Conservatism 1980-1993
History
AIDS
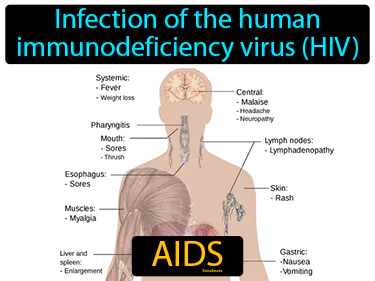
Infection of the human immunodeficiency virus HIV. AIDS. AIDS is a disease that emerged in the late 20th century, known for severely weakening the immune system.
apartheid

Racial segregation that existed in Africa apartheid. Apartheid was a system in South Africa where laws enforced the separation and unequal treatment of non-white people.
budget deficit

When expenses exceed revenue. Budget deficit. In history, a budget deficit is when a government spends more money than it collects in taxes.
Contras

US backed, right-wing rebel groups in Nicaragua. Contras. The Contras were anti-communist rebel groups in Nicaragua funded by the US during the 1980s to fight the Sandinista government.
deregulation

Removing or reducing state regulations. Deregulation. In history, deregulation refers to the process of reducing government oversight and rules in industries to promote more competition and efficiency.
divest

The reduction of a financial asset. Divest. In History, divest means selling off parts of a business or withdrawing from certain countries or industries.
Douglas Wilder

The first African American to serve as governor Douglas Wilder. Douglas Wilder made history by becoming the first African American elected as a U.S. state governor, serving Virginia from 1990 to 1994.
entitlement program

A government program that provides guaranteed benefits is called an entitlement program. In history, entitlement programs are systems where the government ensures certain benefits, like Social Security or Medicare, to eligible citizens.
George H W Bush

The 41st president of the United States, 1989 - 1993, George H W Bush. George H W Bush was the U.S. leader during the end of the Cold War.
Geraldine Ferraro

The first female vice presidential candidate, Geraldine Ferraro. Geraldine Ferraro was the first woman nominated for vice president by a major American political party in 1984.
glasnost

A political slogan for increased government transparency in the Soviet Union glasnost. Glasnost was a policy that encouraged openness and transparency in government, initiated by Mikhail Gorbachev in the 1980s.
Iran Contra affair

The Regan government secretly facilitated the sale of arms to Iran. Iran-Contra affair. The Iran-Contra affair was a political scandal in the 1980s involving the secret sale of weapons to Iran to fund Nicaraguan rebels.
liberal

A supporter of liberalism, a political philosophy founded on ideas of liberty and equality. Liberal. Liberalism advocates for individual freedoms, equality, and democratic governance.
Manuel Noriega

The ruler of Panama from 1983 to 1989, Manuel Noriega. Manuel Noriega was a military leader and de facto dictator of Panama involved in drug trafficking activities.
Mikhail Gorbachev

The eighth and last leader of the Soviet Union 1988 - 1991. Mikhail Gorbachev. He was the leader who introduced reforms leading to the end of the Cold War and the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
Moral Majority

A political organization associated with the Christian right and Republican Party Moral Majority. Moral Majority was a prominent conservative group in the 1980s that aimed to influence U.S. politics by promoting traditional family values and conservative policies.
national debt
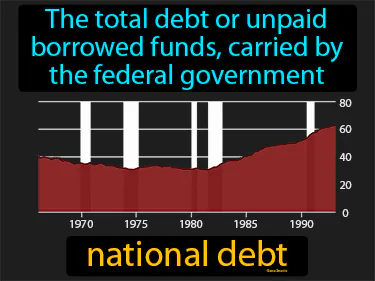
The total debt or unpaid borrowed funds, carried by the federal government. National debt. National debt is the money a government borrows to cover expenses beyond its income, which has been a practice since ancient times.
Nelson Mandela

An anti-apartheid revolutionary, who served as President of South Africa Nelson Mandela. Nelson Mandela was a key leader in ending apartheid and became the first black president of South Africa, symbolizing the country's transition to equality.
New Right

A right-wing ideology embracing liberal economics and traditional social values. New Right. The New Right is a political movement that gained prominence in the late 20th century, combining free-market principles with conservative social policies.
Operation Desert Storm

A war waged by coalition forces from 35 nations against Iraq. Operation Desert Storm. It was a military operation in 1991 to expel Iraqi forces from Kuwait.
Reaganomics

Economic policies promoted by US President Ronald Reagan during the 1980s. Reaganomics. Reaganomics is the economic strategy of reducing taxes, cutting government spending, and promoting free-market activity to stimulate growth.
reverse discrimination

A discrimination against members of a majority group. Reverse discrimination. In historical contexts, reverse discrimination refers to actions that favor minority groups at the expense of majority groups, often as an attempt to correct past inequalities.
Ronald Reagan

The 40th president of the United States 1981 - 1989, Ronald Reagan. Ronald Reagan was a former actor who became a conservative leader and played a key role in ending the Cold War.
Sandinistas

A socialist political party in Nicaragua. Sandinistas. The Sandinistas are a political group that led a revolution in Nicaragua to overthrow a dictatorship in 1979 and established a socialist government.
Sandra Day O Connor

The first woman to serve on the Supreme Court Sandra Day O'Connor. She was a pioneering figure in U.S. history as the first female justice, appointed in 1981.
Savings and Loan crisis

The failure of 1,043 of savings and loan associations from 1986 to 1995. Savings and Loan crisis. This crisis involved financial institutions collapsing due to risky investments and poor regulations in the U.S. during the 1980s.
school voucher

Government funding for a school chosen by the student, or students parents. School voucher. In history, a school voucher is a government-funded certificate that allows parents to enroll their child in a private or alternative school of their choice instead of a public school.
Strategic Defense Initiative

A proposed missile defense system to protect the US from attack by nuclear weapons. Strategic Defense Initiative. The Strategic Defense Initiative was a plan announced by President Ronald Reagan in 1983 to develop technology to intercept and destroy incoming nuclear missiles, often nicknamed "Star Wars."
supply-side economics

That economic growth can be created by lowering taxes and decreasing regulation. Supply-side economics. This theory gained popularity in the 1980s with policies emphasizing tax cuts and deregulation to stimulate production and economic growth.
Tiananmen Square

A square in the center of Beijing, where students led demonstrations in 1989. Tiananmen Square. It is a famous location in China where pro-democracy protests occurred and were violently suppressed.
unfunded mandate

A regulation that requires government to perform action, with no money provided. Unfunded mandate. In U.S. history, an unfunded mandate refers to laws requiring states to follow certain rules without providing federal funds to assist them.