Ancient Middle East and Egypt 3200BC-500BC
History
Abraham

The common patriarch of Christianity, Islam, Judaism and some other religions. Abraham is a key historical figure believed to be the founding father of these monotheistic faiths.
Akhenaton

A pharaoh of the 18th Dynasty, noted for abandoning traditional Egyptian polytheism. Akhenaton. Akhenaton was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh known for promoting the worship of a single god, Aten, marking a significant shift away from Egypt's traditional polytheistic beliefs.
alphabet

A set of letters that represent the phonemes of spoken language used for its written form. Alphabet. The alphabet is a system of symbols used by ancient civilizations like the Phoenicians to represent sounds in their language for writing and communication.
Amun-Re

A major ancient Egyptian deity, the Sun god. Amun-Re. Amun-Re is a central figure in ancient Egyptian religion, often considered the king of the gods and a symbol of the sun.
barter economy

A system of exchange where goods or services are exchanged for other goods or services. Barter economy. In history, a barter economy was used before money existed, where people directly traded items they needed.
bureaucracy

An organizational structure with the task of implementing the decisions and policies of its governing body. Bureaucracy. In history, bureaucracy refers to a system of government where state officials, not elected representatives, manage policies and procedures.
cataract

A shallow length of the Nile River, between Khartoum and Aswan. Cataract. In historical terms, a cataract is a part of a river that has rapids or waterfalls, making navigation difficult.
civil law

A legal system intellectualized within the framework of Roman law. civil law. Civil law is a legal system that is based on written codes and laws, originating from Roman law, and is used in many parts of the world.
codification

The process of collecting and forming a legal code, i.e. codex of law. Codification. In history, codification is the organizing and writing down of laws into a systematic, accessible, and official legal code.
colony

A territory under the complete political control and occupied by settlers of a state. Colony. In history, a colony is a region governed and settled by people from another country.
covenant

A formal alliance or agreement made by God with humanity. Covenant. In history, a covenant is like a sacred promise or contract, often seen in religious contexts, where God sets terms with humans.
criminal law

The law that relates to crime the first written codes were designed by the Sumerians. Criminal law is a system of laws concerned with punishment for those who commit crimes.
cuneiform

One of the earliest systems of writing, invented by Sumerians. Cuneiform is an ancient writing system using wedge-shaped marks on clay tablets.
David

The third king of the United Monarchy of Israel and Judah, according to the Hebrew Bible. David. David was a biblical king known for uniting the tribes of Israel and establishing Jerusalem as its capital.
decipherment

The discovery of the meaning of texts written in ancient languages or scripts. Decipherment. Decipherment is the process of figuring out and understanding old, mysterious writings.
Diaspora

The dispersion of a population from their native land. Diaspora. In history, diaspora refers to the movement and scattering of people away from their ancestral homelands.
dynasty

A sequence of rulers from the same family dynasty. A dynasty is a series of rulers from the same family line who govern a country over several generations.
Epic of Gilgamesh

An epic poem from ancient Mesopotamia. Epic of Gilgamesh. It is one of the earliest known works of literature, telling the story of a legendary Sumerian king.
ethics

A part of philosophy that deals with concepts of right and wrong conduct. ethics. Ethics in history examines how moral values and rules have guided human behavior over time.
Fertile Crescent
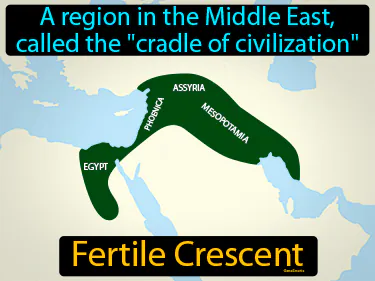
A region in the Middle East, called the "cradle of civilization". Fertile Crescent. It is a historically rich area where early human civilizations like Mesopotamia and Ancient Egypt developed due to fertile land and abundant water sources.
Hammurabi

The sixth king of the First Babylonian dynasty of the Amorite tribe, Hammurabi. Hammurabi is best known for creating one of the earliest and most complete written legal codes.
Hatshepsut

The fifth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Hatshepsut. She was one of the few female pharaohs and is known for building impressive monuments.
hierarchy

An arrangement of units into related levels of different weights or ranks. Hierarchy. In history, hierarchy refers to the way societies are organized into levels of power, status, or authority, like kings, nobles, and peasants.
hieroglyph

