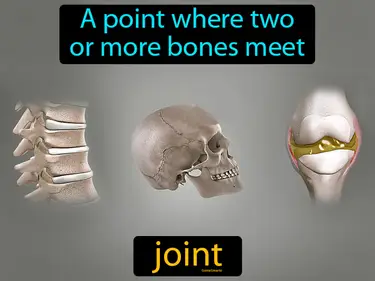
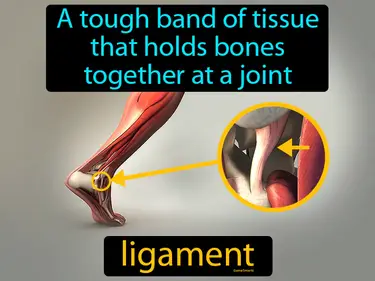
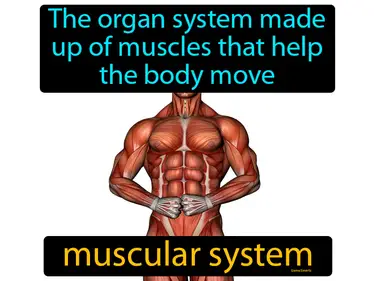
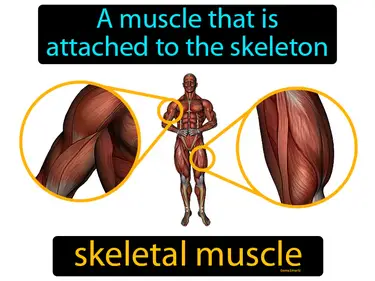
Skeleton, Muscular, Protection and Movement
Science
actin
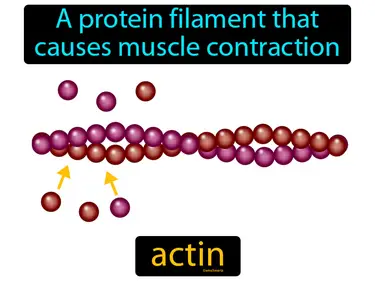
A protein filament that causes muscle contraction. Actin. Actin is a protein that helps muscles move by working with another protein called myosin.
appendicular skeleton
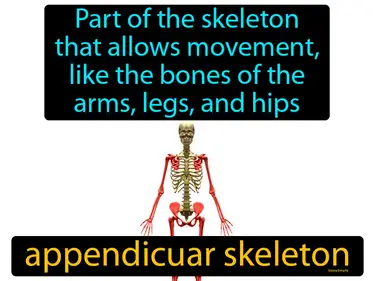
The part of the skeleton that allows movement, like bones of the arms, legs, and hips appendicular skeleton. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones that help you move, like your arms and legs.
axial skeleton
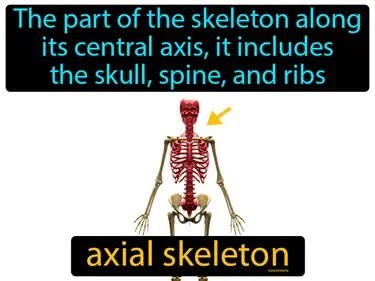
The part of the skeleton along its central axis, it includes the skull, spine, and ribs. Axial skeleton. The axial skeleton is the central part of the skeleton that supports the head and trunk.
bone marrow
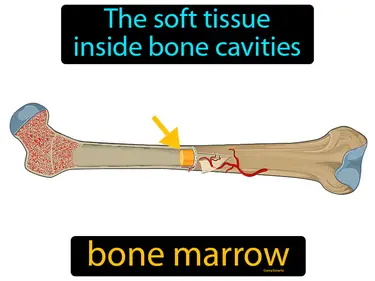
The soft tissue inside bone cavities. Bone marrow. Bone marrow is a spongy tissue in bones that produces blood cells.
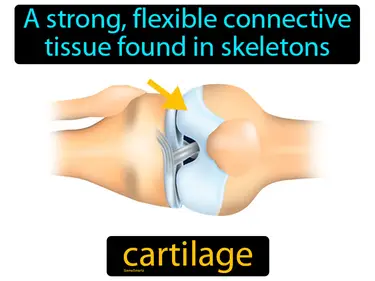
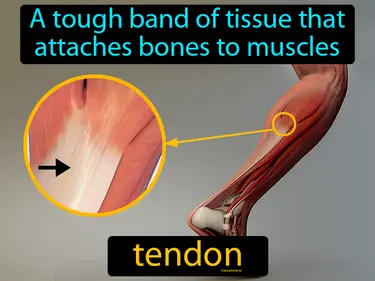
connective tissue
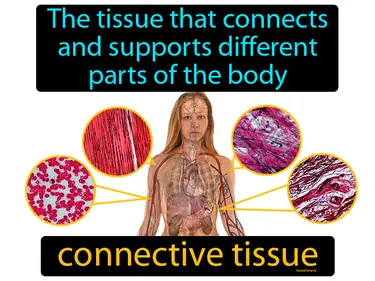
The tissue that connects and supports different parts of the body. Connective tissue. Connective tissue is the biological material that holds organs and tissues together, providing support and structure throughout the body.
