Technology and Expansion
History
Amerigo Vespucci

An Italian explorer from whose name the term America is derived, Amerigo Vespucci. He was one of the first to realize that the lands discovered by Columbus were part of a new continent, not Asia.
Atahualpa

The last Inca Emperor before the Spanish conquest. Atahualpa. He was the final ruler of the Inca Empire before being captured and executed by Spanish conquistadors.
ban

A decree that prohibits something. Ban. In History, a ban is an official order that legally stops people from doing something.
Bartolome de las Casas

A Spanish priest and writer who condemned the treatment of Indians in the Spanish empire. Bartolome de las Casas. He was a historical figure who spoke out against the mistreatment of indigenous people by Spanish colonizers.
Bartolomeu Dias

A Portuguese explorer who sailed around the southernmost tip of Africa. Bartolomeu Dias. Bartolomeu Dias was the first European to round the Cape of Good Hope, opening a sea route to Asia.
caravel

A small highly-maneuverable sailing ship developed in the 15th century. Caravel. A caravel is a small, fast ship used by explorers during the Age of Discovery in the 15th and 16th centuries.
Christopher Columbus

An Italian explorer, navigator and colonist who completed four voyages across the Atlantic. Christopher Columbus. He is known for discovering the Americas for Europe in 1492.
conquistador

The knights, soldiers and explorers of the Spanish and the Portuguese Empire. Conquistador. A conquistador was a Spanish or Portuguese explorer and warrior who claimed large parts of the Americas in the 15th and 16th centuries.
cotton gin

A machine that separates cotton fibers from their seeds. Cotton gin. The cotton gin is a device invented by Eli Whitney in 1793 that revolutionized the cotton industry by greatly speeding up the process of removing seeds from cotton fibers.
Creole

Ethnic groups which originated from mixing between European with non-European peoples. Creole. Creole refers to communities that emerged from the blending of European, African, and Indigenous cultures, often as a result of colonialism and the Atlantic slave trade.
Elizabeth Veale

An Anglo-Australian pastoralist and merchant. Elizabeth Veale. Elizabeth Veale was a pioneering woman in the early Australian colony who contributed to the development of the wool industry.
Enlightenment

An 18th century intellectual and philosophical movement. Enlightenment. It was a time when people emphasized reason, science, and individual rights to improve society.
Ferdinand Magellan

A Portuguese explorer and the first to sail around the world. Ferdinand Magellan. He led the first expedition to successfully circumnavigate the globe.
Francisco Pizarro

A Spanish conquistador who conquered the Inca Empire. Francisco Pizarro. He was the leader who overthrew the Inca civilization in present-day Peru during the early 1500s.
Galileo

An Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, considered the father of modern science. Galileo revolutionized our understanding of the universe by championing heliocentrism, which means the Earth revolves around the Sun.
geocentric

Belief that the Earth is fixed at the centre of the Universe. Geocentric. The geocentric model is an ancient belief that placed Earth at the center of the universe, with all other heavenly bodies revolving around it.
haciendas

Estates in the colonies of the Spanish Empire. Haciendas. Haciendas were large estates that functioned as farms or plantations in Spanish colonial territories.
heliocentric
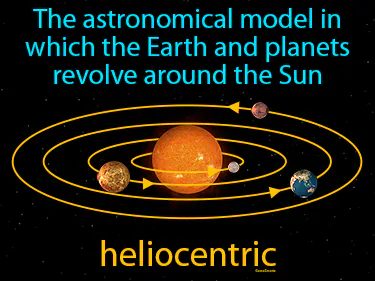
The astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around the Sun. Heliocentric. In history, heliocentric refers to the revolutionary idea by Copernicus that placed the Sun, not the Earth, at the center of our solar system.
Henry Hudson

Henry Hudson was an English navigator, best known for his explorations of northeastern America. He is a historical figure who discovered the Hudson River.
Hernan Cortes

A Spanish Conquistador who conquered the Aztec Empire. Hernan Cortes. He was the leader who led the expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire in the early 16th century.
Isaac Newton

An English physicist, mathematician, and astronomer, one of the most influential scientists of all time. Isaac Newton. He formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation, laying the foundation for classical mechanics.
Jacques Cartier