A character of the ancient Egyptian writing system. Hieroglyph. Hieroglyphs are symbols used in ancient Egypt to represent words and sounds.
Isis

A major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion. Isis was worshipped as a goddess of magic and motherhood.
Mesopotamia

A historical region of Western Asia situated within the TigrisEuphrates river system. Mesopotamia. It is often called the "Cradle of Civilization" because it is where some of the earliest human civilizations, like Sumer and Babylon, began.
money economy

When money replaces barter for the exchange of goods. Money economy. A money economy is a system where people use currency instead of trading goods directly.
monotheism

The belief in the existence of only one god. Monotheism. Monotheism is the idea that there is just one all-powerful god, which was a central belief in ancient religions like Judaism.
Moses

A prophet who led the Hebrew people out of Egypt and received the Ten Commandments. Moses. He is a key figure in the Bible known for leading the Israelites to freedom and receiving laws from God.
mummification

A process in which the skin and flesh of a corpse can be preserved. Mummification is an ancient method used primarily by Egyptians to preserve bodies for the afterlife.
Nebuchadnezzar

The fourth king of the Second Dynasty of Isin and Fourth Dynasty of Babylon. Nebuchadnezzar. Nebuchadnezzar was an ancient Babylonian king known for his construction of the Hanging Gardens of Babylon and the Babylonian exile of the Jews.
Nile Delta

The delta was a major constituent of Lower Egypt. Nile Delta. The Nile Delta is a fertile area where the River Nile spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea, playing a crucial role in the development of ancient Egyptian civilization.
Osiris

The god of fertility, agriculture, the afterlife, resurrection and life in ancient Egyptian religion. Osiris. Osiris is an ancient Egyptian god who ruled over the afterlife and was associated with rebirth and regeneration.
papyrus

A material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. Papyrus. In ancient Egypt, papyrus was used to make scrolls for writing, much like early books.
patriarchy

A social system in which men hold primary power. Patriarchy. Throughout history, patriarchy has meant that men typically dominated roles of political leadership, moral authority, and control over family property.
pharaoh

The common title of the monarchs of ancient Egypt pharaoh. A pharaoh was the ruler of ancient Egypt, similar to a king.
prophet

An individual who is regarded as being in contact with a divine being. Prophet. In history, a prophet is someone who claims to convey messages from a god or divine source.
Ramses II

The third pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Ramses II. He was a powerful ancient Egyptian king known for his military leadership and building many monuments.
Rosetta Stone

A granodiorite stele which is inscribed with three versions of a decree issued in Egypt. Rosetta Stone. The Rosetta Stone is an ancient artifact that helped scholars understand Egyptian hieroglyphs because it has the same text in three different scripts.
Sabbath

A day set aside for rest and worship. Sabbath. In history, the Sabbath is a weekly day of rest observed by Jews and some Christians, traditionally on Saturday or Sunday.
Sargon

The first ruler of the Akkadian Empire 24th - 23rd c. BC Sargon. Sargon was a powerful leader who established one of the world's first empires in Mesopotamia.
Solomon

According to the Hebrew Bible, a wealthy and wise king of the United Kingdom of Israel. Solomon. Solomon was a biblical king known for his wisdom and building the First Temple in Jerusalem.
Sumer

The earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia. Sumer. Sumer was one of the first human civilizations, where people developed writing and built early cities.
Thutmose III

The sixth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty, Thutmose III. He was a powerful ancient Egyptian ruler known for expanding Egypt's empire through military conquests.
Torah

The Hebrew Bible, consisting of Written Torah and the Oral Torah. Torah. The Torah is the central reference of the Jewish tradition, containing teachings and laws that have guided Jewish life and culture throughout history.
vizier

The highest official in ancient Egypt to serve the pharaoh. Vizier. A vizier was the pharaohs top advisor and the most powerful official in ancient Egypt.
ziggurat

A type of massive structure built in ancient Mesopotamia. Ziggurat. A ziggurat is a large, terraced pyramid-like building that served as a temple in ancient Mesopotamian cities.
Zoroaster

An ancient Iranian spiritual leader who founded Zoroastrianism. Zoroaster. Zoroaster was the prophet who established one of the world's oldest monotheistic religions.