Civilization in East and Southeast Asia 500-1650
History
archipelago

A chain, cluster, or collection of islands. Archipelago. In History, archipelago often refers to groups of islands that played significant roles in trade and exploration.
bushido

A codes of honour and ideals that dictated the samurai way of life. Bushido. Bushido is the code of conduct followed by Japanese samurai warriors, emphasizing virtues like loyalty, courage, and discipline.
Celadon

A term for ceramics meaning both a type of glaze and the jade green color. Celadon. Celadon is a type of ancient Chinese pottery known for its distinctive pale green color, resembling jade.
cultural appropriation

The adoption of elements of one culture by members of another culture. Cultural appropriation. It is when people from one culture take aspects of another culture, often without understanding or respecting its original meaning, which has happened throughout history.
dowry

A transfer of parental property, gifts, or money at the marriage of a daughter bride. Dowry. Historically, a dowry is the wealth transferred from the bride's family to the groom or his family as part of the marriage arrangements.
Genghis Khan

The founder and first Great Khan and Emperor of the Mongol Empire, Genghis Khan. He was a powerful leader who united the Mongolian tribes and built one of the largest empires in history.
gentry

The elite who held privileged status through passing the Imperial exams. gentry. The gentry were landowners in history who had social status and income but were not nobility.
Goryeo
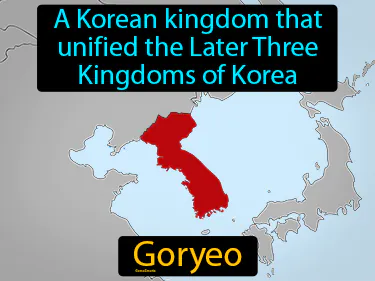
A Korean kingdom that unified the Later Three Kingdoms of Korea. Goryeo. Goryeo was a medieval Korean dynasty that ruled from 918 to 1392, known for unifying the Korean peninsula.
hangul

The Korean alphabet invented by King Sejong. Hangul. Hangul is the unique writing system created in the 15th century to improve literacy among Koreans.
Joseon
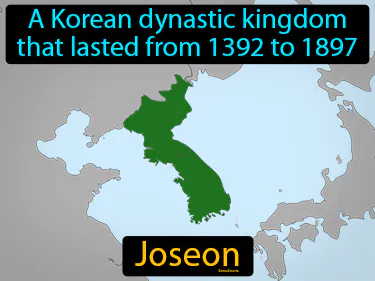
A Korean dynastic kingdom that lasted from 1392 to 1897. Joseon. Joseon was a long-lasting Korean dynasty known for reinforcing Confucian ideals and developing Korean culture and technology.
kana

The syllabaries that form parts of the Japanese writing system. Kana. Kana is a set of characters used in Japanese writing, developed to simplify the complex Chinese characters.
King Sejong

The fourth king of the Joseon dynasty of Korea. King Sejong. King Sejong was a visionary ruler who created the Korean alphabet, Hangul.
Kublai Khan

The fifth Great Khan of the Mongol Empire and founder of the Yuan dynasty. Kublai Khan was a Mongol ruler who established control over China and started the Yuan dynasty.
land reform

The changing of laws, regulations or customs regarding land ownership. Land reform. In history, land reform refers to the redistribution or restructuring of agricultural land to improve equity and productivity.
literacy rate

A percentage of people who can read, write and make simple calculations. Literacy rate. In history, literacy rate shows how many people had basic reading and writing skills at a certain time and place.
Marco Polo

An Italian trader and explorer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road. Marco Polo. Marco Polo was a historical figure known for his journeys to Asia and documenting his experiences along the Silk Road.
matrilineal

An individual's family membership that derives from their mother's lineage. Matrilineal refers to a system in history where ancestry and inheritance are traced through the mother's side of the family.
Ming dynasty

The ruling dynasty of China from 1368 to 1644. Ming dynasty. The Ming dynasty was a period in China known for restoring traditional Chinese rule and fostering great cultural and economic growth.
paddy

A flooded parcel of arable land used for growing semiaquatic crops. Paddy. In history, paddies have been essential in cultivating rice, a staple food for many Asian civilizations.
pagoda

A tiered tower with multiple eaves common in eastern and southeastern Asia. Pagoda. In history, a pagoda is a traditional structure often used for religious purposes, particularly in Buddhist and Hindu cultures.
samurai

A military nobility and officer caste of medieval Japan. Samurai. The samurai were warriors in medieval Japan who served as protectors and enforcers for their lords.
Shinto

A polytheistic religion originating from Japan. Shinto. Shinto is an ancient Japanese belief system that focuses on the worship of kami spirits and emphasizes harmony with nature and ancestral traditions.
Silla
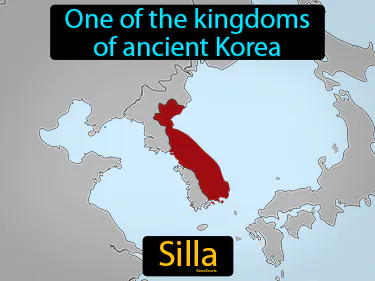
One of the kingdoms of ancient Korea. Silla was a powerful kingdom that existed from 57 BC to 935 AD and played a key role in unifying Korea.
Song dynasty

An imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. Song dynasty. The Song Dynasty was a period in Chinese history known for advancements in technology, economy, and culture.
steppe

An ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees. Steppe. Historically, the steppe has been home to nomadic cultures and important trade routes like the Silk Road.
stupa

A hemispherical structure that is used as a place of meditation. Stupa. A stupa is a dome-shaped monument that serves as a Buddhist shrine.
Tang dynasty

An imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, Tang dynasty. The Tang dynasty was a golden age of Chinese culture and power marked by prosperity and cultural brilliance.
Tang Taizong

The second emperor and co-founder of the Tang dynasty, Tang Taizong. Tang Taizong was a key leader in ancient China who strengthened and expanded the Tang dynasty, fostering a golden age of culture and prosperity.
tributary state
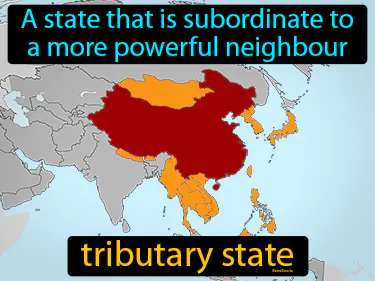
A state that is subordinate to a more powerful neighbour. Tributary state. In history, a tributary state is a country that pays tribute or provides goods to a more powerful nation in exchange for protection or to maintain autonomy.
Yuan dynasty

The empire and ruling dynasty of China established by Kublai Khan. Yuan dynasty. The Yuan dynasty was a period in Chinese history when Mongols ruled China, starting in 1271 and lasting until 1368.
Zen

A Chinese school of Mahayana Buddhism accepted by Japan, Korea and Vietnam. Zen. Zen is a meditative tradition focused on achieving enlightenment through direct insight and personal experience.
Zheng He

A Chinese explorer, diplomat, and admiral during Ming dynasty. Zheng He. He was a famous maritime leader known for his seven major expeditions to Southeast Asia, South Asia, and Africa.

