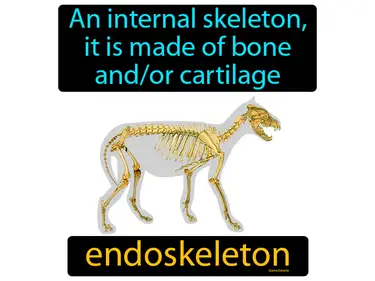
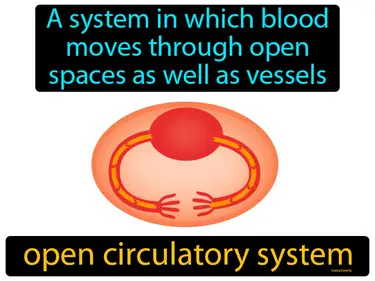
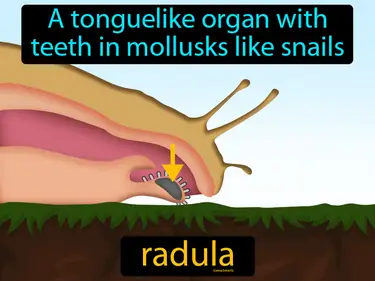
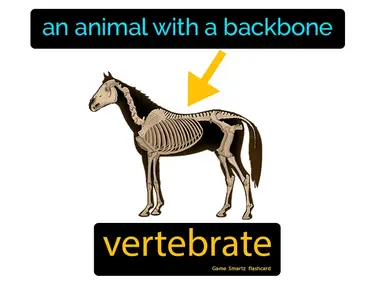
Animals, Invertebrates, Cnidarians, Mollusks
Science
cephalization
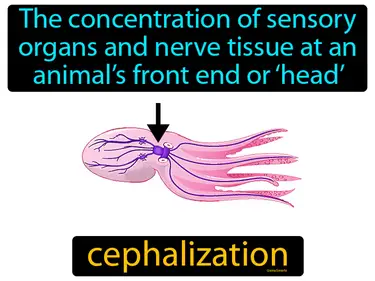
The concentration of sensory organs and nerve tissue at an animals front end or head. Cephalization is when animals have most of their important sensory parts at their head.
cnidocyte
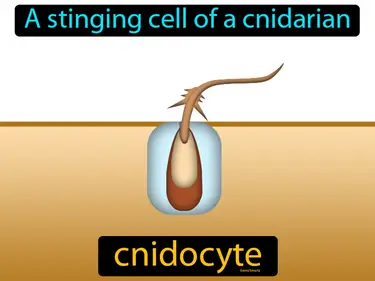
A stinging cell of a cnidarian. Cnidocyte. A cnidocyte is a specialized cell found in jellyfish and similar animals that is used to capture prey and defend against predators.
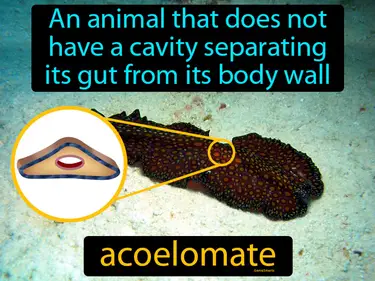
coelom
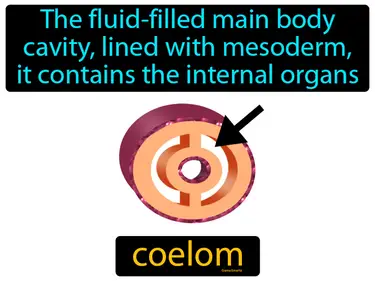
The fluid-filled main body cavity, lined with mesoderm, it contains the internal organs. Coelom. The coelom is a hollow space within the body that houses and protects internal organs, allowing them to move independently from the body wall.
deuterostome
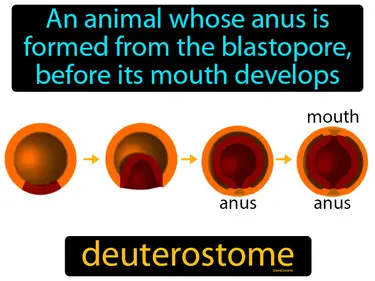
An animal whose anus is formed from the blastopore, before its mouth develops. Deuterostome. Deuterostomes are animals, like humans, where the anus forms before the mouth during early development.
ectoderm
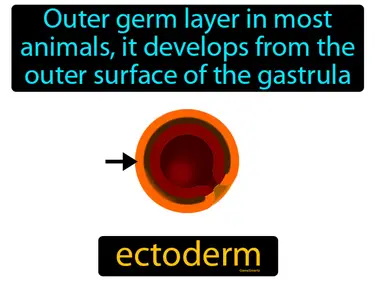
Outer germ layer in most animals, it develops from the outer surface of the gastrula. Ectoderm. Ectoderm is the layer of cells in an embryo that forms structures like the skin and nervous system.
endoderm
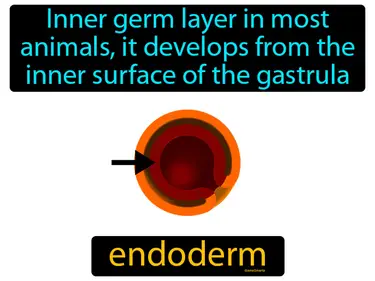
Inner germ layer in most animals, it develops from the inner surface of the gastrula. Endoderm. The endoderm is the innermost layer of cells in an embryo that develops into the lining of the digestive and respiratory systems.
external fertilization

