Slavery Divides the Nation
History
abolitionist

A supporter of ending a slavery. abolitionist. An abolitionist was a person who wanted to end slavery, fighting for freedom and equality for all.
Abraham Lincoln

The 16th president of the U.S. from March 1861 until his assassination in April 1865. Abraham Lincoln. He is known for leading the country during the Civil War and abolishing slavery.
Angelina Grimke

An abolitionist, political activist, women's rights advocate. Angelina Grimke. She was a 19th-century figure who fought against slavery and for women's rights in America.
Compromise of 1850

A series of laws that defused a political confrontation between slave and free states. Compromise of 1850. It was a set of laws aimed at calming tensions over slavery in new U.S. territories.
Confederacy

An unrecognized republic in North America that existed from 1861 to 1865. Confederacy. The Confederacy was a group of Southern states that seceded from the United States to form their own government during the American Civil War.
Dred Scott Decision

A Supreme Court decision that descended from slaves were not citizens of the US. Dred Scott Decision. The Dred Scott Decision was an infamous 1857 ruling stating that African Americans, whether enslaved or free, could not be American citizens and had no standing to sue in federal court.
Elizabeth Cady Stanton

A suffragist, social activist, abolitionist, and pioneer of women's rights movement, Elizabeth Cady Stanton. She was a leader in the fight for women's right to vote in the United States.
Elizabeth Jennings

An African-American teacher and key figure in the movement for civil rights, Elizabeth Jennings. She is known for challenging racial segregation in public transportation in 1854.
Frederick Douglass

A social reformer, abolitionist, orator, writer, and statesman, Frederick Douglass. He was a former enslaved person who became a key leader in the fight to end slavery in the United States.
Fugitive Slave Law

A law that provided for the return of slaves who escaped from one state into another. Fugitive Slave Law. The Fugitive Slave Law was a law that required escaped enslaved people to be returned to their enslavers even if they were found in free states.
Harriet Beecher Stowe

An abolitionist and author best known for her novel, Uncle Tom's Cabin. Harriet Beecher Stowe. She was a writer whose book helped change public opinion against slavery in the United States.
Harriet Tubman

An American abolitionist and political activist, she rescued around 70 enslaved people. Harriet Tubman was a courageous leader who helped enslaved people escape to freedom via the Underground Railroad.
Henry Clay

A politician who helped pass the Missouri Compromise and the Compromise of 1850. Henry Clay. Henry Clay was a prominent 19th-century U.S. statesman known as the "Great Compromiser" for his role in brokering major agreements to ease tensions between North and South.
Jefferson Davis

The only President of the Confederate States of America 1861 - 1865. Jefferson Davis. He was the leader of the Confederate states during the American Civil War.
John Brown

An abolitionist who led a raid on the federal armory at Harpers Ferry. John Brown. He was a radical activist who aimed to end slavery in the United States.
Kansas-Nebraska Act
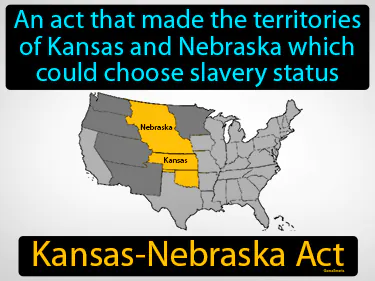
An act that made the territories of Kansas and Nebraska which could choose slavery status. Kansas-Nebraska Act. The Kansas-Nebraska Act allowed the people living in Kansas and Nebraska to decide for themselves whether to allow slavery or not.
Levi Coffin

An abolitionist and leader of the Underground Railroad in Indiana and Ohio, Levi Coffin. Levi Coffin was known as the "President of the Underground Railroad" for his efforts in helping enslaved people escape to freedom.
Lucretia Mott

An abolitionist and women's rights activist who co-wrote the Declaration of Sentiments. Lucretia Mott. She was a key figure in the early women's rights movement in the United States.
Missouri Compromise

Legislation that provided for the admission of Maine to the US as a free state along with Missouri as a slave state. Missouri Compromise. The Missouri Compromise was an agreement in 1820 that aimed to maintain the balance of power in Congress between free and slave states.
Nat Turner

An enslaved African-American preacher who led a two-day rebellion. Nat Turner. He was a key figure in American history for leading a significant slave revolt in 1831.
prejudice

A preconceived opinion that is not based on reason or actual experience. Prejudice. In history, prejudice is when people are unfairly judged or treated poorly because of characteristics like skin color, religion, or nationality.
Sarah Grimke

An abolitionist, known as mother of the women's suffrage, Sarah Grimke. Sarah Grimke was a 19th-century activist who fought for the rights of women and the abolition of slavery.
secede

When part of one country breaks away or leaves that country to start a new country secede. Secede means when a region separates from its country to become independent, like when the Southern states left the United States at the start of the Civil War.
Seneca Falls

The first women's rights convention, social, civil, and religious rights were discussed. Seneca Falls. Seneca Falls is a historic meeting that marked the beginning of the women's rights movement in the United States.
Sojourner Truth

Born Isabella Baumfree, an African-American abolitionist and women's rights activist, Sojourner Truth. She was a former enslaved person who became a powerful voice for abolition and women's rights in the 19th century.
states rights
A political powers are held for the state governments rather than the federal government. States' rights. States' rights refer to the idea that U.S. states have the power to govern themselves and make their own laws, separate from the federal government.
Underground Railroad

A network of secret routes used by enslaved African-Americans to escape into free states. Underground Railroad. The Underground Railroad was a system of safe houses and secret routes that helped enslaved people escape to freedom in the 19th century.
William Lloyd Garrison

One of the founders of the American Anti-Slavery Society, William Lloyd Garrison. He was a prominent abolitionist who advocated for the immediate end of slavery in the United States.