The first European to describe and map the Saint Lawrence River. Jacques Cartier was a French explorer who claimed parts of Canada for France in the 16th century.
James Cook

A British captain who reached the eastern Australia and the Hawaiian Islands. James Cook. James Cook was an 18th-century explorer known for mapping the Pacific, including Australia and Hawaii.
John Locke

An English philosopher and physician, one of the influential Enlightenment thinkers. John Locke. He is considered the "Father of Liberalism" due to his ideas on liberty and the social contract.
Kamehameha

The founder and first ruler of the Kingdom of Hawaii. Kamehameha. Kamehameha was the king who united the Hawaiian Islands into one kingdom.
Line of Demarcation

A geopolitical border, often agreed upon as part of an armistice or ceasefire. Line of Demarcation. In history, a line of demarcation is a boundary set between two territories, like the one established by the Treaty of Tordesillas separating Spanish and Portuguese lands in the New World.
mestizo

A person of combined European and Indigenous American descent is called a mestizo. In history, mestizo refers to individuals born from unions between European colonizers and Indigenous peoples in the Americas.
Middle Passage

The triangular trade in which millions of Africans were forcibly transported to the New World. Middle Passage. The Middle Passage was the horrific sea journey that transported enslaved Africans to the Americas.
missionary

A member of a religious group sent into an area to promote their faith is called a missionary. Historically, missionaries have traveled to different parts of the world to spread their religion and facilitate cultural exchanges.
Moctezuma

The Aztec emperor who was captured and imprisoned by Hernan Cortes. Moctezuma. Moctezuma was a leader of the Aztec Empire during the Spanish conquest of Mexico.
Nicolaus Copernicus

A Prussian astronomer who formulated a heliocentric model of the universe. Nicolaus Copernicus. He was a scientist who proposed that the planets, including Earth, orbit around the Sun.
Northwest Passage

The sea route between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean. Northwest Passage. The Northwest Passage is a historical sea route explored by Europeans seeking a shorter route from Europe to Asia.
Olaudah Equiano

An important African involved in the British movement for the abolition of the slave trade Olaudah Equiano. Olaudah Equiano was a former enslaved African who became a prominent activist and author, helping to end the British transatlantic slave trade.
patroon

A Dutch landholder with manorial rights to large tracts of land in North America. Patroon. In early American history, a patroon was a landowner in the Dutch colonies who had manorial rights and controlled large estates.
Pedro Cabral

A Portuguese navigator and explorer regarded as the European discoverer of Brazil. Pedro Cabral was the first European to officially land in Brazil in 1500.
penal colony

A settlement used to hold prisoners and use them for working in a remote location. Penal colony. A penal colony is a place where people are sent as punishment for their crimes, often to perform hard labor, in a distant or isolated area.
Prince Henry

A central figure in the 15th century European maritime discoveries and expansion, Prince Henry. Prince Henry, known as "the Navigator," sponsored explorations that led to the discovery of new lands and sea routes.
Queen Liliuokalani

The last sovereign monarch of the Hawaiian Kingdom 1891-1893. Queen Liliuokalani. She was the final ruler of Hawaii before it was annexed by the United States.
Rene Descartes

A French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, one of the founders of modern philosophy, Rene Descartes. Rene Descartes is known for the phrase "I think, therefore I am," which laid the foundation for a new approach to philosophy and science.
strait

A naturally formed, narrow waterway that connects two larger bodies of water. Strait. In History, straits have often been crucial for trade and military strategy as they control maritime passage.
triangular trade
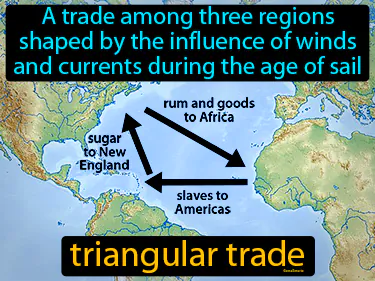
A trade among three regions shaped by the influence of winds and currents during the age of sail. Triangular trade. It was a historical trading system where ships transported goods and enslaved people between Africa, the Americas, and Europe.
Vasco da Gama

A Portuguese explorer and the first European to reach India by sea. Vasco da Gama was a pioneering navigator who established a sea route from Europe to Asia.





