The English Colonies 1600-1800
History
Anne Hutchinson

A religious reformer who established the settlement of Portsmouth Anne Hutchinson. She was a key figure in early American history who challenged religious norms and helped shape religious freedom.
Bacons Rebellion

An armed rebellion held by Virginia settlers against Colonial Governor. Bacon's Rebellion. It was a 1676 uprising in Virginia where settlers protested against the governor's policies, demanding more protection from Native American tribes and more land.
Captain John Smith

An English soldier who was a leader of the first settlements at the Virginia Colony. Captain John Smith. He was an early leader and helped establish the Jamestown settlement in America.
English Bill of Rights

The constitutional law of England that sets out certain basic civil rights. English Bill of Rights. It is a 1689 document that limited the powers of the monarchy and ensured certain parliamentary and individual rights.
Enlightenment

A period of intellectual ferment in the thirteen American colonies which led to the American Revolution. Enlightenment. The Enlightenment was an 18th-century movement that emphasized reason and individualism over tradition in shaping societal progress and governance.
Great Awakening

A number of periods of religious revival in American Christian history. Great Awakening. The Great Awakening was a series of religious revivals in the 18th and early 19th centuries that emphasized emotional preaching and a personal connection to Christianity.
immigrants

People who legally move to another country. Immigrants. Throughout history, immigrants have played a crucial role in shaping societies by bringing diverse cultures, skills, and ideas.
indentured servant

A worker in a contract with an employer for a certain length of time. Indentured servant. In history, an indentured servant was someone who agreed to work for a set number of years in exchange for passage to a new country, housing, and sometimes land.
Jamestown

The first permanent English settlement in the Americas. Jamestown. It was established in 1607 in Virginia by English colonists looking for new opportunities.
John Locke

An English philosopher and physician, one of the influential Enlightenment thinkers. John Locke. He is known for his ideas about natural rights and government by consent, which shaped modern democracy.
John Winthrop

An English lawyer and the leading figure in founding the Massachusetts Bay Colony. John Winthrop. He was a key leader in establishing one of the first major settlements in New England during the early 1600s.
Jonathan Edwards

An American revivalist, theologian and president of Princeton University, Jonathan Edwards. Jonathan Edwards was a key figure in the Great Awakening, a religious revival in the 18th century.
Mayflower Compact

The first governing document of Plymouth Colony Mayflower Compact. It was an agreement created by the Pilgrims in 1620 to establish rules and order for their new settlement.
Olaudah Equiano

An important African involved in the British movement for the abolition of the slave trade Olaudah Equiano. Olaudah Equiano was a former enslaved African who became a prominent abolitionist and author, helping to end the slave trade.
Peter Stuyvesant

The last Dutch director-general of the colony of New Netherland. Peter Stuyvesant. He was a leader who governed the area that later became New York City before the English took control.
Pilgrims

The English settlers who established the Plymouth Colony. Pilgrims. Pilgrims were a group of people who traveled from England to America in 1620 seeking religious freedom.
Pocahontas

A Native American woman who converted to Christianity and married John Rolfe. Pocahontas was a Native American figure known for her association with the colonial settlement at Jamestown, Virginia, and her role in fostering peace between English settlers and Native Americans.
Pontiac

An Odawa war chief who led the war against the British in the Great Lakes region. Pontiac was a Native American leader known for starting Pontiac's War against British forces.
Puritans

An English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries. Puritans. Puritans were a religious group who wanted to purify the Church of England from practices they believed were too similar to the Catholic Church.
Quakers

A Christian denomination known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Quakers. They are a religious group that emerged in 17th-century England, known for their commitment to pacifism and social equality.
salutary neglect

A policy of avoiding strict execution of British laws, as long as colonies remained loyal to the England salutary neglect. Salutary neglect was a British policy that allowed American colonies to operate with relative independence as long as they supported Britain economically and politically.
slave codes

Laws relating to slavery and enslaved people. Slave codes. Slave codes were rules that controlled the lives and rights of enslaved people in the past.
Squanto

A Native American who helped the Pilgrims survive in the New World. Squanto. Squanto was a Native American who taught the Pilgrims vital survival skills in farming and fishing.
staple crops

A crop that can be stored easily and eaten throughout the year. Staple crops. Staple crops are essential foods that have been historically relied upon for daily nutrition around the world, like rice, wheat, and maize.
Toleration Act of 1649

A law passed in Maryland that protected Christians from fights and discrimination. Toleration Act of 1649. This act granted religious freedom to all Christians in colonial Maryland.
town meeting

a form democracy in which the people come together to legislate policy. town meeting. A town meeting is a historical form of direct democracy where local community members gather to discuss and vote on policies and budget issues.
triangular trade
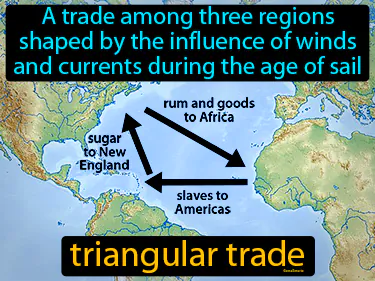
A trade among three regions shaped by the influence of winds and currents during the age of sail. Triangular trade. It was a system where ships transported goods and enslaved people between Europe, Africa, and the Americas.
William Penn

Founder of the English North American colony the Province of Pennsylvania. William Penn. William Penn was an early Quaker leader who established Pennsylvania as a place for religious freedom.