Ancient India and China 2600BC-550AD
History
acculturation

A process of social and cultural change that stems from the balancing of two cultures. Acculturation. In History, acculturation refers to the way cultural traits and social patterns of one group are adopted and blended with those of another group.
acupuncture
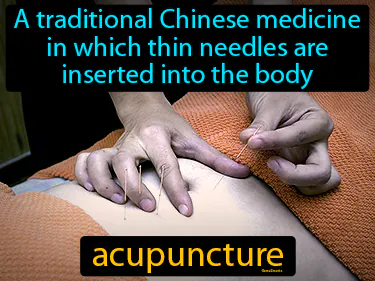
A traditional Chinese medicine in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is an ancient practice from China used to promote healing and relieve pain.
ahimsa

Means 'not to injure' and 'compassion' and refers to a key virtue in Indian religions. Ahimsa is a principle of non-violence and respect for all living beings, central to the teachings of figures like Mahatma Gandhi.
Asoka

An Indian emperor of the Maurya Dynasty, who ruled almost all of the Indian subcontinent. Asoka. Asoka was a powerful ruler known for spreading Buddhism and promoting peace after initially expanding his empire through warfare.
atman

A Sanskrit word that means inner self, spirit or soul the essence of an individual. Atman. In history, atman is a core concept in ancient Indian philosophy, signifying the true self beyond physical existence.
brahman

The highest Universal Principle, the Ultimate Reality in the universe in Hinduism brahman. In history, brahman is considered the supreme, unchanging reality, beyond the physical world, in Hindu philosophy.
calligraphy

A visual art related to writing calligraphy. Calligraphy is the artistic practice of creating decorative handwriting or lettering with a pen or brush.
caste

A form of social stratification based on hereditary status, endogamy and social barriers. Caste is a system in which people are divided into rigid social groups in some societies, notably in India, based on birth.
Chandragupta Maurya

The founder of the Maurya Empire in ancient India. Chandragupta Maurya. He was a brilliant leader who united most of the Indian subcontinent under one rule for the first time.
character

A sign or symbol used in writing. Character. In History, a character is a written symbol used in ancient scripts to record events and communicate.
civil servant

An individual who works as part of bureaucracy. civil servant. A civil servant is a government employee who helps implement policies and services.
clan

A group of people united by actual or perceived kinship and descent. Clan. In History, a clan is a social group consisting of families or communities linked by common ancestry or association.
Confucius

A Chinese philosopher who emphasized morality, justice, kindness, and sincerity. Confucius. Confucius was an influential teacher whose ideas shaped Chinese society and culture over centuries.
decimal system

Has ten as a starting point or base and was invented during the Golden Age in India. The decimal system is a way of counting that uses the digits 0-9, making calculations simpler and more efficient.
dharma

A key concept with multiple meanings in Indian religions, dharma. In history, dharma refers to the moral and ethical duties or laws people are expected to follow.
dissent

A philosophy of non-agreement with a prevailing idea or entity. Dissent. In history, dissent is when individuals or groups challenge or oppose established norms or authorities.
dowry

A transfer of parental property, gifts, or money at the marriage of a daughter bride. Dowry. Historically, a dowry is a payment from the brides family to the grooms family as part of the marriage arrangement.
dynastic cycle

A theory in the Chinese history that each dynasty rises, then declines due to moral corruption and falls. Dynastic cycle It explains how dynasties in China historically rose to power, became corrupt, and eventually were replaced.
Eightfold Path

A summary of the path of Buddhist practices leading to liberation from samsara Eightfold Path. The Eightfold Path is a set of principles in Buddhism designed to guide individuals towards ethical living, mental discipline, and wisdom to achieve enlightenment.
expansionism
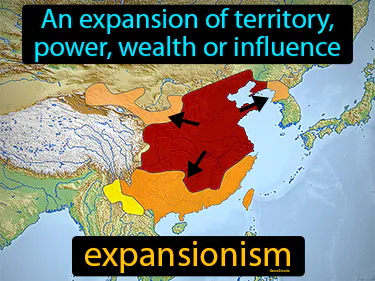
An expansion of territory, power, wealth, or influence. Expansionism. In history, expansionism refers to the policy or practice of a country increasing its land or influence over other regions.
feudalism
A system of holding of land in exchange for service or labor. Feudalism. In history, feudalism was a medieval structure where lords gave land to vassals in return for military and other services.
filial piety

A virtue of respect for one's parents, elders and ancestors filial piety. In History, filial piety refers to the Confucian principle emphasizing respect and devotion to one's family, particularly in ancient Chinese culture.
Four Noble Truths