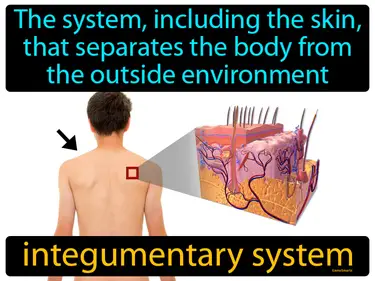
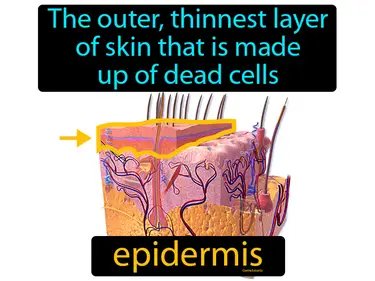
epithelial tissue
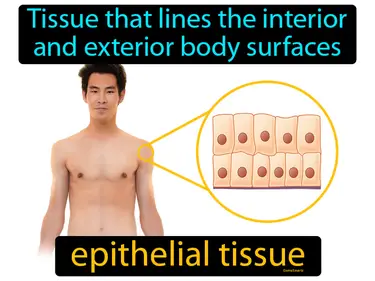
Tissue that lines the interior and exterior body surfaces. Epithelial tissue. Epithelial tissue is a protective layer of cells that covers body surfaces and organs, acting as a barrier and involved in absorption and secretion.
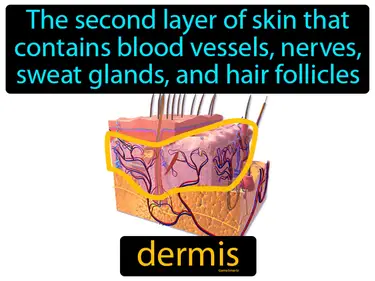
hair follicle

A pit in the dermis from which hair grows. Hair follicle. A hair follicle is the skin structure that anchors and grows hair.
keratin

A hard, waterproof protein that forms hair and nails, and is found in skin. Keratin is a protein that helps build and protect our hair, nails, and skin.
melanin
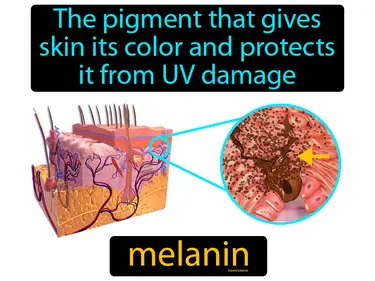
The pigment that gives skin its color and protects it from UV damage. Melanin. Melanin is a natural pigment found in the skin, hair, and eyes that helps protect against sun damage by absorbing ultraviolet light.
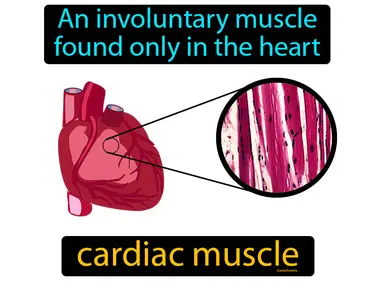
muscle fiber
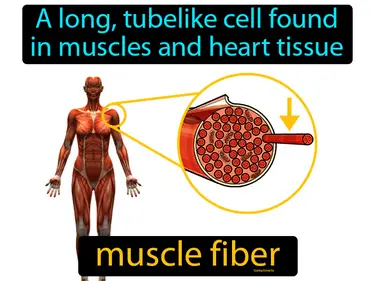
A long, tubelike cell found in muscles and heart tissue. Muscle fiber. Muscle fibers are the basic building blocks that make muscles work by contracting and relaxing to create movement.