The union of sperm and eggs outside the females body. External fertilization. It is when sperm and eggs come together outside the female's body to create new life.
filter feeder

An organism that eats by straining food particles from water. Filter feeder. A filter feeder is an animal that feeds by passing water through a part of its body to capture tiny food particles.
ganglion
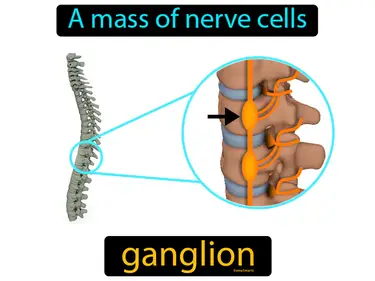
A mass of nerve cells. Ganglion. A ganglion is a cluster of nerve cells found in the peripheral nervous system that helps transmit signals in the body.
gastrovascular cavity
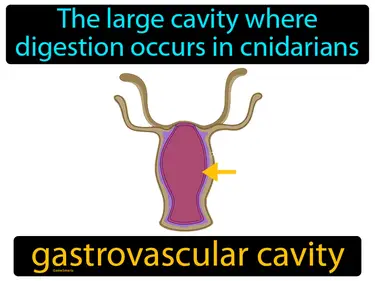
The large cavity where digestion occurs in cnidarians gastrovascular cavity. The gastrovascular cavity is a central body chamber that helps with both digestion and circulation in simple animals like jellyfish and corals.
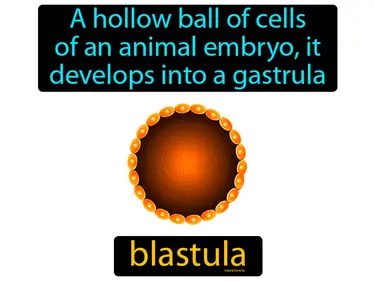
gastrula
Embryo development stage with two or three cell layers, it follows the blastula stage. Gastrula. The gastrula is an early stage in embryonic development where the embryo starts forming distinct layers that will become different tissues and organs.
gizzard

Muscular digestive structure that grinds down food, found in birds and earthworms. Gizzard It's a part of the digestive system that uses muscles to help break down food mechanically.
hermaphrodite

An animal that can produce both eggs and sperm. Hermaphrodite. In simple terms, a hermaphrodite is an organism that has both male and female reproductive organs and can produce both eggs and sperm.
hydrostatic skeleton

The fluid-filled cavity that aids movement in animals like earthworms hydrostatic skeleton. A hydrostatic skeleton is a structure in some soft-bodied animals where a fluid-filled cavity is used to support the body and help with movement.
internal fertilization
The union of sperm and eggs inside the females body. Internal fertilization. This process occurs when sperm fertilizes an egg within the body of an organism.
mesoderm
The cell layer between the ectoderm and endoderm, it develops into the circulatory, reproductive, and excretory systems. Mesoderm is the middle layer of an embryo that forms muscles, bones, and other internal organs.
nematocyst
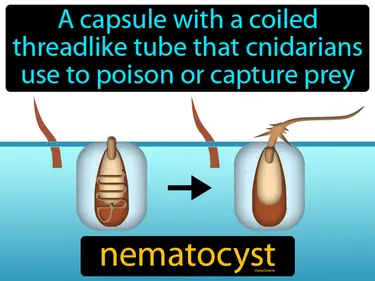
A capsule with a coiled threadlike tube that cnidarians use to poison or capture prey. Nematocyst is a tiny, stinging structure used by jellyfish and other cnidarians to catch food.
nephridium