The truths for the spiritually worthy ones dukkha, samudaya, nirodha, and magga. Four Noble Truths. In history, the Four Noble Truths are the core teachings of Buddhism that explain the nature of suffering and the path to overcoming it.
golden age

A periods in India where the country saw many innovations, around the 4th and 6th century CE, golden age. A golden age is a time of great cultural, economic, and scientific achievements in a civilization.
Harappa

An archaeological site of Bronze Age fortified city, located in Punjabi. Harappa was a major city of the ancient Indus Valley Civilization, known for its advanced urban planning and architecture.
Indian subcontinent
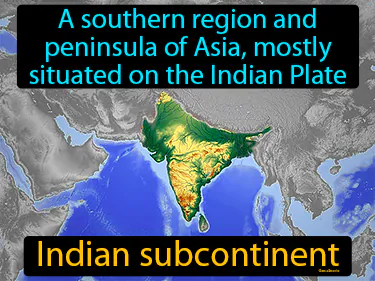
A southern region and peninsula of Asia, mostly situated on the Indian Plate. Indian subcontinent. The Indian subcontinent is a historical region where ancient civilizations like the Indus Valley thrived.
Indra

The most important among the Indo-Aryan gods. Indra. Indra is a major deity in ancient Indian history, known as the god of rain and thunder.
joint family
An family arrangement, consisting of many generations living in the same household. Joint family. In history, a joint family is a traditional family structure where grandparents, parents, and children all live together, sharing responsibilities and resources.
karma

The cycle of cause and effect done by individuals actions. Karma. In history, karma is like the idea that actions have consequences over time.
Laozi

A Chinese philosopher and founder of Taoism. Laozi. Laozi is an ancient thinker who laid the foundations for Taoism, focusing on harmony with the natural world.
missionary

A member of a religious group sent into an area to promote their faith is called a missionary. In history, missionaries traveled to spread their religion and often influenced local cultures and societies.
Mohenjo Daro

An archaeological site of one of the largest ancient settlements built 2500 BCE, located in Pakistan. Mohenjo Daro. Mohenjo Daro was a major city of the ancient Indus Valley Civilization known for its advanced urban planning.
moksha

The ultimate goal of personal spiritual development for some schools of Hinduism is moksha. Moksha is the liberation from the cycle of rebirth and suffering, seeking unity with the divine.
monopoly

When a specific person or enterprise is the only supplier of a particular commodity monopoly. Historically, a monopoly is when one company completely controls the market for a product, like when Standard Oil dominated the U.S. oil industry in the late 1800s.
mystic

A person who can directly experience God or true reality through visions or dreams. Mystic. In history, a mystic is someone renowned for having deep, spiritual connections and insights beyond the ordinary understanding.
nirvana

The state of perfect peace reached by not wanting more than you have. Nirvana. In Buddhism, Nirvana is the ultimate goal where one is free from suffering and desire.
oracle bone

Pieces of ox scapula or turtle plastron, which were used for pyromancy in ancient China. Oracle bone. Oracle bones are ancient Chinese artifacts used by priests to predict the future by burning and interpreting cracks on them.
philosophy

The study of questions about existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language. Philosophy. In history, philosophy is like a guide that helps us understand how people have thought about lifes big questions over time.
rajah

A title for a monarch equivalent to king or princely ruler in India and Southeast Asia rajah. A rajah is a local king or prince in parts of India and Southeast Asia.
reincarnation

The idea that people are born again in another body after they die. Reincarnation. In history, reincarnation is a belief held by many ancient cultures, such as in Hinduism and Buddhism, where the soul is reborn into a new body after death.
Sect

A subgroup of a religious or philosophical belief system. Sect. In history, a sect is a small branch that breaks away from a larger religious group, often due to differing beliefs or practices.
Shi Huangdi

The founder of the Qin dynasty and was the first emperor of a unified China. Shi Huangdi. He was the ruler who united several warring states into one empire in ancient China.
Siddhartha Gautama

A spiritual teacher who founded Buddhism. Siddhartha Gautama. He was an ancient Indian prince who became the Buddha, spreading teachings on overcoming suffering and achieving enlightenment.
Vedas

A large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Vedas. The Vedas are ancient Indian scriptures that form the foundation of Hinduism and include hymns, rituals, and philosophical teachings.
veneration

The act of honoring a saint or deceased ones. Veneration. In history, veneration refers to the deep respect and reverence people show towards saints or important figures.
warlord

A leader able to exercise military, economic, and political control over a subnational territory. Warlord. In history, a warlord is a powerful figure who rules a region through military force without the central government's consent.
Wudi

The seventh emperor of the Han dynasty of China. Wudi. He was a powerful ruler known for expanding the empire and promoting Confucianism.





