The Renaissance and Reformation 1300-1650
History
Albrecht Durer

A German painter, printmaker, and theorist. Albrecht Durer. Durer was a key figure in the Northern Renaissance, known for his detailed woodcuts and engravings.
Baldassare Castiglione

An Italian courtier, diplomat, soldier and author known for The Book of the Courtier. Baldassare Castiglione. He was a Renaissance writer who described the ideal qualities of a courtier in his famous book.
calculus
A branch of mathematics which studies changes between values that are related by a function. Calculus. Developed in the late 17th century, calculus revolutionized mathematics and science by providing tools to analyze change and motion.
canonization

The process of declaring saints by church canonization. Canonization is when the church officially recognizes someone as a saint due to their holy life and acts.
Charles V

A Holy Roman Emperor, Archduke of Austria, King of Spain, and Lord of the Netherlands. Charles V. He was a powerful ruler in the 16th century who controlled a vast European empire, shaping the politics and religious landscape of his time.
compromise

A deal between different parties where each party gives up part of their demand. Compromise. In history, compromise is when conflicting groups agree to meet halfway to resolve a dispute.
Council of Trent

The 19th ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. Council of Trent. The Council of Trent was a major Catholic meeting in the 16th century that aimed to reform the Church and address issues raised by the Protestant Reformation.
diet

A formal deliberative assembly. Diet. In history, a diet is a formal assembly or meeting, especially historically for governing bodies.
Elizabeth I

The Queen of England and Ireland from 1558 until her death 1603. Elizabeth I. Elizabeth I was a powerful and influential monarch who helped establish England as a major world power.
engraving

The practice of incising a design onto a hard, flat surface, by carving into it. engraving. Engraving is an ancient technique used to create images or text on materials like metal or stone in historical artifacts.
Erasmus

A Dutch philosopher and one of the greatest scholars of the northern Renaissance. Erasmus. Erasmus was a key figure in the Renaissance, known for promoting humanism and reforming religious thought.
Flanders

The Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium. Flanders. Historically, Flanders was a prosperous medieval region known for its trade and textile industry.
Florence

A centre of medieval European trade, the birthplace of the Renaissance. Florence. It is a city in Italy known for its significant role in art and culture during the Renaissance period.
Francis Bacon

An English philosopher and statesman, credited for developing the scientific method. Francis Bacon. He is known for laying the foundations of modern scientific inquiry.
Galileo

An Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, considered the father of modern science. Galileo helped revolutionize our understanding of the universe by supporting the idea that the Earth orbits the Sun.
Geneva

A city in Switzerland where John Calvin established the Republic of Geneva in the 16th century. Geneva. Geneva is a historic city known for being a center of the Protestant Reformation in the 16th century.
ghetto

A part of a city in which members of a minority group live. Ghetto. Throughout history, ghettos have been neighborhoods where specific ethnic or racial groups were isolated, often due to social, economic, or legal pressures.
heliocentric
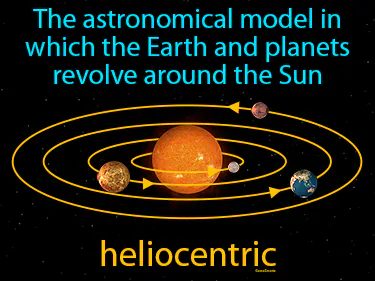
The astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around the Sun. Heliocentric. In history, heliocentric refers to the model proposed by Copernicus, which demonstrated that the Sun, not the Earth, is at the center of the solar system.
Henry VIII

The King of England from 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry VIII. He is famous for his six marriages and breaking away from the Catholic Church to form the Church of England.
humanism

A philosophical stance that emphasizes the value and agency of human beings. Humanism. In History, humanism was a movement during the Renaissance that focused on the study and appreciation of classical antiquity and human potential.
humanities

An academic discipline that studies aspects of human society and culture. Humanities. History is a part of the humanities because it explores past human societies and how they've shaped the present.
Ignatius of Loyola

A Spanish Catholic priest, theologian and co-founder of the Society of Jesus. Ignatius of Loyola. He was a prominent religious leader who helped reform the Catholic Church during the Counter-Reformation.
indulgence

A temporal punishment for sins which have already been forgiven is taken from the sinner. Indulgence. In history, an indulgence was a way for people to reduce punishment for their sins through actions or payments to the Church.
Isaac Newton

An English physicist, mathematician, and astronomer, one of the most influential scientists of all time. Isaac Newton. He is known for discovering gravity and formulating the laws of motion.
Johann Gutenberg

A German inventor, printer, and publisher who invented the printing press, Johann Gutenberg. He revolutionized the spread of information in Europe by introducing movable-type printing.
Johannes Kepler

