Life in the Industrial Age 1800-1915
History
Alfred Nobel

A Swedish chemist, engineer and inventor who held 355 patents. Alfred Nobel. He is best known for inventing dynamite and establishing the Nobel Prizes.
assembly line
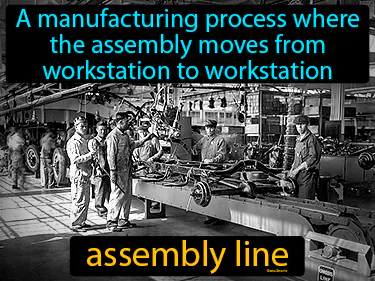
A manufacturing process where the assembly moves from workstation to workstation. Assembly line. Invented by Henry Ford, the assembly line revolutionized production by making it faster and more efficient.
cartel

An organization based on agreement among enterprises with conflicting interests. Cartel. In history, a cartel is a group of competing businesses that collaborate to control prices and limit competition within an industry.
Charles Darwin

An English naturalist and biologist, best known for his work on the theory of evolution. Charles Darwin. He is the scientist who introduced the idea that species change over time through natural selection.
Charles Dickens

An English writer, one of the greatest of the 19th century. Charles Dickens. He was a famous author known for depicting the social struggles of Victorian England.
Claude Monet

A French painter, a founder of French Impressionist painting. Claude Monet was an influential artist who captured the effects of light and nature in his works.
corporation

An organization authorized by the state to act as a single entity. Corporation. In history, a corporation is a group legally treated as a single person, capable of owning property and conducting business.
cult of domesticity

A belief among the upper and middle classes that women should stay at home. Cult of domesticity. The cult of domesticity was a 19th-century ideology that emphasized the role of women as homemakers, focusing on domestic duties and moral guidance within the household.
dynamo
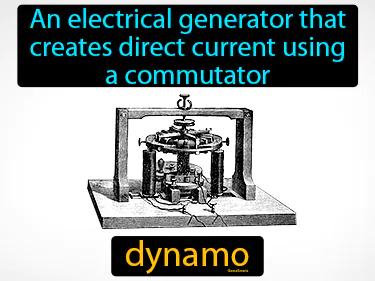
An electrical generator that creates direct current using a commutator. Dynamo. Historically, a dynamo was crucial in the development of early electricity supply systems.
Elizabeth Cady Stanton

A suffragist, social activist, abolitionist, and pioneer of women's rights movement. Elizabeth Cady Stanton. She was a leading figure in the early fight for women's suffrage in the United States.
Florence Nightingale

An English social reformer, statistician and the founder of modern nursing. Florence Nightingale. She revolutionized nursing during the Crimean War by improving sanitary conditions in hospitals.
germ theory
The theory that infectious diseases are caused by microorganisms or germs. Germ theory. Germ theory is the idea in history that tiny organisms we can't see can make us sick.
Guglielmo Marconi

An Italian inventor and electrical engineer, a pioneer of long-distance radio transmission. Guglielmo Marconi. He is famous for developing the first successful wireless telegraphy system.
Gustave Courbet

A French painter who led the Realism movement. Gustave Courbet. He was an artist known for portraying everyday life with truth and accuracy.
Henry Bessemer

An English inventor, who improved steel-making process Henry Bessemer. Henry Bessemer revolutionized industrial production by inventing a method to mass-produce steel efficiently.
impressionism

An art movement characterized by small, visible brush strokes, open composition, and bright colors. Impressionism. It is a 19th-century art movement where artists painted scenes using vibrant light and colors to capture everyday moments.
interchangeable parts
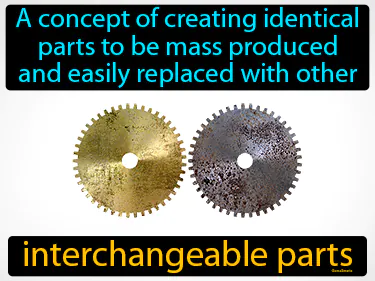
A concept of creating identical parts to be mass produced and easily replaced with other interchangeable parts. In history, interchangeable parts revolutionized manufacturing by allowing items to be quickly and efficiently repaired or assembled with standardized components.
John Dalton

An English chemist and physicist, best known for introducing the atomic theory. John Dalton. He was a pioneer in the study of atomic structure, laying the foundation for modern chemistry.
Joseph Lister

