Immune System and Disease
Science
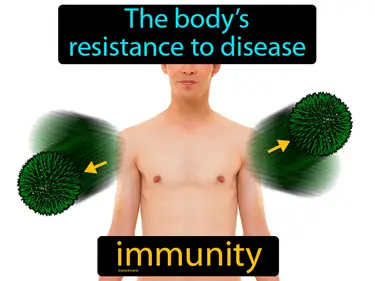
active immunity
Immunity given by antibodies made by the immune system, in response to an antigen. Active immunity. Active immunity is when your body learns to defend itself by making its own antibodies after being exposed to a disease.
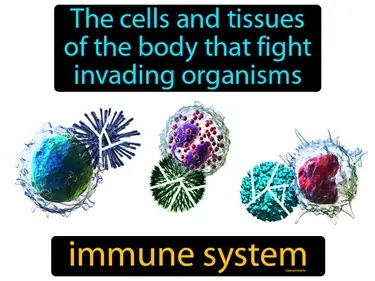
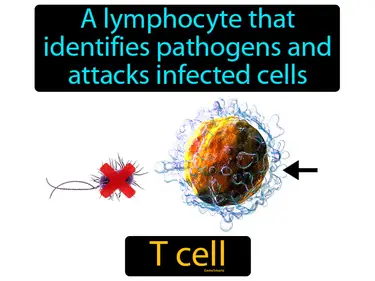
B cell
A white blood cell that makes antibodies, also called a B lymphocyte. B cell. B cells are a type of immune cell that helps protect the body by producing antibodies to fight off infections.
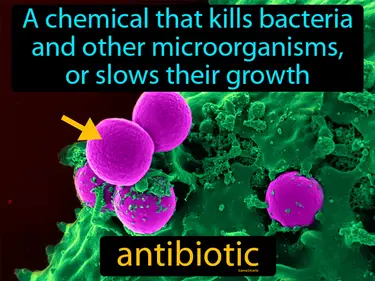
epidemic
Large outbreak of disease in a specific area. Epidemic. An epidemic is when many people in a community get an infectious disease at the same time.
germ theory

The theory that infectious diseases are caused by microorganisms or germs. Germ theory. Germ theory is the idea that tiny organisms called germs cause diseases in humans, animals, and plants.
histamine
A chemical that increases the flow of blood and fluids, it is secreted by mast cells. Histamine. Histamine is a natural chemical in the body that helps fight allergies by causing symptoms like sneezing and itching.
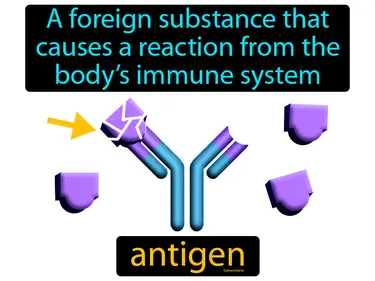
humoral immunity
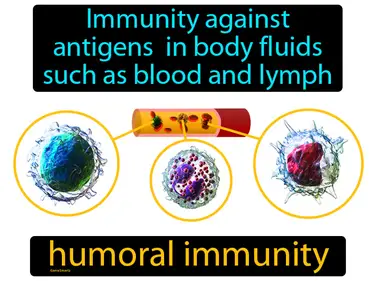
Immunity against antigens in body fluids such as blood and lymph. Humoral immunity. Humoral immunity is the part of the immune system that uses antibodies in blood and lymph to fight off bacteria and viruses.
interferon
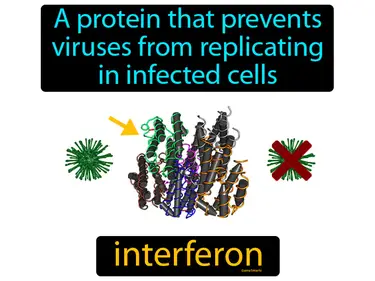
A protein that prevents viruses from replicating in infected cells. Interferon. Interferon is a natural compound in the body that helps fight viral infections by boosting the immune system.
Kochs postulate
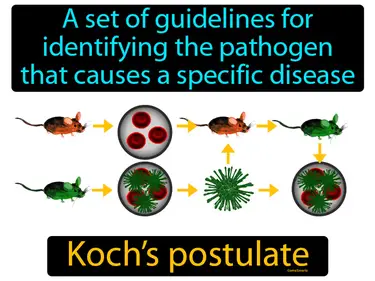
A set of guidelines for identifying the pathogen that causes a specific disease. Koch's postulates are criteria used to establish a relationship between a microbe and a disease.
memory cell
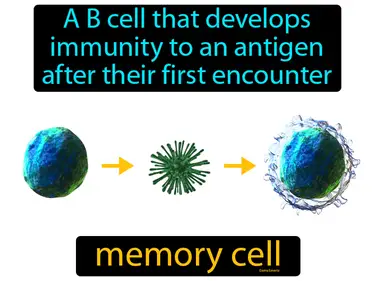
A B cell that develops immunity to an antigen after their first encounter. Memory cell. A memory cell is a specialized immune cell that remembers a pathogen and responds quickly if the body encounters it again.
passive immunity
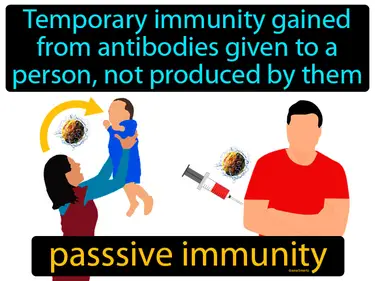
Temporary immunity gained from antibodies given to a person, not produced by them. Passive immunity. Passive immunity is when your body receives ready-made antibodies to fight off infections.