Biology of Fishes
Science
bony fishes

Fishes that have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. Bony fishes. Bony fishes are a type of fish with skeletons made mostly of hard bone instead of cartilage, helping them swim and survive in different water environments.
cartilaginous fishes

Fishes that have skeletons made of cartilage. Cartilaginous fishes. Cartilaginous fishes, like sharks and rays, have skeletons made of flexible cartilage instead of hard bone.
caudal fin

The tail fin, it is used for propulsion. Caudal fin. The caudal fin is the tail of a fish that helps it move through water.
dorsal

The back, or upper side of an organism. dorsal. In simple terms, "dorsal" refers to the back side of an animal or organism.
dorsal fin

A fin located on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates. Dorsal fin. It helps fish and other aquatic animals to stay stable and steer while swimming.
lateral line system
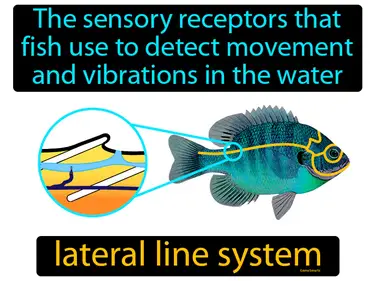
The sensory receptors that fish use to detect movement and vibrations in the water lateral line system. The lateral line system is a network of tiny hairs along a fish's body that helps it sense changes in the water around it.
operculum

The hard flap that covers and protects a fishs gills. Operculum. The operculum is a bony structure that acts like a shield, allowing fish to breathe by covering their delicate gills.
pectoral fin

Fins located on each side, usually kept folded just behind the operculum. Pectoral fin. In simple terms, a pectoral fin is a fish's side fin that helps it steer and balance in water.
spiracle in fish

A small hole behind each eye that opens to the mouth in some fish. Spiracle in fish. Spiracles are openings that help some fish breathe by allowing water to pass to their gills even when their mouth is closed.
ventral
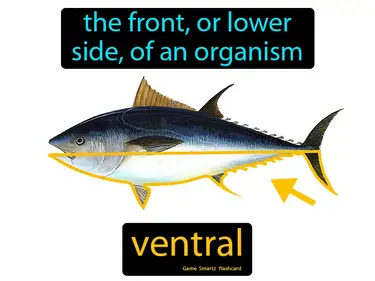
The front, or lower side, of an organism. Ventral. In simple terms, ventral refers to the belly or front side of an animal's body.