A British surgeon and a pioneer of antiseptic surgery. Joseph Lister. Joseph Lister is known for introducing sterilization in medical procedures to prevent infections.
Lord Byron

An English poet and politician, one of the leading figures of the Romantic movement. Lord Byron was a famous 19th-century poet known for his adventurous life and influential works.
Louis Daguerre

A French artist recognized for his invention of the daguerreotype process of photography. Louis Daguerre. Louis Daguerre is known for creating one of the first practical methods of photography.
Louis Pasteur

A French microbiologist and chemist known for developing vaccination, fermentation and pasteurization. Louis Pasteur. He was a pioneer in discovering ways to prevent diseases and spoilage, changing how we understand and manage microbes.
Ludwig van Beethoven

A German composer, one of the greatest in the history. Ludwig van Beethoven. Beethoven was a revolutionary figure who transformed classical music with his innovative compositions.
Michael Faraday

An English scientist who contributed to the study of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. Michael Faraday. He is a pioneer known for his groundbreaking work in understanding electricity and magnetism.
mutual-aid society

A voluntary reciprocal exchange of resources and services for mutual benefit. Mutual-aid society. Historically, a mutual-aid society is a group where members help each other, especially in times of need, by pooling resources and services.
Orville and Wilbur Wright

Aviation pioneers credited with inventing, building and flying the world's first airplane. Orville and Wilbur Wright were brothers who made history by achieving the first powered, controlled flight in 1903.
racism

The belief in the natural superiority of one race over another. Racism. Throughout history, racism is when people are treated unfairly or unequally because of their race or skin color.
realism

The general attempt to depict subjects truthfully in different forms of the arts. Realism. In history, realism refers to a movement aiming to portray everyday life and people as they truly are, without idealization.
Robert Koch

A German physician and microbiologist, one of the founders of bacteriology. Robert Koch. He was a pioneer who discovered the bacteria causing diseases like tuberculosis.
romanticism

A movement characterized by its emphasis on emotion and individualism. Romanticism. It was an artistic and cultural movement in the late 18th to mid-19th century that celebrated nature, emotion, and imagination over reason.
Social Gospel Movement

A movement that applied Christian ethics to social problems, like child labor. Social Gospel Movement. It was a religious movement in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that aimed to improve society by addressing social issues through Christian principles.
Sojourner Truth

Born Isabella Baumfree, an African-American abolitionist and women's rights activist, Sojourner Truth. She was a powerful advocate for both the abolition of slavery and women's rights in the 19th century.
standard of living

The economic level of an individual, family, or nation. Standard of living. Throughout history, the standard of living refers to the degree of wealth and comfort available to a person or society.
stock

All of the shares into which ownership of the corporation is divided. Stock. In history, stock is a way for people to own a small part of a company, allowing them to share in its profits and growth.
temperance movement

A social movement against the consumption of alcoholic beverages. Temperance movement. The temperance movement was a campaign in the 19th and early 20th centuries to limit or ban alcohol consumption.
Thomas Alva Edison

Inventor and businessman who has been described as America's greatest inventor. Thomas Alva Edison. He was a key figure in developing technologies like the electric light bulb and the phonograph.
urban renewal

A program of land redevelopment often used to address urban decay in cities urban renewal. Urban renewal is the process where old or run-down urban areas are revitalized, often involving the demolition of outdated buildings and the construction of new infrastructure and housing.
Victor Hugo

A French poet, novelist, and dramatist of the Romantic movement. Victor Hugo was a major figure in 19th-century French literature, known for works like "Les Misrables" and "The Hunchback of Notre-Dame."
Vincent van Gogh

A Dutch post-impressionist painter, one of the most famous in the history of art. Vincent van Gogh. He is known for his emotional paintings and vibrant use of color.
William Blake

An English poet, visionary, painter, and printmaker. William Blake was an influential figure in the Romantic era who combined art and literature to express revolutionary and mystical ideas.
William Wordsworth

An English Romantic poet who helped to launch the Romantic Age in English literature. William Wordsworth. He was a key figure in the Romantic movement, focusing on nature and human emotion.
womens suffrage

The right of women to vote in elections. Women's suffrage. Women's suffrage is the movement that fought for and achieved the right for women to vote in political elections.