The Constitution of the US
History
Alexander Hamilton

One of the Founding Fathers of the United States, Alexander Hamilton. Alexander Hamilton was the first Secretary of the Treasury and helped shape the U.S. financial system.
amendment

A formal change made to a law, contract, or constitution. Amendment. In history, an amendment allows societies to update and improve their laws or constitutions to reflect changing values and needs.
Antifederalists

A diverse group of Americans who opposed the ratification of the 1787 US Constitution. Antifederalists. They were people who feared that a strong central government would take away individual and state rights.
Articles of Confederation

An agreement among the 13 original states of the US, that served as its first constitution. Articles of Confederation. The Articles of Confederation was the first governing document that loosely united the American states before the current US Constitution.
Bill of Rights

A document of the first ten amendments to the US Constitution. Bill of Rights. The Bill of Rights is a list of fundamental rights and freedoms protected by the Constitution for individuals.
cabinet

A body of high-ranking state officials. Cabinet. In history, a cabinet is a group of advisors to a head of state who help make decisions and run the government.
checks and balances

A system of government in which no branch has more power than any other. Checks and balances. It is a way to ensure that no single part of the government becomes too powerful by allowing each branch to limit the powers of the others.
Daniel Shays

A populist uprising against controversial debt collection and tax policies. Daniel Shays. Daniel Shays was a farmer and former soldier who led Shays' Rebellion against economic injustices in post-Revolutionary War America.
democracy

A form of government in which the people exercise the authority of government. Democracy. In history, democracy is when citizens have the power to vote and make decisions about their leaders and laws.
executive branch

A branch of government responsible for the governance of a state. Executive branch. The executive branch enforces laws and is led by the president or prime minister.
federalism
A combination of a general government with regional governments in a single political system. Federalism. In history, federalism is a system where power is shared between a central government and individual states.
Federalists

Statesmen and public figures supporting the proposed Constitution of the U.S. Federalists. Federalists were people who supported a strong national government and the ratification of the U.S. Constitution in the late 18th century.
George Mason

One of three delegates who refused to sign the Constitution, George Mason. George Mason was a Founding Father who helped draft the Bill of Rights.
George Washington

An American political leader, military general, and the first president of the United States. George Washington. He is often called the "Father of His Country" for leading the U.S. to independence.
Gouverneur Morris

A Founding Father of the US, and a signatory to the US Constitution Gouverneur Morris. Gouverneur Morris was a key figure in drafting the U.S. Constitution and is credited with writing its preamble.
Great Compromise

An agreement that large and small states established a two-house legislature under the US Constitution. Great Compromise. The Great Compromise was a historic agreement during the Constitutional Convention that created a two-house legislature, balancing the needs of both large and small states.
James Madison

The fourth president of the United States 1809 - 1817. James Madison. He is known as the "Father of the Constitution" for his pivotal role in drafting and promoting the U.S. Constitution and the Bill of Rights.
judicial branch

A branch of government that administers justice. Judicial branch. The judicial branch interprets laws and ensures they are applied fairly.
legislative branch

A part of government that makes laws. Legislative branch. In history, the legislative branch is the section of government responsible for creating and passing laws.
New Jersey Plan

A plan that called for each state to have equal representation in the legislature. New Jersey Plan. The New Jersey Plan was a proposal during the Constitutional Convention of 1787 that suggested each state should have one vote in Congress, regardless of its population size, to ensure equal representation.
Northwest Ordinance
An act that created the Northwest Territory, the first organized integrated territory. Northwest Ordinance. The Northwest Ordinance was a 1787 law that established a method for admitting new states to the United States from the Northwest Territory.
political party

An organized group of people who have the same political ideology about government. Political party. In History, a political party is a group that works together to influence government decisions and policies.
Preamble

An introduction of the Constitution's purposes and guiding principles. Preamble. In history, the Preamble is the opening statement of the U.S. Constitution that outlines the fundamental goals and principles of the government.
ratify

Give formal consent to, for example, Constitution. ratify. In history, to ratify means to officially approve a document or agreement, often making it legally valid, like when the Constitution was accepted by the states.
republic

A form of government in which the country is considered a public matter. Republic. In history, a republic is a system where officials are chosen by the people to represent their interests.
Richard Allen

An influential Black leader and founder of the African Methodist Episcopal Church Richard Allen. Richard Allen was a pioneering figure who established the first independent Black denomination in the United States, advocating for spiritual and social freedom.
Roger Sherman

A statesman who created the Great Compromise at the Constitutional Convention. Roger Sherman. He was a Founding Father who helped shape the U.S. government by proposing a two-house Congress.
secretary

A senior official who provides services and advice to a cabinet. In History, a secretary is an official who assists leaders by managing correspondence and records.
Shayss Rebellion

An armed uprising in Western Massachusetts in opposition to a debt crisis. Shays's Rebellion was a protest by American farmers in the 1780s against state and local enforcement of tax collections and judgments for debt.
statehood
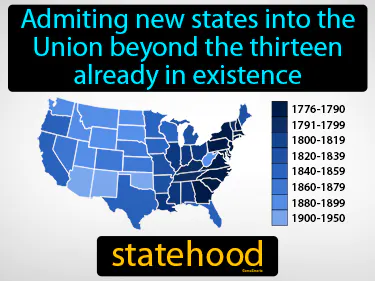
Admitting new states into the Union beyond the thirteen already in existence. Statehood. Statehood is the process by which a U.S. territory becomes a full member of the United States with equal standing to the original thirteen states.
Supreme Court

The highest court in the federal judiciary of the USA. Supreme Court. The Supreme Court is the top legal authority in the United States that decides important legal questions and interprets the Constitution.
territories
An area that is under the jurisdiction of a sovereign state. Territories. Historically, territories are regions that a country controls but have not yet become states or fully integrated parts of the country.
veto

Action by which the President prevents an act passed by Congress from becoming law. Veto. A veto is when the President rejects a bill, stopping it from becoming law unless Congress overrides the decision.
Virginia Plan

A proposal to the Constitutional Convention for the creation a government with 3 branches equal in power. Virginia Plan. The Virginia Plan was a proposal to structure the U.S. government with three branches and proportional representation in Congress.