Ancient China
History
ambassador

The highest ranking diplomat who represents a nation. Ambassador. An ambassador is an official sent by a government to represent its interests and build relationships in another country.
Chang Jiang Valley

The longest river in Asia, cradle of ancient Chinese civilization. Chang Jiang Valley. The Chang Jiang Valley is a region in China where early civilizations flourished around the Yangtze River.
Changan

An ancient capital of more than ten Chinese dynasties. Changan. Changan, now known as Xi'an, was a major center for politics and culture in ancient China.
character

A sign or symbol used in writing. Character. In history, a character refers to a letter or symbol used in ancient scripts to record and communicate information.
Confucianism

A system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Confucianism. Confucianism is a philosophical and ethical system based on the teachings of Confucius, focusing on family loyalty, social harmony, and moral conduct.
Confucius

A Chinese philosopher who emphasized morality, justice, kindness, and sincerity. Confucius was an influential teacher and thinker in ancient China whose ideas shaped East Asian culture and ethical systems.
dialect

A form of a language spoken by a group of people. Dialect. In history, a dialect refers to the distinct form of a language used by people in a specific region or community.
diviner

One who foretells the future by reading signs, events, or omens. Diviner. In history, a diviner is a person who predicts future events or gives insights by interpreting natural signs or omens.
feudalism
A system of holding of land in exchange for service or labor. Feudalism. Feudalism was a medieval social system where nobles granted land to vassals in exchange for military service and loyalty.
filial piety

A virtue of respect for one's parents, elders and ancestors filial piety. In history, filial piety is a fundamental Confucian value emphasizing respect and duty towards one's family lineage in East Asian cultures.
heritage

Events or processes that have a special meaning in group memory. Heritage. Heritage is the traditions, achievements, and beliefs that are part of the history of a group or nation.
Huang Di

A deity in Chinese religion, one of the legendary Chinese sovereigns and culture heroes. Huang Di. Huang Di, also known as the Yellow Emperor, is considered a foundational ruler and cultural hero in ancient Chinese history and mythology.
Huang He Valley

A river in China, birthplace of ancient Chinese civilization. Huang He Valley. The Huang He Valley is where ancient Chinese civilization began, along the Yellow River.
Liu Pang

The founder and first emperor of the Han dynasty. Liu Pang. Liu Pang, also known as Liu Bang, was the ruler who established the Han dynasty in ancient China.
Mandate of Heaven

Chinese political and religious doctrine used to justify the rule of the emperor of China. Mandate of Heaven. It is the belief that the emperor's right to rule is granted by a divine power, and this right can be lost if the ruler becomes unjust or tyrannical.
oracle bone

Pieces of ox scapula or turtle plastron, which were used for pyromancy in ancient China. Oracle bone. Oracle bones are ancient artifacts used by Chinese people to predict the future through divination.
Shen Nong

A mythological Chinese ruler who has become a deity in Chinese folk religion, Shen Nong. Shen Nong is a legendary figure credited with teaching ancient Chinese people agriculture and the use of herbal medicine.
Silk Road
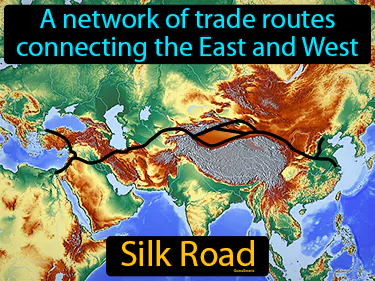
A network of trade routes connecting the East and West. Silk Road. The Silk Road was an ancient trade network that facilitated the exchange of goods and culture between Asia and Europe.
Sima Qian

A Chinese historian who is considered the father of Chinese historiography. Sima Qian. He wrote "Records of the Grand Historian," which is a comprehensive history of China.
steppe

An ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees is called a steppe. Historically, the steppe was home to nomadic tribes who traveled these vast grasslands on horseback.
Tang Taizong

The second emperor and co-founder of the Tang dynasty, Tang Taizong. Tang Taizong was a prominent Chinese ruler known for expanding and stabilizing the Tang dynasty during the 7th century.
terrace farming

A method of farming that consists of steps built into the side of a mountain or hill. Terrace farming. Terrace farming is an ancient agricultural practice used by civilizations like the Incas to prevent soil erosion and manage water on steep terrain.
virtue

A trait or quality that is deemed to be morally good. Virtue. In history, virtue often refers to the admirable qualities of individuals, like courage and justice, that have been valued across different cultures and time periods.
Wei River Valley
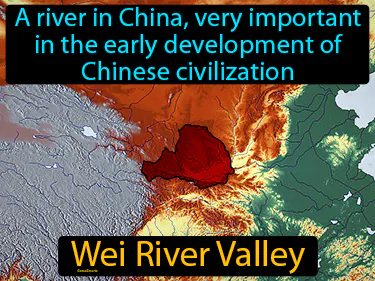
A river in China, very important in the early development of Chinese civilization. Wei River Valley. The Wei River Valley is an important ancient region where early Chinese civilization flourished due to its fertile land and strategic location.
Wu Hou

The only female monarch in the history of China, Wu Hou. Wu Hou, also known as Wu Zetian, was the first and only empress to rule China in her own name during the Tang dynasty.
Wudi

The seventh emperor of the Han dynasty of China. Wudi. Wudi was a powerful ruler who helped expand China's territory and strengthen its central government.
Xian

One of the Chinese Four Great Ancient Capitals and the starting point of the Silk Road. Xian. Xian is an ancient city in China known for its historical significance as a major hub for trade and culture.
Xianyang

An ancient Chinese city which was capital of the state of Qin. Xianyang was the capital where the first emperor of China, Qin Shi Huang, united the country.
Xilingshi

A legendary Chinese empress who discovered sericulture, and invented the silk loom. Xilingshi. Xilingshi is an important historical figure credited with starting silk production in ancient China.
Yu the Great

A king in ancient China who was famed for his introduction of flood control, Yu the Great. Yu the Great was a legendary figure known for taming floods and establishing the Xia Dynasty.