The Indus River Valley
History
architecture
The process of planning, designing, and constructing buildings or other structures. Architecture. Throughout history, architecture has shaped the environments people live and work in by creating functional and aesthetic spaces.
Asoka

An Indian emperor of the Maurya Dynasty, who ruled almost all of the Indian subcontinent. Asoka. Asoka was a historic ruler known for spreading Buddhism and promoting peace and tolerance across his empire.
Buddhism

A religion based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. Buddhism. Buddhism is an ancient spiritual tradition that began in India over 2,500 years ago, founded by Siddhartha Gautama, who sought to understand and overcome suffering.
caste

A form of social stratification based on hereditary status, endogamy and social barriers. Caste is a historical system in which people are divided into rigid social groups, often determining their occupation and social interactions.
Chandragupta I

A king of the Gupta dynasty, who ruled in northern India. Chandragupta I. Chandragupta I was the founder of the Gupta Empire, marking the start of a golden age in ancient Indian history.
Chandragupta II

One of the most powerful emperors of the Gupta Empire, Chandragupta II. Chandragupta II was a ruler who expanded and strengthened the Gupta Empire in ancient India.
Chandragupta Maurya

The founder of the Maurya Empire in ancient India. Chandragupta Maurya. He was a powerful Indian ruler who established one of the largest empires in ancient India around 321 BCE.
citadel

The core fortified area of a town or city. Citadel. In History, a citadel is a strong, central fortress designed to protect a city from attacks.
dharma

A key concept with multiple meanings in Indian religions dharma. In history, dharma refers to the moral duty, righteousness, or law guiding human conduct in society.
Eightfold Path

A summary of the path of Buddhist practices leading to liberation from samsara Eightfold Path. The Eightfold Path is a historical Buddhist guide to ethical and mental development leading to enlightenment and the end of suffering.
Four Noble Truths

The truths for the spiritually worthy ones dukkha, samudaya, nirodha and magga. Four Noble Truths. In history, the Four Noble Truths are the foundation of Buddhist teachings, addressing the nature of suffering and the path to liberation.
Hinduism

An Indian religion and dharma, or way of life. Hinduism. Hinduism is an ancient religion originating from the Indian subcontinent that encompasses diverse beliefs and practices.
Indian subcontinent
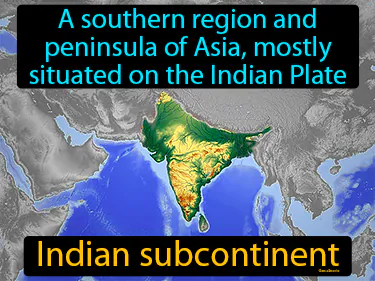
A southern region and peninsula of Asia, mostly situated on the Indian Plate. Indian subcontinent. It is a region in Asia that was the birthplace of ancient civilizations like the Indus Valley.
Kalidasa

An author who is considered ancient India's greatest playwright and dramatist, Kalidasa. Kalidasa was a classical Sanskrit writer known for his beautiful plays and poetry, reflecting Indian culture and traditions.
karma

The cycle of cause and effect done by individuals actions. Karma. In history, karma can be seen as the idea that people's actions, good or bad, ultimately lead to corresponding consequences over time.
Middle Way

Teaching in Buddhism which advises a path of moderation Middle Way. The Middle Way is a historical Buddhist concept that suggests avoiding extremes by following a balanced and moderate life path.
monk

A person who practices religious asceticism. Monk. In history, a monk is someone who lives a life of devotion and simplicity, often in a community, dedicated to religious and spiritual practices.
reincarnation

The idea that people are born again in another body after they die. Reincarnation. In history, many cultures and religions, like Hinduism and Buddhism, have believed that souls are reborn into new bodies after death.
Samudragupta

A ruler of the Gupta Empire, son of Chandragupta I. Samudragupta. Samudragupta was a powerful emperor known for expanding the Gupta Empire and promoting arts and culture in ancient India.
Siddhartha Gautama

A spiritual teacher who founded Buddhism, Siddhartha Gautama. He is known as the Buddha, who taught the path to enlightenment in ancient India.
tribute

A wealth that one party gives to another as a sign of respect, submission, or allegiance. Tribute. In history, tribute is a payment made by one nation or ruler to another as a sign of submission or for protection.
Vedas

A large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Vedas. The Vedas are ancient Hindu scriptures that form the foundation of Indian religious and philosophical traditions.