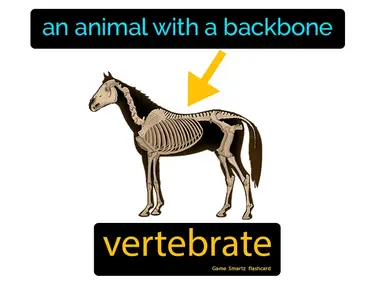
Vertebrates, Fishes, Amphibians, Reptiles and Birds
Science
air sac
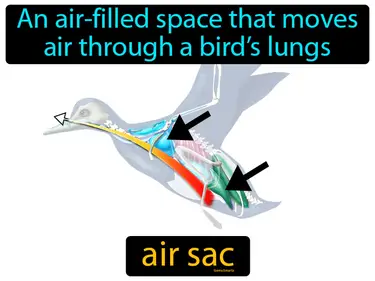
An air-filled space that moves air through a birds lungs. Air sac. An air sac is part of a bird's respiratory system that helps move air efficiently through their lungs for breathing.
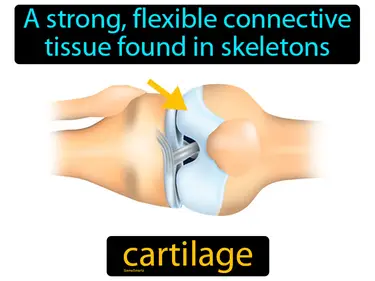
carapace

The shell of a turtle or tortoise, or the plate that covers the head of a crustacean. Carapace. A carapace is a protective shell on the back of some animals, like turtles and crustaceans, which helps shield them from predators and environmental hazards.
feather

A structure on a birds skin that enables flight and gives it insulation. Feather. Feathers are specialized structures made of keratin that help birds fly and stay warm.
Jacobsons organ
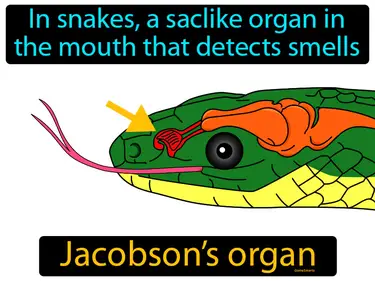
In snakes, a saclike organ in the mouth that detects smells. Jacobson's organ. It is an organ that helps animals sense and interpret smells from their environment.
lateral line system
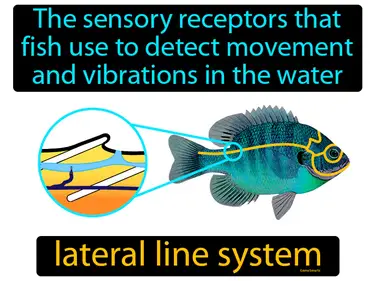
The sensory receptors that fish use to detect movement and vibrations in the water lateral line system. The lateral line system is a network of canals and sensory cells in fish and some amphibians that helps them sense movements and vibrations in the surrounding water.
operculum

The hard flap that covers and protects a fishs gills. Operculum. It is a bony plate that shields the delicate gills from harm and helps fish breathe by opening and closing.
oviparous

A species whose eggs develop outside the parents body. Oviparous. Oviparous animals lay eggs that hatch outside the mother's body.
ovoviviparous

A species whose eggs develop inside the parent's body. Ovoviviparous. In ovoviviparous animals, the young hatch from eggs inside the mother and are then born live.
plastron

The bottom or ventral part of a turtles shell is called the plastron. In simple terms, the plastron is the flat underside of a turtle's shell that helps protect its belly.
sternum

The breastbone in birds, flight muscles are attached to it. Sternum. The sternum is a flat bone located in the center of the chest, connecting the rib cage and helping protect the heart and lungs.
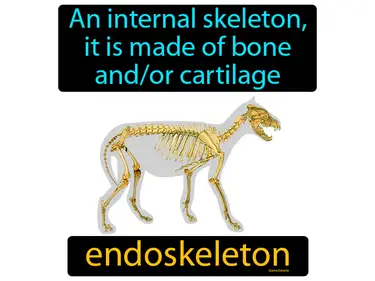
tetrapod

An animal with four limbs. Tetrapod. A tetrapod is a type of vertebrate animal that has four limbs or leg-like appendages.
tympanic membrane
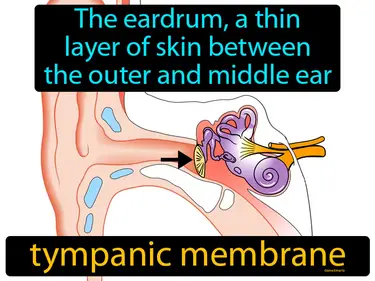
The eardrum, a thin layer of skin between the outer and middle ear. Tympanic membrane. It is a vital part of the ear that helps us hear by vibrating when sound waves hit it.
viviparous

Reproductive strategy where the embryo develops within the mother's body. Viviparous. Viviparous animals give birth to live young rather than laying eggs.