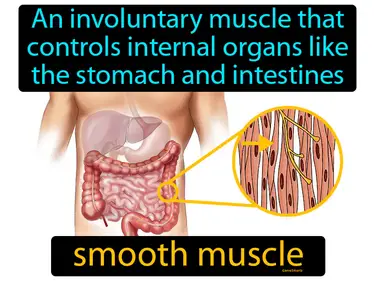
muscle tissue
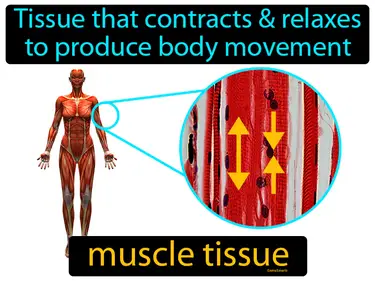
The tissue that contracts and relaxes to produce body movement. Muscle tissue. Muscle tissue is a type of body tissue that enables movement by contracting and relaxing.
myofibril
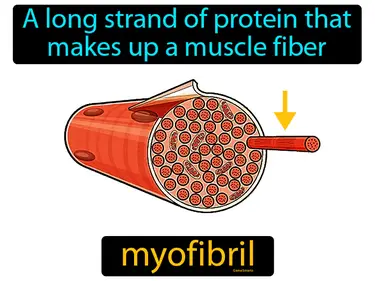
A long strand of protein that makes up a muscle fiber. Myofibril. Myofibrils are tiny threads in muscle cells that help them contract and produce movement.
myosin
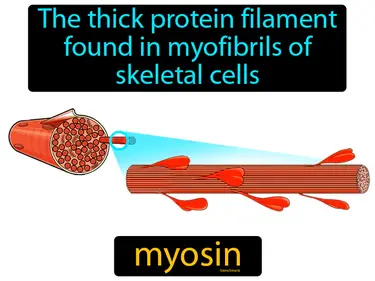
The thick protein filament found in myofibrils of skeletal cells. Myosin. Myosin is a protein that helps muscles contract by converting chemical energy into mechanical work.
nervous tissue
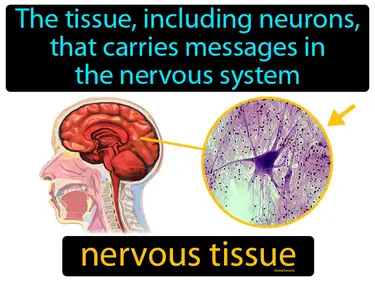
The tissue, including neurons, that carries messages in the nervous system. Nervous tissue. Nervous tissue is the body's communication network that transmits signals between different parts of the body.
ossification
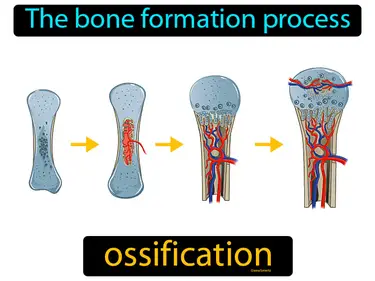
The bone formation process. Ossification. Ossification is the process by which new bone is formed in the body.
osteoblast
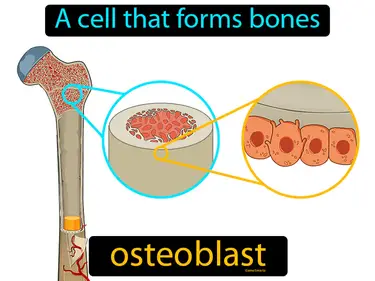
A cell that forms bones. Osteoblast. In simple terms, an osteoblast is a cell responsible for bone formation in the body.
osteocyte
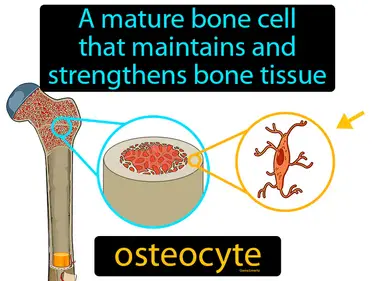
A mature bone cell that maintains and strengthens bone tissue. Osteocyte. An osteocyte is a type of cell that helps keep bones strong and healthy by maintaining the bone tissue.
sarcomere
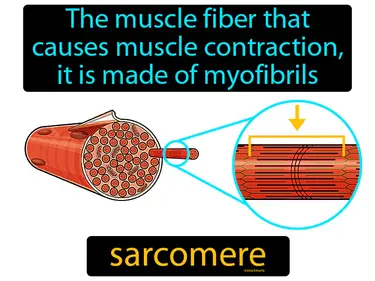
The muscle fiber that causes muscle contraction is made of myofibrils. Sarcomere is the basic unit of a muscle that allows it to contract.