestor

The most recent individual from which two or more species are descended. Common ancestor. In Science, a common ancestor is an ancient organism from which different species have evolved.
dominance hierarchy

Animal behavior where some individuals have higher social rank and more privileges. Dominance hierarchy. In science, dominance hierarchy refers to a social structure in which individuals are ranked according to their level of authority and access to resources.
dominance hierarchy

Animal behavior where some individuals have higher social rank and more privileges
excretion

The process by which waste is removed from the body. Excretion. Excretion is when your body gets rid of things it doesn't need, like pee and sweat.
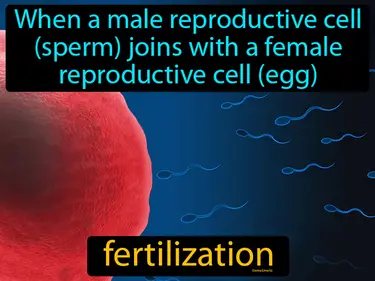
growth

A process of increasing in size. Growth. In Science, growth is when living things get bigger or develop over time by adding more cells or increasing their size.
halophiles

An extremophiles that thrive in high salt concentrations. halophiles. Halophiles are microorganisms that love and live in salty environments like salt flats or salty lakes.
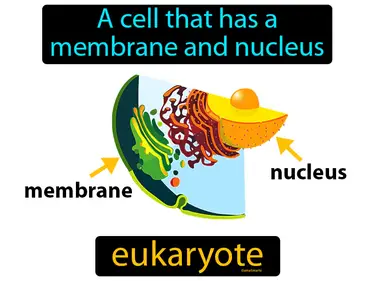
life activities
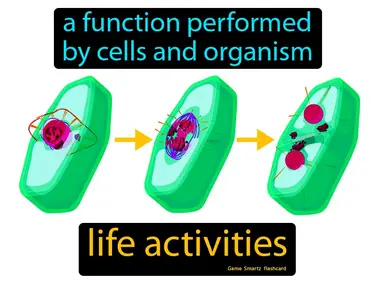
A function performed by cells and organism life activities. Life activities are the essential tasks that organisms perform to survive and grow, like eating, breathing, and moving.
methanogens

A microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct. Methanogens. Methanogens are tiny organisms that create methane gas, often found in environments without oxygen like swamps or animal guts.
nutrition
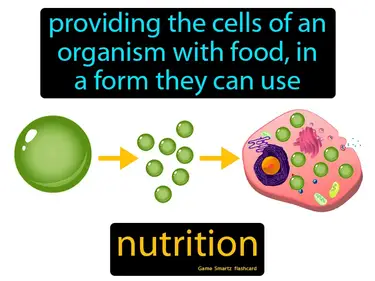
Providing the cells of an organism with food, in a form they can use. Nutrition. Nutrition is how living things get the energy and nutrients needed for growth and maintenance.
regulation
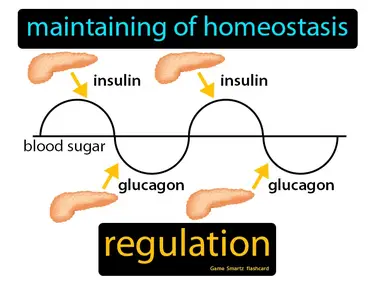
Maintaining of homeostasis. regulation. Regulation is the process by which living organisms control their internal conditions to stay balanced and healthy.
thermophiles

An organism that thrives at high temperatures. Thermophiles. They are microorganisms that live and grow in extremely hot environments, like hot springs.
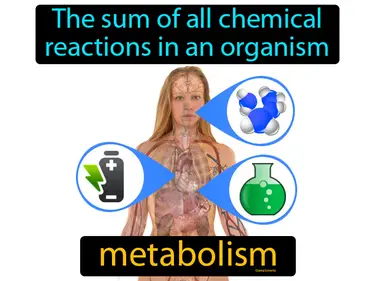
transport
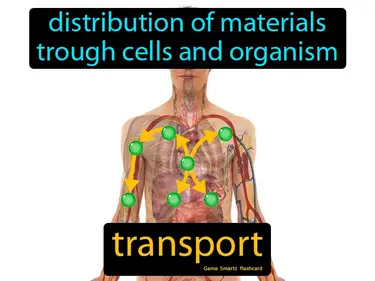
Distribution of materials through cells and organisms. Transport. Transport is the movement of substances within a living thing to where they are needed.