The World Before 1500
History
Aristotle

A Greek philosopher and polymath, student of Plato. Aristotle was an ancient thinker who made significant contributions to many fields, shaping Western knowledge and thought.
Askia Muhammad

An emperor, commander, and political reformer of the Songhai Empire, Askia Muhammad. Askia Muhammad was a ruler who strengthened and expanded the Songhai Empire in West Africa.
Berbers

An ethnic group mostly concentrated in North Africa. Berbers. Berbers are indigenous people of North Africa known for their rich history and diverse cultures, playing significant roles in ancient civilizations like Carthage and the Roman Empire.
Bering Land Bridge
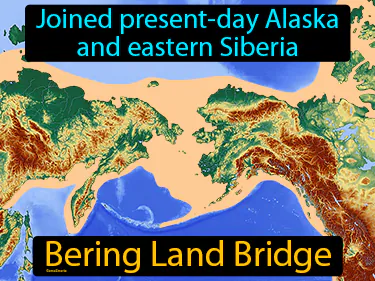
Joined present-day Alaska and eastern Siberia. Bering Land Bridge. The Bering Land Bridge was a land connection that allowed people and animals to migrate between Asia and North America during the Ice Age.
Black Death

The most fatal pandemic recorded in human history Black Death. The Black Death was a devastating plague in the 14th century that killed millions across Europe, Asia, and Africa.
culture

The social behavior and norms found in human societies like art, music, dance, and religion culture. Culture is the collection of beliefs, customs, and arts of a particular society throughout history.
democracy

A form of government in which the people exercise the authority of government. Democracy. In history, democracy means that citizens have the power to vote and make decisions about how their country is run.
hajj

An annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca. Hajj. Hajj is a religious journey that Muslims are required to make at least once in their lifetime if they can afford it, reflecting a tradition established by the Prophet Muhammad.
hunter gatherers

A society who lives from edible plants and animals from the wild, by foraging and hunting. Hunter gatherers. Hunter-gatherers are people who collect food by foraging for wild plants and hunting animals rather than farming.
Iroquois League

A historically powerful northeast Native American confederacy in North America. Iroquois League. The Iroquois League was a union of several Native American tribes that worked together for mutual defense and decision-making.
Johann Gutenberg

A German inventor, printer, and publisher who invented the printing press Johann Gutenberg. Johann Gutenberg introduced the movable type printing press, which revolutionized the way books were made and spread knowledge throughout Europe.
joint-stock company

A business entity in which shares of the company's stock can be bought and sold by shareholders. Joint-stock company. In History, a joint-stock company was a way for explorers and settlers to fund voyages to the New World by pooling resources and sharing profits and losses.
kiva

A room used by Puebloans for rites and political meetings. Kiva. A kiva is a ceremonial structure used by Puebloan peoples for rituals and community gatherings.
Leonardo

An Italian polymath, scientist, inventor, painter, architect, and paleontologist. Leonardo was a Renaissance genius known for his art and numerous innovations.
Mansa Musa

The tenth Mansa of the Mali Empire, known as the wealthiest person of the Middle Ages. Mansa Musa was a ruler famed for his immense wealth and significant cultural and economic influence in the 14th century.
matrilineal

An individual's family membership that derives from their mother's lineage. Matrilineal societies trace ancestry and inheritance through the mothers side of the family.
Michelangelo

An Italian sculptor, painter, architect and poet. Michelangelo. He was a Renaissance artist known for masterpieces like the Sistine Chapel ceiling and the statue of David.
Paleo Indians

The first peoples who entered, and inhabited the Americas during the Pleistocene period. Paleo Indians. The Paleo Indians were the earliest humans to live in the Americas, arriving during the last Ice Age.
Plato

Athenian philosopher and founder of the Platonist school of thought. Plato. Plato was an ancient Greek philosopher who established foundational ideas in Western philosophy and taught his student, Aristotle.
pueblo

Communities of Native Americans in the Southwestern US. Pueblo. A pueblo is a type of village or community historically built by Native American groups, characterized by multi-story adobe buildings.
reason

A way of thinking that uses logic and facts. Reason. In history, reason is the tool people use to understand and explain past events using evidence and logical thinking.
Socrates

A classical Greek philosopher credited as one of the founders of Western philosophy. Socrates was an ancient thinker who encouraged questioning and dialogue to explore philosophical ideas.
teepee

A tent made of animal skins upon wooden poles. Teepee. A teepee is a traditional Native American dwelling known for its cone shape and portability.
totems

A spirit beings, sacred objects, or symbols that serves as an emblem of a group of people. Totems. Totems are symbols or objects that hold spiritual significance and represent clans or tribes in various cultures.