A German astronomer, astrologer, mathematician and best known for his laws of planetary motion. Johannes Kepler. Johannes Kepler was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution who discovered the laws that describe how planets move around the sun.
John Calvin

A French theologian, pastor and reformer, a developer of Calvinism. John Calvin. He was a key figure in the Protestant Reformation, promoting the idea of predestination and a disciplined, pious lifestyle.
Leonardo

An Italian polymath, scientist, inventor, painter, architect, and paleontologist. Leonardo da Vinci was a genius of the Renaissance who made significant contributions to art and science.
Martin Luther

A French theologian, pastor and reformer, a developer of Calvinism. Martin Luther. Martin Luther was a German monk who initiated the Protestant Reformation by challenging the practices of the Catholic Church.
Mary Tudor

The queen of England from 1553 until her death 1558, Mary Tudor. Mary Tudor, also known as "Bloody Mary," was the first reigning queen of England and is known for her attempt to restore Catholicism in England.
Michelangelo

An Italian sculptor, painter, architect and poet. Michelangelo was a Renaissance artist known for masterpieces like the Sistine Chapel ceiling and the statue of David.
Niccolo Machiavelli

An Italian diplomat, philosopher and writer, best known for Il Principe. Niccolo Machiavelli. Machiavelli is known for his work on political theory, particularly the idea that rulers must be cunning and pragmatic to maintain power.
Nicolaus Copernicus

A Prussian astronomer who formulated a heliocentric model of the universe. Nicolaus Copernicus. He was a revolutionary thinker who proposed that the Earth orbits the Sun.
patron

A person or organization that supports another is called a patron. In History, patrons often funded artists or scholars, allowing them to create their work.
perspective

A formation of an image in a picture viewed from a fixed point. Perspective. In history, perspective is the technique of depicting spatial depth in art, showing objects in the distance as smaller to create a sense of realism.
Petrarch

An Italian scholar and poet, one of the earliest humanists. Petrarch. Often called the "Father of Humanism," Petrarch helped to spark the Renaissance by reviving interest in ancient Greek and Roman culture.
predestination

The doctrine in Christian theology claiming that all events have been willed by God predestination. In history, predestination refers to the belief that God has predetermined the fate of individuals and events.
Raphael

An Italian painter and architect of the High Renaissance. Raphael. He was a master artist known for his beautiful paintings and contributions to the architecture of his time.
Rene Descartes

A French philosopher, scientist and mathematician, one of the founders of modern philosophy. Ren Descartes. He is famous for his statement "I think, therefore I am" and his contributions to developing analytical geometry.
Robert Boyle

An Anglo-Irish natural philosopher, physicist and one of the founders of modern chemistry. Robert Boyle. He is often called the "father of modern chemistry" for his work in developing the scientific method and Boyle's Law.
Sect

A subgroup of a religious or philosophical belief system. Sect. In history, a sect is a smaller group that breaks away from a larger religious or philosophical tradition, often to follow a different interpretation or leader.
Shakespeare

An English poet, playwright, and actor, one of the world's greatest dramatists. Shakespeare was a famous writer from the 16th century known for his influential plays and sonnets.
Teresa of Avila

A Spanish mystic, Roman Catholic saint, Carmelite nun and theologian. Teresa of Avila was a key figure in the Catholic Reformation, known for reforming the Carmelite order and her influential spiritual writings.
theocracy

A form of government in which God or a deity is recognized as the supreme civil ruler. Theocracy. In history, a theocracy is when religious leaders govern a country based on divine guidance.
Thomas Cranmer

An Archbishop of Canterbury and one of the founders of the Church of England. Thomas Cranmer played a key role in the English Reformation by helping to establish Protestantism in England.
Thomas More

An English lawyer, social philosopher, author, statesman, and noted humanist. Thomas More was a key advisor to King Henry VIII and is famous for his book "Utopia."
Tycho Brahe

A Danish astronomer known for his accurate astronomical observations. Tycho Brahe. Tycho Brahe was a pioneering scientist in the late 16th century who made detailed observations of the stars and planets, laying the groundwork for future discoveries in astronomy.
utopian

An imagined community that possesses perfect qualities for its citizens. Utopian. In history, the term "utopian" refers to idealistic societies that aim for perfection and harmony.
vernacular

The speech variety used by the general population in a geographical or social territory. Vernacular. In history, vernacular refers to the everyday language spoken by ordinary people in a specific region or community.
Wittenberg

A town in Germany, close connected with Martin Luther and the Protestant Reformation. Wittenberg. Wittenberg is the place where Martin Luther famously nailed his 95 Theses, sparking the Protestant Reformation.





