Launching the Nation 1785-1805
History
Alexander Hamilton

One of the Founding Fathers of the United States, Alexander Hamilton. He was the first Secretary of the Treasury and helped establish the U.S. financial system.
Alien and Sedition Acts

An acts about immigration and against false statements made about the government. Alien and Sedition Acts. The Alien and Sedition Acts were laws passed in 1798 that allowed the U.S. government to deport non-citizens deemed dangerous and to limit free speech critical of the government.
Bank of the United States

The second national bank in the US which became a private corporation in 1836. Bank of the United States. The Bank of the United States was a central bank created to stabilize American currency and manage government funds.
Battle of Fallen Timbers

The final battle of the Northwest Indian War, Battle of Fallen Timbers. The Battle of Fallen Timbers was a conflict in 1794 between American forces and Native American tribes that led to U.S. control of the Northwest Territory.
bonds

An instrument of indebtedness of the bond issuer to the holders. Bonds. In history, bonds were used by governments to raise money for wars and other large projects.
Democratic Republican Party

An American political party founded by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison. The Democratic-Republican Party was an early political party in the United States that promoted states' rights and opposed strong central government.
electoral college

A set of electors who choose among candidates for a President and Vice President. Electoral College. The Electoral College is a group of people chosen from each state in the U.S. to formally vote for the President and Vice President based on the popular vote in their state.
Federalist Party

The first political party in the US led by Alexander Hamilton. Federalist Party. The Federalist Party was a political group in the early United States that supported a strong central government and helped establish the nation's financial system.
French Revolution

A period of fundamental political and societal change in France 1789 - 1799. French Revolution. The French Revolution was when the people of France overthrew their monarchy to establish a republic.
George Washington

An American political leader, military general and the first president of the United States. George Washington. He was a key figure in the founding of the United States and led the country to independence.
Jays Treaty

A treaty between the US and Britain in the years following the American Revolution. Jay's Treaty. It was an agreement in 1794 that aimed to resolve lingering conflicts and ease tensions between the US and Britain after the Revolutionary War.
John Adams

The second president of the United States 1797-1801. John Adams. He was an important leader in America's fight for independence and a Founding Father.
John Marshall

A politician and lawyer who served as the fourth Chief Justice of the US 1801-1835. John Marshall. He helped establish the principle of judicial review, strengthening the judicial branch.
judicial review

A process under which executive or legislative actions are subject to review by the judiciary. Judicial review. In history, judicial review is when courts decide if government actions follow the Constitution.
Judiciary Act of 1789

A US federal statute which established the federal judiciary of the United States. Judiciary Act of 1789. It created the basic structure of the U.S. court system, including the Supreme Court and lower courts.
Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions

The Kentucky and Virginia condemned federal Alien and Sedition Acts as unlawful. The Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions argued that states could declare federal laws unconstitutional.
Little Turtle

A chief of the Miami people who led native warriors to a few major victories against US. Little Turtle. Little Turtle was a Native American leader known for successfully defending his people's territory against U.S. forces in the late 18th century.
loose construction

The claim that the US Constitution holds a dynamic meaning that evolves. Loose construction. In history, loose construction is the idea that the Constitution can be interpreted broadly to adapt to changing times and circumstances.
Louisiana Purchase
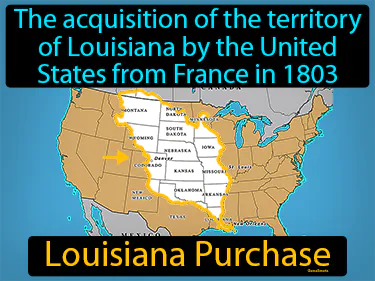
The acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from France in 1803. Louisiana Purchase. The Louisiana Purchase was when the U.S. bought a large area of land from France, doubling the size of the country.
Marbury v Madison

A Supreme Court case that established the principle of judicial review in the US. Marbury v Madison. This case gave the Supreme Court the power to decide if laws are constitutional or not.
Martha Washington

The wife of George Washington who, joined him during the Revolution. Martha Washington. Martha Washington was the first First Lady of the United States.
Meriwether Lewis

Best known for his role as the leader of the Lewis and Clark Expedition, Meriwether Lewis. Meriwether Lewis was an American explorer who co-led a journey to map and explore the western territories of the United States in the early 1800s.
national debt
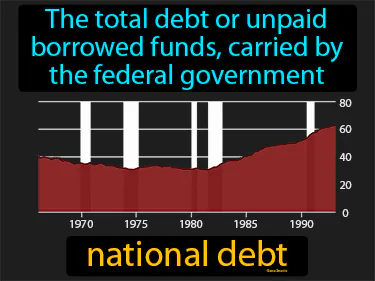
The total debt or unpaid borrowed funds, carried by the federal government. National debt. Throughout history, national debt has been the money a country owes, like when governments borrow to pay for wars or big projects.
Neutrality Proclamation

A George Washington's announcement about neutrality in the conflict between France and Britain. Neutrality Proclamation. The Neutrality Proclamation was a 1793 statement by President George Washington declaring that the United States would not take sides in the conflict between France and Britain.
Pinckneys Treaty

A treaty which defined the boundaries of the US with the Spanish colonies. Pinckney's Treaty. It was an agreement in 1795 that set the border between the US and Spanish Florida and allowed American access to the Mississippi River.
political party

An organized group of people who have the same political ideology about government. Political party. In history, a political party is a group that seeks to gain power in government by winning elections and shaping policies according to their ideas.
precedent

George Washington's decision to retire after two terms which created the 22nd Amendment. Precedent. In history, a precedent is an action or decision that sets an example for others to follow.
privateer

A private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Privateer. In history, a privateer was a privately-owned ship authorized by a government to attack enemy ships during wartime.
Sacagawea

A Lemhi Shoshone woman who met and helped the Lewis and Clark Expedition. Sacagawea. She was a guide and interpreter who played a crucial role in the success of the Lewis and Clark Expedition in the early 1800s.
speculators

Ones who buy a stock in the expectation that in the very short-term it will rise in value speculators. In history, speculators often fueled economic bubbles by rapidly trading assets based on anticipated price increases.
strict construction

A restriction of judicial interpretation only to the exact wording of the law. Strict construction. In history, strict construction refers to interpreting the U.S. Constitution based only on its text and original meaning, as favored by some early American leaders like Thomas Jefferson.
Thomas Jefferson

The third president of the United States 1801 - 1809. Thomas Jefferson. He was the main author of the Declaration of Independence.
Treaty of Greenville

A 1795 treaty between the US and indigenous nations of the Northwest Territory Treaty of Greenville. The Treaty of Greenville was an agreement that ended conflicts with Native American tribes and allowed for U.S. settlement in present-day Ohio.
Whiskey Rebellion

A protest in the US against the first tax imposed on a domestic product. Whiskey Rebellion. The Whiskey Rebellion was an uprising in the 1790s where farmers protested against a federal tax on whiskey.
William Clark

Helped lead the Lewis and Clark Expedition across the Louisiana Purchase. William Clark. William Clark was an American explorer known for co-leading the first American expedition to explore the western territories of the United States.
XYZ affair

A political episode involving a confrontation between the US and France. XYZ affair. The XYZ Affair was a diplomatic incident in 1797-98 where French officials demanded bribes from American negotiators.