The excretory organ that removes waste from an annelids body is called nephridium. A nephridium is an organ in some animals, like earthworms, that helps remove waste from their bodies.
nerve net

A cnidarians nervous system, made of a network of nerve cells spread through its body. Nerve net. A nerve net is a simple system with interconnected nerve cells that allow cnidarians to respond to their environment without a central brain.
proglottid
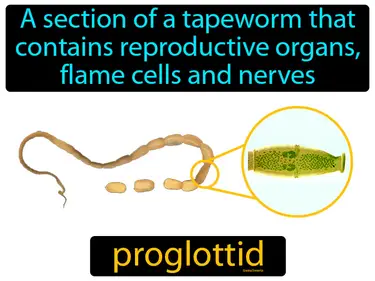
A section of a tapeworm that contains reproductive organs, flame cells and nerves. Proglottid. In simple terms, a proglottid is a segment of a tapeworm that contains its reproductive structures.
protostome
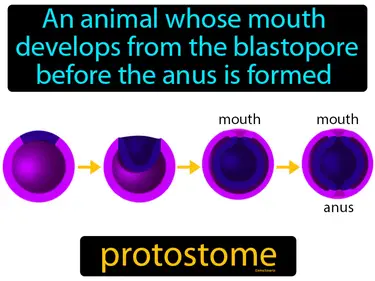
An animal whose mouth develops from the blastopore before the anus is formed. Protostome. In protostomes, the mouth forms first during early embryonic development.
pseudocoelom
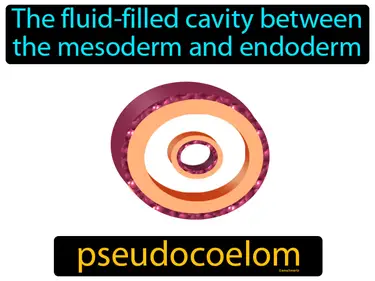
The fluid-filled cavity between the mesoderm and endoderm. Pseudocoelom. A pseudocoelom is a body cavity in some organisms that is not fully lined with mesoderm, unlike a true coelom.
scolex
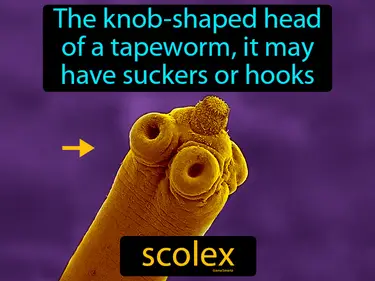
The knob-shaped head of a tapeworm, it may have suckers or hooks. Scolex. The scolex is the part of a tapeworm that attaches to the host's intestines.
sessile

Describes an organism that is unable to move from a location. Sessile. In science, sessile refers to organisms, like barnacles, that are fixed in one place and do not move around.
siphon

A hollow tube that mollusks use for sucking in and expelling water. Siphon. In science, a siphon is a tube used to move liquid from one level to a lower one using gravity.
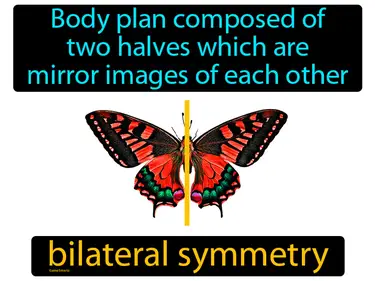
symmetry
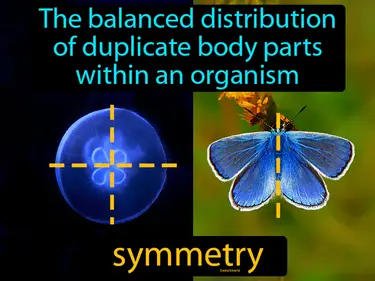
The balanced distribution of duplicate body parts within an organism. Symmetry. Symmetry in science is when parts of an object or organism mirror each other in size, shape, and position.